
Canada has a vast geography that occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing a land border with the contiguous United States to the south and the U.S. state of Alaska to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast with a shared border on Hans Island. To the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area, Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world's largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.

The Canadian Shield, also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton, the ancient geologic core of the North American continent. Glaciation has left the area with only a thin layer of soil, through which exposures of igneous bedrock resulting from its long volcanic history are frequently visible. As a deep, common, joined bedrock region in eastern and central Canada, the Shield stretches north from the Great Lakes to the Arctic Ocean, covering over half of Canada and most of Greenland; it also extends south into the northern reaches of the United States.

James Bay is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. Both bodies of water extend from the Arctic Ocean, of which James Bay is the southernmost part. Despite bordering the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario, the bay and the islands within it, the largest of which is Akimiski Island, are politically part of Nunavut.

Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 0.5 per cent of Canada's population.
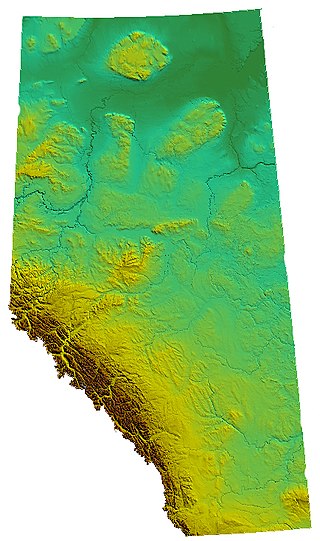
Alberta is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. Located in Western Canada, the province has an area of 661,190 km2 (255,290 sq mi) and is bounded to the south by the United States state of Montana along 49° north for 298 km (185 mi); to the east at 110° west by the province of Saskatchewan for 1,223 km (760 mi); and at 60° north the Northwest Territories for 644 km (400 mi). The southern half of the province borders British Columbia along the Continental Divide of the Americas on the peaks of the Rocky Mountains, while the northern half borders British Columbia along the 120th meridian west. Along with Saskatchewan it is one of only two landlocked provinces or territories.

Foxe Basin is a shallow oceanic basin north of Hudson Bay, in Nunavut, Canada, located between Baffin Island and the Melville Peninsula. For most of the year, it is blocked by sea ice and drift ice made up of multiple ice floes.
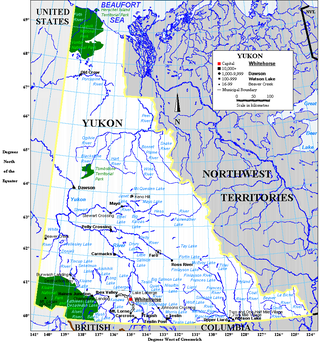
Yukon is in the northwestern corner of Canada and is bordered by Alaska and the Northwest Territories. The sparsely populated territory abounds with natural scenic beauty, with snowmelt lakes and perennial white-capped mountains, including many of Canada's highest mountains. The territory's climate is Arctic in territory north of Old Crow, subarctic in the region, between Whitehorse and Old Crow, and humid continental climate south of Whitehorse and in areas close to the British Columbia border. Most of the territory is boreal forest with tundra being the main vegetation zone only in the extreme north and at high elevations.
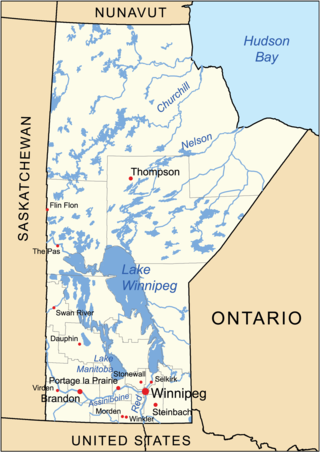
The geography of Manitoba addresses the easternmost of the three prairie Canadian provinces, located in the longitudinal centre of Canada. Manitoba borders on Saskatchewan to the west, Ontario to the east, Nunavut to the north, and the American states of North Dakota and Minnesota to the south. Although the border with Saskatchewan appears straight on large-scale maps, it actually has many right-angle corners that give the appearance of a slanted line. In elevation, Manitoba ranges from sea level on Hudson Bay to 2727 ft (831 m) on top of Baldy Mountain. The northern sixty percent of the province is on the Canadian Shield. The northernmost regions of Manitoba lie permafrost, and a section of tundra bordering Hudson Bay.

