
Chandra, also known as Soma, is the Hindu god of the Moon, and is associated with the night, plants and vegetation. He is one of the Navagraha and Dikpala.

Jyotisha or Jyotishya is the traditional Hindu system of astrology, also known as Hindu astrology, Indian astrology and more recently Vedic astrology. The term Hindu astrology has been in use as the English equivalent of Jyotiṣa since the early 19th century, whereas Vedic astrology is a relatively recent term, entering common usage in the 1970s with self-help publications on Āyurveda or yoga.

A panchāngam is a Hindu calendar and almanac, which follows traditional units of Hindu timekeeping, and presents important dates and their calculations in a tabulated form. It is sometimes spelled Panchāngamu, Pancanga, Panchanga, Panchaanga, or Panchānga, and is often pronounced Panchāng. Panchangas are used in Jyotisha.

Rāhu (☊) is one of the nine major celestial bodies (navagraha) in Hindu texts. Unlike most of the others, Rahu is a shadow entity, one that causes eclipses and is the king of meteors. Rahu represents the ascension of the moon in its precessional orbit around the earth. Rahu is the north lunar node (ascending) and it along with Ketu is a "shadow planet" that causes eclipses. Rahu has no physical shape. It is an imaginary planet but considering the importance of Rahu in astrology, it has been allocated the status of the planet by Rishis

In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30 degree sectors that make up Earth's 360 degree orbit around the Sun. The signs enumerate from the first day of spring known as the First Point of Aries which is the vernal equinox. The Western astrological signs are Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius and Pisces. The Western zodiac originated in Babylonian astrology, and was later influenced by Hellenistic culture. Each sign was named after a constellation the sun annually moved through while crossing the sky. This observation is emphasized in the simplified and popular sun sign astrology. Over the centuries, Western astrology's zodiacal divisions have shifted out of alignment with the constellations they were named after by axial precession while Hindu astrology measurements correct for shifting.Astrology has developed in Chinese and Tibetan cultures as well.
Nakshatra is the term for lunar mansion in Hindu astrology and Indian Astronomy. A nakshatra is one of 28 sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to a prominent star or asterisms in or near the respective sectors.
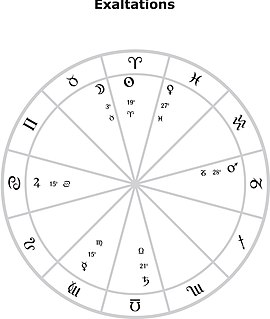
In astrology, exaltation is one of the five essential dignities of a planet. The exaltation is a place of awareness for the planet, whereas the fall is a position of weakness concerning the function of the planet. The sign position directly opposite a planet's sign of exaltation is considered to be its fall.
The term ‘benefic’ is derived from the Greek term agathopoios which literally means “good-doer”. According to Ancient Greek culture, planets were believed to have influences and provide guidance to humans, as they lived their lives. The planet's nature determines if it is Benefic or not, based on whether it helps the affected areas, with money problems for example. A planet with negative attributes would be classified as Malefic, from the Greek term kakopoios which literally means “bad-doer”. Planets are naturally Malefic or Benefic, however, a planet can change because of the astrological signs they house. Changes are dependent upon, and specific to each individual person. Horoscopes and their Zodiac sign indicate the goal of the planet for each person, as to which will be Malefic and which will be Benefic. This system is also used in Vedic astrology.

Ketu is the descending lunar node in Vedic, or Hindu astrology. According to accounts in Hinduism, Ketu belongs to Jaimini Gotra, whereas Rahu is from Paiteenasa gotra; hence the two are entirely different entities with distinct characteristics but nonetheless are two parts of a common body. Ketu is generally referred to as a "shadow" planet. It is believed to have a tremendous impact on human lives and also the whole creation. In some special circumstances it helps someone achieve the zenith of fame. Ketu is often depicted with a gem or star on his head signifying a mystery light.

Punarvasu is a Nakshatra in Hindu astrology, which refers to the two brightest stars in the constellation of Gemini: Castor and Pollux.

Rohini (रोहिणी) is a goddess in Hinduism and the favorite consort of Chandra, the moon god. She is a daughter of Daksha and sister of the 26 other Nakshatras. Of the lunar mansions the asterism Kṛttikā, Revati and Rohini are often described as deified beings and “mothers”.
Often called lunar mansion, a lunar station or lunar house is a segment of the ecliptic through which the Moon passes in its orbit around the Earth. The concept was used by several ancient cultures as part of their calendrical system.
Dasha The dasha pattern shows which planets according to Jyotish will be ruling at particular times.

Budha is a Sanskrit word that connotes the planet Mercury. Budha, in Puranic Hindu legends, is also a deity.

The Burmese zodiac is the traditional Burmese system of astronomy and astrology. While it is still an important component of the Burmese calendar, today, the zodiac is closely identified with Burmese astrology, called Bedin (ဗေဒင်). Largely derived from Hindu astronomy and Vedic astrology, the Burmese zodiac consists of not only the same 12 signs of the Western zodiac but also 27 lunar mansions of the month and eight weekday signs.

Planets in astrology have a meaning different from the astronomical understanding of what a planet is. Before the age of telescopes, the night sky was thought to consist of two very similar components: fixed stars, which remained motionless in relation to each other, and "wandering stars", which moved relative to the fixed stars over the course of the year.

In Hindu astrology, yoga is the relationship between one planet, sign, or house to another by placement, aspect, or conjunction. It is the consideration of the planetary dasha's directional effects, the most important factor which distinguishes Hindu astrology from Western astrology.

In Vedic astrology a constant reference is made to the Navamsa occupied by planets and the Lagna-point. Both, the Rasi-chart and the Navamsa-chart are deemed equally important and therefore, consulted together. Whereas the Rasi-chart provides overall information regarding the location of planets and sensitive-points such as the Lagna, the latter provides vital information regarding their active quality and strength. A planet may be well-placed in the natal-chart Rasi-wise but its full effects may not materialise if its situation in the navamsa-chart is not supportive.

Trikonasthanas or trikonas or trines are conventionally the Lagna or the Birth-ascendant, the fifth and the ninth bhava or house counted from the Lagna. They form the Dharma-trikona and are also known as the Lakshmisthanas, these bhavas and their lords signify luck and prosperity. The Lagna is both, a kendrasthana and a trikonasthana.

Sarvatobhadra Chakra in Hindu astrology is a unique technique for prediction based on the Nakshatras. It is an ancient system because it takes into account Abhijit nakshatra which is now not referred to in matters pertaining to methods that are generally employed for making astrological predictions. Janardan Harji in his Mansagari has described it as - संप्रवक्ष्यामि चक्रं त्रिलोक्यदीपिकम् - the trust-worthy quickly-revealing Trilokyadeepika Chakra.The term, Sarvatobhadra, derived from Sarva (सर्व) meaning – all, and Bhadra (भद्र)) meaning – good or auspicious, means overall auspiciousness. Abhijit nakshatra is located between Uttarashada and Sravana, it is the last quarter of Uttarashada and the first half of Sravana nakshatra.












