
Ticks are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. The timing of the origin of ticks is uncertain, though the oldest known tick fossils are from the Cretaceous period, around 100 million years old. Ticks are widely distributed around the world, especially in warm, humid climates.

The Argasidae are the family of soft ticks, one of the three families of ticks. The family contains 193 species, although the composition of the genera is less certain, and more study is needed before the genera can become stable. The currently accepted genera are Antricola, Argas, Nothoaspis, Ornithodoros, and Otobius. The Argasidae are very common in South Asia, along with 96 other species of ticks, making South Asia the region with the highest biodiversity of ticks worldwide. Soft ticks are resistant to desiccation and can live for several years in arid conditions.

Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) is a viral disease. Symptoms of CCHF may include fever, muscle pains, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, and bleeding into the skin. Onset of symptoms is less than two weeks following exposure. Complications may include liver failure. In those who survive, recovery generally occurs around two weeks after onset.

Orthonairovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Nairoviridae of the order Bunyavirales that include viruses with circular, negative-sense single stranded RNA. It got its name from the Nairobi sheep disease that affects the gastrointestinal tracts of sheep and goats. The vast majority, and perhaps all viruses in this genus are tick-borne viruses that can have human or other vertebrate hosts.

Argas persicus, also known as fowl tick or poultry tick, is a small soft-bodied tick that is found primarily on domestic fowl such as chickens, ducks, and geese. It was first recorded by Lorenz Oken in 1818 in Mianeh, Persia, and named Rhynochoprion persicum.

Theropithecus brumpti was a large terrestrial monkey that lived in the mid to late Pliocene. It is an extinct species of papionin.

Euthecodon is an extinct genus of long-snouted crocodile. It was common throughout much of Africa during the Neogene, with fossils being especially common in Kenya, Ethiopia, and Libya. Although superficially resembling that of gharials, the long snout was a trait developed independently from that of other crocodilians and suggests a diet of primarily fish. Euthecodon coexisted with a wide range of other crocodiles in the areas it inhabited before eventually going extinct during the Pleistocene.

African tick bite fever (ATBF) is a bacterial infection spread by the bite of a tick. Symptoms may include fever, headache, muscle pain, and a rash. At the site of the bite there is typically a red skin sore with a dark center. The onset of symptoms usually occurs 4–10 days after the bite. Complications are rare but may include joint inflammation. Some people do not develop symptoms.
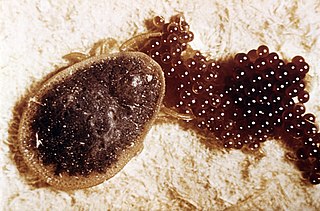
Argas is a genus of tick.

Nyavirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses in the family Nyamiviridae. Ticks and birds serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus.

Ticks of domestic animals directly cause poor health and loss of production to their hosts. Ticks also transmit numerous kinds of viruses, bacteria, and protozoa between domestic animals. These microbes cause diseases which can be severely debilitating or fatal to domestic animals, and may also affect humans. Ticks are especially important to domestic animals in tropical and subtropical countries, where the warm climate enables many species to flourish. Also, the large populations of wild animals in warm countries provide a reservoir of ticks and infective microbes that spread to domestic animals. Farmers of livestock animals use many methods to control ticks, and related treatments are used to reduce infestation of companion animals.

Gertrud Theiler was a South African parasitologist and teacher most noted for her work with nematodes and ticks.
Jane Brotherton Walker was a Kenyan-South African scholar in the field of tick taxonomy, particularly in Africa.
Argas africolumbae , ' is a small soft-bodied tick that is found primarily on chickens and birds including the pale crag martin.
Argas walkerae Kaiser & Hoogstraal, 1969, as its common name "fowl tampan" reflects, is a soft-bodied argasid tick primarily parasitizing chickens and other domestic fowl. In South Africa its natural range spans the eastern region of Eastern Cape Province from the warmer coastal regions on the Indian Ocean in the south to the cooler mountainous Drakensberg range in the northeast of the Province, with local distribution more strongly associated with the presence of fowls and wooden fowl houses, than climate alone.
Makram Nasri Kaiser (1930–1996) was a medical and veterinary acarologist who was the world's leading authority on ticks of the genus Hyalomma.

Gerald Augustus Harold Bedford was a British entomologist of the 20th century who specialised in ticks from South Africa.

Quaranjavirus is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family Orthomyxoviridae. The genome is single-stranded, negative-sense segmented RNA, generally with six segments. The genus contains two species: Johnston Atoll virus and Quaranfil virus; it has been proposed to contain species or strains including Cygnet River virus, Lake Chad virus, Tyulek virus and Wellfleet Bay virus. Quaranjaviruses predominantly infect arthropods and birds; As of March 2015, Quaranfil quaranjavirus is the only member of the genus to have been shown to infect humans. The Quaranfil and Johnston Atoll viruses are transmitted between vertebrates by ticks, resembling members of Thogotovirus, another genus of Orthomyxoviridae.

Nyamiviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Ecdysozoa and birds serve as natural hosts. The name is a portmanteau of Nyamanini Pan and Midway Atoll and the suffix -viridae used to denote a virus family. There are seven genera in this family.

Natalia Aleksandrovna Filippova was a world authority on the taxonomy of mites and especially ticks. Her monographs on the identification, morphology, development, distribution and behaviour of the family Argasidae and the sub-families of Ixodinae and Amblyomminae are standard works on these important vectors of disease.