The Arctic Cordillera is a terrestrial ecozone in northern Canada characterized by a vast, deeply dissected chain of mountain ranges extending along the northeastern flank of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago from Ellesmere Island to the northeasternmost part of the Labrador Peninsula in northern Labrador and northern Quebec, Canada. It spans most of the eastern coast of Nunavut with high glaciated peaks rising through ice fields and some of Canada's largest ice caps, including the Penny Ice Cap on Baffin Island. It is bounded to the east by Baffin Bay, Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea while its northern portion is bounded by the Arctic Ocean.

The Hudson Bay Lowlands is a vast wetland located between the Canadian Shield and southern shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Most of the area lies within the province of Ontario, with smaller portions reaching into Manitoba and Quebec. Many wide and slow-moving rivers flow through this area toward the saltwater of Hudson Bay: these include the Churchill, Nelson and Hayes in Manitoba, Severn, Fawn, Winisk, Asheweig, Ekwan, Attawapiskat, and Albany in Ontario, and the Harricana, Rupert and Eastmain in Quebec. This is the largest wetland in Canada, and one of the largest in the world. The region can be subdivided into three bands running roughly northwest to southeast: the Coastal Hudson Bay Lowland, Hudson Bay Lowland, and James Bay Lowland.

The Taiga Shield Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is an ecozone which stretches across Canada's subarctic region. Some regions exhibit exposed Precambrian bedrock of the Canadian Shield, the oldest of the world's geological formations. The world's oldest rocks, dating to four billion years, are found in the Canadian Shield north of Great Slave Lake.

The Taiga Plain Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian terrestrial ecozone that covers most of the western Northwest Territories, extending to northwest Alberta, northeast British Columbia and slightly overlapping northeastern Yukon.

The Taiga Cordillera Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a rugged, mountainous terrestrial ecozone of Canada spanning most of northern Yukon and significant portions of the border between the Yukon and the Northwest Territories.

The Southern Arctic Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian terrestrial ecozone which spans the northern coast of mainland Northwest Territories, most of northern mainland Nunavut excepting the northeast peninsula, and a portion of northwestern Quebec. Its two constituent territories are interrupted by Hudson Bay. The ecozone can also be described as including the northernmost part of the Interior Plains of Western Canada and parts of the Canadian Shield located on both sides of northern Hudson Bay.

The Northern Arctic Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian terrestrial ecozone which includes most of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the Boothia and Melville Peninsulas of Nunavut, and the northwestern tip of Quebec. Its marine borders are with the Arctic Archipelago Marine Ecozone, and it is adjacent to the mainland Southern Arctic Ecozone.

The Northwest Atlantic Marine Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian marine ecozone forming a transitional region between the cold northern waters of the Arctic Ocean and the more temperate waters in its southern extent.

The Hudson Plains Ecoregion is a vast, flat, and waterlogged landscape. This ecoregion covers a 369,000 square kilometer area along the south shoreline of the Hudson Bay, which includes the Canadian provinces of Eastern Quebec, Northern Ontario and Western Manitoba. Because of the location of the ecoregion, winter prevails for many months of the year and rising temperatures, along with melting ice, makes fog common. The short summers provide a home for thousands of migrating birds. The region is used by humans for its mineral resources and hydroelectric power as a result of the abundance of water and emergent societal needs. Though relatively uninhabited and undisturbed, the natural resources of the Hudson Plains are still subject to anthropogenic activities. Its climatic, geographic, and evolutionary patterns categorize it as one of many ecoregions in North America.

The Canadian Arctic tundra is a biogeographic designation for Northern Canada's terrain generally lying north of the tree line or boreal forest, that corresponds with the Scandinavian Alpine tundra to the east and the Siberian Arctic tundra to the west inside the circumpolar tundra belt of the Northern Hemisphere.

The Southern Hudson Bay taiga is a terrestrial ecoregion, as classified by the World Wildlife Fund, which extends along the southern coast of Hudson Bay and resides within the larger taiga biome. The region is nearly coterminous with the Hudson Plain, a Level I ecoregion of North America as designated by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC) in its North American Environmental Atlas.



















