
Legio I Italica was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded by emperor Nero on September 22, 66. Originally named Legio Phalanx Alexandri Magni, it was stationed in Italy during the year of four emperors and gained the name Italica. It was later stationed at Novae, near modern-day Svishtov (Bulgaria). There are still records of the I Italica on the Danube border at the beginning of the 5th century. The emblem of the legion was a boar.

Theridiidae, also known as the tangle-web spiders, cobweb spiders and comb-footed spiders, is a large family of araneomorph spiders first described by Carl Jakob Sundevall in 1833. This diverse, globally distributed family includes over 3,000 species in 124 genera, and is the most common arthropod found in human dwellings throughout the world.

Legio III Italica was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in 165 AD by the emperor Marcus Aurelius for his campaign against the Marcomanni tribe. The cognomen Italica suggests that the legion's original recruits were drawn for the defence of Italy. The legion was still active in Raetia and other provinces in the early 5th century.

Populus nigra, the black poplar, is a species of cottonwood poplar, the type species of section Aigeiros of the genus Populus, native to Europe, southwest and central Asia, and northwest Africa.

Italica was an ancient Roman city in Hispania; its site is close to the town of Santiponce in the province of Seville, Spain. It was founded in 206 BC by Roman general Scipio as a colonia for his Italic veterans and named after them. Italica later grew attracting new migrants from the Italian peninsula and also with the children of Roman soldiers and native women. Among the Italic settlers were a branch of the gens Ulpia from the Umbrian city of Tuder and a branch of the gens Aelia from the city of Hadria, either co-founders of the town or later migrants who arrived at an unknown time; the Ulpi Traiani and the Aelii Hadriani were the respective stirpes of the Roman emperors Trajan and Hadrian, both born in Italica.

Psechridae is a family of araneomorph spiders with about 70 species in two genera. These are among the biggest cribellate spiders with body lengths up to 2 centimetres (0.79 in) and funnel webs more than 1 metre in diameter.

Symphytognathidae is a family of spiders with 90 described species in eight genera. They occur in the tropics of Central and South America and the Australian region. Exceptions include Anapistula benoiti, Anapistula caecula, and Symphytognatha imbulunga, found in Africa, Anapistula ishikawai, found in Japan, and Anapistula jerai, found in Southeast Asia.

Mysmenidae is a spider family with about 180 described species in seventeen genera. The family is one of the least well known of the orb-weaving spiders because of their small size and cryptic behaviour. These spiders are found in humid habitats such as among leaf litter and in caves.

Orchis italica, the naked man orchid or the Italian orchid, is a species of orchid native to the Mediterranean Basin. It gets its common name from the lobed lip (labellum) of each flower which mimics the general shape of a naked man. In Italy, it is believed that the consumption of the plant is conducive to virility. It prefers partial shade and low nutrient soil, and flowers in April. Orchis italica grows up to 50 centimetres (20 in) in height, with bright pink, densely clustered flowers.

The Euctenizidae are a family of mygalomorph spiders. They are now considered to be more closely related to Idiopidae.

Histopona is a genus of funnel weavers first described as a sub-genus of Hadites by Tamerlan Thorell in 1870. It was elevated to genus by Brignoli in 1972.
Niklas Westring was a Swedish entomologist and arachnologist.

Asagena is a genus of comb-footed spiders that was first described by Carl Jakob Sundevall in 1833.
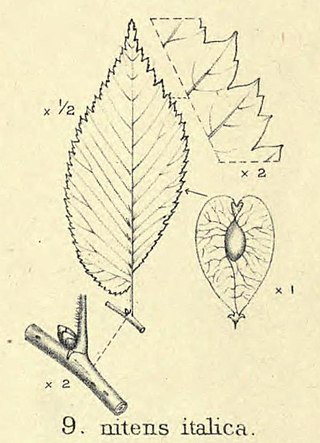
Ulmus minorvar.italica was first described by Augustine Henry in 1913, as a 'variety' of field elm from Italy, Spain, Portugal and Algeria. He called it Ulmus nitens var. italica, 'Mediterranean Elm'. The variety was accepted by Krüssman (1984), despite the wide source-area claimed for it, as a non-clonal cultivar, U. carpinifolia var. italicaHenry. Bean (1988), however, considered it "a variety of rather dubious standing", and it was ignored by Richens (1983), who listed instead a "small-leaved U. minor of Spain" and a "narrow-leaved U. minor of northern and central Italy", as well as "the densely hairy leaved U. minor of southern Italy", the latter being Ulmus minor subsp. canescens, formerly Melville's Ulmus canescens.
Asagena pulcher is a species of cobweb spider in the family Theridiidae. It is found in the United States.
Asagena fulva is a species of cobweb spider in the family Theridiidae. It is found in the United States and Mexico.
Asagena brignolii is a species of cobweb spider in the family Theridiidae. It is found in Greece.
Asagena semideserta is a species of cobweb spider in the family Theridiidae. It is found in Kazakhstan and Mongolia.

Asagena phalerata is a species of cobweb spider in the family Theridiidae. It is found throughout Europe and Eurasia, as far east as Korea. They are typically found in sparsely vegetated environments.
Asagena meridionalis is a species of cobweb spider in the family Theridiidae. It is found throughout central, south, and east Europe, as well as the Caucasus.














