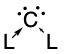Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.
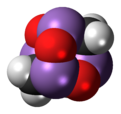
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to other atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge.
Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe(C5H5)2. The molecule is a complex consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings sandwiching a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor that sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation Fe(C5H5)+2. Ferrocene and the ferrocenium cation are sometimes abbreviated as Fc and Fc+ respectively.

Tetrahedrane is a hypothetical platonic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C4H4 and a tetrahedral structure. The molecule would be subject to considerable angle strain and has not been synthesized as of 2023. However, a number of derivatives have been prepared. In a more general sense, the term tetrahedranes is used to describe a class of molecules and ions with related structure, e.g. white phosphorus.
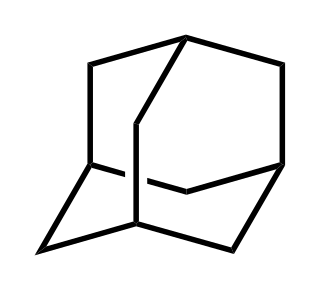
Adamantane is an organic compound with formula C10H16 or, more descriptively, (CH)4(CH2)6. Adamantane molecules can be described as the fusion of three cyclohexane rings. The molecule is both rigid and virtually stress-free. Adamantane is the most stable isomer of C10H16. The spatial arrangement of carbon atoms in the adamantane molecule is the same as in the diamond crystal. This similarity led to the name adamantane, which is derived from the Greek adamantinos (relating to steel or diamond). It is a white solid with a camphor-like odor. It is the simplest diamondoid.
A superbase is a compound that has a particularly high affinity for protons. Superbases are of theoretical interest and potentially valuable in organic synthesis. Superbases have been described and used since the 1850s.

A polyyne is any organic compound with alternating single and triple bonds; that is, a series of consecutive alkynes, (−C≡C−)n with n greater than 1. These compounds are also called polyacetylenes, especially in the natural products and chemical ecology literature, even though this nomenclature more properly refers to acetylene polymers composed of alternating single and double bonds (−CR=CR′−)n with n greater than 1. They are also sometimes referred to as oligoynes, or carbinoids after "carbyne" (−C≡C−)∞, the hypothetical allotrope of carbon that would be the ultimate member of the series. The synthesis of this substance has been claimed several times since the 1960s, but those reports have been disputed. Indeed, the substances identified as short chains of "carbyne" in many early organic synthesis attempts would be called polyynes today.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.

Dewar benzene (also spelled dewarbenzene) or bicyclo[2.2.0]hexa-2,5-diene is a bicyclic isomer of benzene with the molecular formula C6H6. The compound is named after James Dewar who included this structure in a list of possible C6H6 structures in 1869. However, he did not propose it as the structure of benzene, and in fact he supported the correct structure previously proposed by August Kekulé in 1865.

Hexamethyltungsten is the chemical compound W(CH3)6 also written WMe6. Classified as a transition metal alkyl complex, hexamethyltungsten is an air-sensitive, red, crystalline solid at room temperature; however, it is extremely volatile and sublimes at −30 °C. Owing to its six methyl groups it is extremely soluble in petroleum, aromatic hydrocarbons, ethers, carbon disulfide, and carbon tetrachloride.
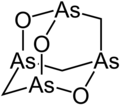
Organoarsenic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing a chemical bond between arsenic and carbon. A few organoarsenic compounds, also called "organoarsenicals," are produced industrially with uses as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. In general these applications are declining in step with growing concerns about their impact on the environment and human health. The parent compounds are arsane and arsenic acid. Despite their toxicity, organoarsenic biomolecules are well known.

In organometallic chemistry, a metallacycle is a derivative of a carbocyclic compound wherein a metal has replaced at least one carbon center; this is to some extent similar to heterocycles. Metallacycles appear frequently as reactive intermediates in catalysis, e.g. olefin metathesis and alkyne trimerization. In organic synthesis, directed ortho metalation is widely used for the functionalization of arene rings via C-H activation. One main effect that metallic atom substitution on a cyclic carbon compound is distorting the geometry due to the large size of typical metals.

Iron tetracarbonyl dihydride is the organometallic compound with the formula H2Fe(CO)4. This compound was the first transition metal hydride discovered. The complex is stable at low temperatures but decomposes rapidly at temperatures above –20 °C.
3-Alkylpyridinium (3-AP) compounds are natural chemical compounds that are found in marine sponges belonging to the order Haplosclerida. Some polymers derived from 3-APs are anticholinesterase agents and show hemolytic and cytotoxic activities. More than 70 structurally different 3-APs have been isolated from marine sponges. However, not all such sponges contain 3-AP compounds. Variation in content of 3-APs has been detected even within a single sponge species collected from different geographical area. Although 3-APs look structurally quite simple, the structure elucidation by NMR spectroscopy is complicated by the fact that most of the methylene groups in the alkyl chains show the same chemical shift. Therefore, the 3-APs are an ideal test case for a combined approach of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.

Lacking an immune system, protective shell, or mobility, sponges have developed an ability to synthesize a variety of unusual compounds for survival. C-nucleosides isolated from Caribbean Cryptotethya crypta, were the basis for the synthesis of zidovudine (AZT), aciclovir (Cyclovir), cytarabine (Depocyt), and cytarabine derivative gemcitabine (Gemzar).
Arsenidosilicates are chemical compounds that contain anions with arsenic bonded to silicon. They are in the category of tetrelarsenides, pnictidosilicates, or tetrelpnictides. They can be classed as Zintl phases or intermetallics. They are analogous to the nitridosilicates, phosphidosilicates, arsenidogermanates, and arsenidostannates. They are distinct from arsenate silicates which have oxygen connected with arsenic and silicon, or arsenatosilicates with arsenate groups sharing oxygen with silicate.
Suzanne Cathleen Bart an American chemist who is a professor of inorganic chemistry at Purdue University. Her group's research focuses on actinide organometallic chemistry, and especially the characterization of low-valent organouranium complexes, actinide complexes with redox-active ligands, and discovery of new reactions that utilize these compounds. Bart's research has applications in the development of carbon-neutral fuel sources and the remediation of polluted sites.
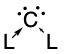
Carbones are a class of molecules containing a carbon atom in the 1D excited state with a formal oxidation state of zero where all four valence electrons exist as unbonded lone pairs. These carbon-based compounds are of the formula CL2 where L is a strongly σ-donating ligand, typically a phosphine (carbodiphosphoranes) or a N-heterocyclic carbene/NHC (carbodicarbenes), that stabilises the central carbon atom through donor-acceptor bonds. Carbones possess high-energy orbitals with both σ- and π-symmetry, making them strong Lewis bases and strong π-backdonor substituents. Carbones possess high proton affinities and are strong nucleophiles which allows them to function as ligands in a variety of main group and transition metal complexes. Carbone-coordinated elements also exhibit a variety of different reactivities and catalyse various organic and main group reactions.

Organoberyllium chemistry involves the synthesis and properties of organometallic compounds featuring the group 2 alkaline earth metal beryllium (Be). The area remains understudied, relative to the chemistry of other main-group elements, because although metallic beryllium is relatively unreactive, its dust causes berylliosis and compounds are toxic. Organoberyllium compounds are typically prepared by transmetallation or alkylation of beryllium chloride.
The stabilization of bismuth's +3 oxidation state due to the inert pair effect yields a plethora of organometallic bismuth-transition metal compounds and clusters with interesting electronics and 3D structures.