
Basque is a language spoken by Basques and others of the Basque Country, a region that straddles the westernmost Pyrenees in adjacent parts of northern Spain and southwestern France. Linguistically, Basque is a language isolate. The Basques are indigenous to, and primarily inhabit, the Basque Country. The Basque language is spoken by 28.4% (751,500) of Basques in all territories. Of these, 93.2% (700,300) are in the Spanish area of the Basque Country and the remaining 6.8% (51,200) are in the French portion.

Carnivora is an order of placental mammals that have specialized in primarily eating flesh, whose members are formally referred to as carnivorans. The order Carnivora is the fifth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species.

Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country mostly in South America with insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Ecuador and Peru to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 departments. The Capital District of Bogotá is also the country's largest city hosting the main financial and cultural hub. Other major urbes include Medellín, Cali, Barranquilla, Cartagena, Santa Marta, Cúcuta, Ibagué, Villavicencio and Bucaramanga. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers, and has a population of around 52 million. Its rich cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a colony, fusing cultural elements brought by mass immigration from Europe and the Middle East, with those brought by the African diaspora, as well as with those of the various Indigenous civilizations that predate colonization. Spanish is the official language, although English and 64 other languages are recognized regionally.

The jaguar is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus Panthera native to the Americas. With a body length of up to 1.85 m and a weight of up to 158 kg (348 lb), it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the third largest in the world. Its distinctively marked coat features pale yellow to tan colored fur covered by spots that transition to rosettes on the sides, although a melanistic black coat appears in some individuals. The jaguar's powerful bite allows it to pierce the carapaces of turtles and tortoises, and to employ an unusual killing method: it bites directly through the skull of mammalian prey between the ears to deliver a fatal blow to the brain.

The lion is a large cat of the genus Panthera native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adult male lions are larger than females and have a prominent mane. It is a social species, forming groups called prides. A lion's pride consists of a few adult males, related females, and cubs. Groups of female lions usually hunt together, preying mostly on large ungulates. The lion is an apex and keystone predator; although some lions scavenge when opportunities occur and have been known to hunt humans, lions typically do not actively seek out and prey on humans.
Panthera is a genus within the family Felidae that was named and described by Lorenz Oken in 1816 who placed all the spotted cats in this group. Reginald Innes Pocock revised the classification of this genus in 1916 as comprising the tiger, lion, jaguar, and leopard on the basis of common cranial features. Results of genetic analysis indicate that the snow leopard also belongs to the genus Panthera, a classification that was accepted by IUCN Red List assessors in 2008.

Monocotyledons, commonly referred to as monocots, are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which the flowering plants have traditionally been divided; the rest of the flowering plants have two cotyledons and are classified as dicotyledons, or dicots.

Henry IV, also known by the epithets Good King Henry or Henry the Great, was King of Navarre from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monarch of France from the House of Bourbon, a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. He pragmatically balanced the interests of the Catholic and Protestant parties in France as well as among the European states. He was assassinated in 1610 by a Catholic zealot, and was succeeded by his son Louis XIII.
Order is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families.

Jasmine is a genus of shrubs and vines in the olive family of Oleaceae. It contains around 200 species native to tropical and warm temperate regions of Eurasia, Africa, and Oceania. Jasmines are widely cultivated for the characteristic fragrance of their flowers. A number of unrelated plants contain the word "jasmine" in their common names.
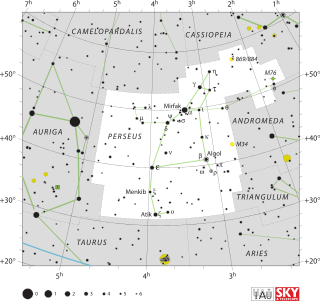
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose asterism was named together as Perseus et Caput Medusae; however, this never came into popular usage.

A mongoose is a small terrestrial carnivorous mammal belonging to the family Herpestidae. This family is currently split into two subfamilies, the Herpestinae and the Mungotinae. The Herpestinae comprises 23 living species that are native to southern Europe, Africa and Asia, whereas the Mungotinae comprises 11 species native to Africa. The Herpestidae originated about 21.8 ± 3.6 million years ago in the Early Miocene and genetically diverged into two main genetic lineages between 19.1 and 18.5 ± 3.5 million years ago.

De Stijl, also known as Neoplasticism, was a Dutch art movement founded in 1917 in Leiden. De Stijl consisted of artists and architects. In a more narrow sense, the term De Stijl is used to refer to a body of work from 1917 to 1931 founded in the Netherlands. Proponents of De Stijl advocated pure abstraction and universality by a reduction to the essentials of form and colour; they simplified visual compositions to vertical and horizontal, using only black, white and primary colors.

Colubridae is a family of snakes. With 249 genera, it is the largest snake family. The earliest species of the family date back to the Oligocene epoch. Colubrid snakes are found on every continent except Antarctica.

The ocelot is a medium-sized spotted wild cat that reaches 40–50 cm (15.7–19.7 in) at the shoulders and weighs between 7 and 15.5 kg on average. It is native to the southwestern United States, Mexico, Central and South America, and the Caribbean islands of Trinidad and Margarita. Carl Linnaeus scientifically described it in 1758. Two subspecies are recognized.

The Felinae are a subfamily of the family Felidae. This subfamily comprises the small cats having a bony hyoid, because of which they are able to purr but not roar.

Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers 1,972,550 km2, making it the world's 13th-largest country by area; with a population of over 126 million, it is the 10th-most-populous country and has the most Spanish speakers. Mexico is organized as a federal republic comprising 31 states and Mexico City, its capital.
J, or j, is the tenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual name in English is jay, with a now-uncommon variant jy. When used in the International Phonetic Alphabet for the voiced palatal approximant, it may be called yod or jod.

Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of 2,780,400 km2 (1,073,500 sq mi), making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica.

Neanderthals, also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. The reasons for Neanderthal extinction are disputed. Theories for their extinction include demographic factors such as small population size and inbreeding, competitive replacement, interbreeding and assimilation with modern humans, climate change, disease, or a combination of these factors.

















