
Viola is a genus of flowering plants in the violet family Violaceae. It is the largest genus in the family, containing over 680 species. Most species are found in the temperate Northern Hemisphere; however, some are also found in widely divergent areas such as Hawaii, Australasia, and the Andes.

Rhagionidae or snipe flies are a small family of flies. They get their name from the similarity of their often prominent proboscis that looks like the beak of a snipe.

The Saturniinae or saturniines are a subfamily of the family Saturniidae, also known as giant silkmoths. They are commonly known as emperor moths or wild silk moths. They are easily spotted by the eyespots on the upper surface of their wings. Some exhibit realistic eye-like markings, whilst others have adapted the eyespots to form crescent moon or angular shapes or have lost their wing scales to create transparent windows. They are medium to very large moths, with adult wingspans ranging from 7.5 to 15 cm, in some cases even more. They consist of some of the largest sized Lepidoptera, such as the luna moth, atlas moth, and many more. The Saturniinae is an important source of wild silk and human food in many different cultures.
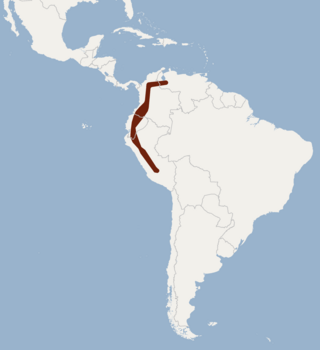
The bidentate yellow-shouldered bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found in South America.

Charopidae is a taxonomic family of small air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Punctoidea.

Trematosaurus is an extinct genus of trematosaurid temnospondyl amphibian found in Germany and Russia. It was first named by Hermann Burmeister in 1849 and the type species is Trematosaurus brauni.

The Battle Cruiser Fleet, (BCF), later known as Battle Cruiser Force, a naval formation of fast battlecruisers of the Royal Navy, operated from 1915 to 1919.

Thomas's fruit-eating bat, sometimes also popularly called Watson's fruit-eating bat, is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found from southern Mexico, through Central America to Colombia. Its South American range is to the west of the Andes. The species name is in honor of H. J. Watson, a plantation owner in western Panama who used to send specimens to the British Natural History Museum, where Oldfield Thomas would often describe them.

Callidrepana is a genus of moths belonging to the subfamily Drepaninae.

Tridrepana is a genus of moths belonging to the subfamily Drepaninae.
Embrithosaurus was a pareiasaur from the Permian of South Africa.
Nitrospirota is a phylum of bacteria. It includes multiple genera, such as Nitrospira, the largest. The first member of this phylum, Nitrospira marina, was discovered in 1985. The second member, Nitrospira moscoviensis, was discovered in 1995.

Eulima is a genus of small, ectoparasitic sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Eulimidae.
Procyclotosaurus is an extinct genus of stenotosaurid capitosaurian temnospondyl. The type species is P. stantonensis. In 1904, English paleontologist Arthur Smith Woodward described it as a species of Capitosaurus, C. stantonensis, based on a partial skull known as R 3174. In 1958, the species was assigned to the new genus. It is known from the Lower Keuper, a European stratigraphic unit that was deposited during the late Middle Triassic. Fossils have been found from Staffordshire, England.
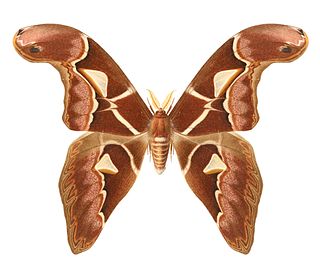
Archaeoattacus staudingeri is a species of moth in the genus Archaeoattacus found on the Malay Peninsula and on Borneo. The species is a deeper, more purplish brown than A. atlas, with a more angular forewing postmedial that is edged distad by grey patches in the spaces and concave distad anterior to the angle. The forewing apical markings are grey rather than pale brown or yellow.
Epicampoptera is a genus of moths in the family Drepanidae. The genus was first described by Felix Bryk in 1913.
Gonoreta is a genus of moths first described by Warren in 1902. It is in the subfamily Drepaninae.

Aglaophenia is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Aglaopheniidae.

Chorismagrion is a monotypic genus of damselflies belonging to the family Synlestidae. The single species of this genus, Chorismagrion risi, known as a pretty relict, is a slender, medium-sized damselfly, mostly black in colour with white markings. It is endemic to north-eastern Australia, where it inhabits streams and large pools in rainforests.
Papposaurus is an extinct genus of proterogyrinid embolomere which lived in the Mississippian of Scotland. It is known from a single species, Papposaurus traquiairi, which is based on an isolated femur discovered in ironstone near Loanhead. Though originally compared closely to reptiles, subsequent study has revealed closer similarity to basal embolomeres such as Proterogyrinus and Archeria. With such limited remains, Papposaurus may not be a valid genus. The femur was redescribed in 1986 by T. R. Smithson, who considered Papposaurus traquairi a nomen vanum possibly synonymous with Proterogyrinus scheelei.














