
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, nuclear decommissioning, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons reprocessing. The storage and disposal of radioactive waste is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment.

The Fulda is a river of Hesse and Lower Saxony, Germany. It is one of two headstreams of the Weser. The Fulda is 220.4 kilometres (137.0 mi) long.

The Waste Isolation Pilot Plant, or WIPP, is the world's third deep geological repository licensed to store transuranic radioactive waste for 10,000 years. The storage rooms at the WIPP are 2,150 feet underground in a salt formation of the Delaware Basin. The waste is from the research and production of United States nuclear weapons only. The plant started operation in 1999, and the project is estimated to cost $19 billion in total.

The Nuclear Waste Policy Act of 1982 is a United States federal law which established a comprehensive national program for the safe, permanent disposal of highly radioactive wastes.

A deep geological repository is a way of storing hazardous or radioactive waste within a stable geologic environment. It entails a combination of waste form, waste package, engineered seals and geology that is suited to provide a high level of long-term isolation and containment without future maintenance. This will prevent any radioactive dangers. A number of mercury, cyanide and arsenic waste repositories are operating worldwide including Canada and Germany and a number of radioactive waste storage sites are under construction with the Onkalo in Finland being the most advanced.
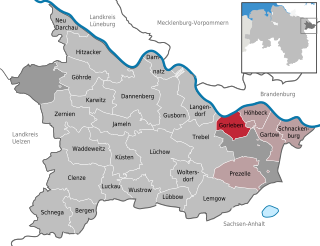
Gorleben is a small municipality (Gemeinde) in the Gartow region of the Lüchow-Dannenberg district in the far north-east of Lower Saxony, Germany, a region also known as the Wendland.
Höfer is a village and a former municipality in the district of Celle, in Lower Saxony, Germany. Since 1 January 2014, it has been part of the municipality Eschede, of which it is an Ortschaft. The Ortschaft Höfer contains the villages Höfer, Aschenberg and Ohe.

Wittmar is a municipality in the district of Wolfenbüttel, in Lower Saxony, Germany.

The Gundremmingen Nuclear Power Plant was a nuclear power station in Germany. It was located in Gundremmingen, district of Günzburg, Bavaria. It was operated by Kernkraftwerk Gundremmingen GmbH, a joint operation of RWE Power AG (75%) and PreussenElektra (25%). Unit B was shut down at the end of 2017. Unit C, the last boiling water reactor in Germany, was shut down on New Year's Eve 2021, as part of the German nuclear phase out. However, Gundremmingen unit C as well as the other two German nuclear reactors shut down that day remain capable of restarting operations as of March 2022. In November 1975, Unit A was the site of the first fatal accident in a nuclear power plant and subsequently of a major incident resulting in a total loss in 1977.

The Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection, abbreviated BMUV, is a cabinet-level ministry of the Federal Republic of Germany. It has branches in Bonn and Berlin.

The anti-nuclear movement in Germany has a long history dating back to the early 1970s when large demonstrations prevented the construction of a nuclear plant at Wyhl. The Wyhl protests were an example of a local community challenging the nuclear industry through a strategy of direct action and civil disobedience. Police were accused of using unnecessarily violent means. Anti-nuclear success at Wyhl inspired nuclear opposition throughout West Germany, in other parts of Europe, and in North America. A few years later protests raised against the NATO Double-Track Decision in West Germany and were followed by the foundation of the Green party.

High-level radioactive waste management addresses the handling of radioactive materials generated from nuclear power production and nuclear weapons manufacture. Radioactive waste contains both short-lived and long-lived radionuclides, as well as non-radioactive nuclides. In 2002, the United States stored approximately 47,000 tonnes of high-level radioactive waste.

The Gorleben salt dome is a proposed deep geological repository in a salt dome in Gorleben in the Lüchow-Dannenberg district in the far north-east of Lower Saxony for low-, medium- and high-level radioactive waste.

The Morsleben Radioactive Waste Repository is a deep geological repository for radioactive waste in the Bartensleben rock salt mine in Morsleben, Börde District, in the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany.

The Konrad mine is a former iron ore mine proposed as a deep geological repository for medium- and low level radioactive waste in the city Salzgitter in the Metropolitan region Hannover-Braunschweig-Göttingen-Wolfsburg in southeast Lower Saxony, Germany, located between Hildesheim and Braunschweig. It has two shafts: Konrad I and Konrad II.

The Bundesamt für Strahlenschutz (BfS) is the German Federal Office for Radiation Protection. The BfS was established in November 1989; the headquarters is located in Salzgitter, with branch offices in Berlin, Bonn, Freiburg, Gorleben, Oberschleißheim and Rendsburg. It has 708 employees and an annual budget of around 305 million Euro (2009). Since 2009 the BfS is also responsible for the storage site of radioactive waste, Schacht Asse II.

Long-term nuclear waste warning messages are communication attempts intended to deter human intrusion at nuclear waste repositories in the far future, within or above the order of magnitude of 10,000 years. Nuclear semiotics is an interdisciplinary field of research, first done by the American Human Interference Task Force in 1981.
The Andreev Bay nuclear accident took place at Soviet naval base 569 in February 1982. Andreev Bay is a radioactive waste repository 55 km northwest of Murmansk and 60 km from the Norwegian border, on the western shore of the Zapadnaya Litsa. The repository entered service in 1961. In February 1982, a nuclear accident occurred in which radioactive water was released from a pool in building #5. Cleanup of the accident took place from 1983 to 1989. About 700,000 tonnes of highly radioactive water leaked into the Barents Sea during that time. About 1,000 people took part in the cleanup effort. Vladimir Konstantinovich Bulygin, who was in charge of the naval fleet's radiation accidents, received the Hero of the Soviet Union distinction for his work.
The Czech Radioactive Waste Repository Authority was established on 1 June 1997 as a state organisation established by the Ministry of Industry and Trade. In 2001, SÚRAO assumed the status of a government agency. The Authority is headed by its managing director, Dr. Jiří Slovák. The governing body of SÚRAO consists of its Board which is made up of representatives from the government, radioactive waste producers and the general public. The managing director and members of the Board of SÚRAO are directly appointed by the Minister of Industry and Trade.

The Bundesgesellschaft für Endlagerung mbH is a German federally owned company based in Peine, Lower Saxony, Germany.



















