
A diatom is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion tonnes of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fresh-water lakes.

Navicula is a genus of boat-shaped diatom algae, comprising over 1,200 species. Navicula is Latin for "small ship", and also a term in English for a boat-shaped incense-holder.
In botany, a zoid or zoïd is a reproductive cell that possesses one or more flagella, and is capable of independent movement. Zoid can refer to either an asexually reproductive spore or a sexually reproductive gamete. In sexually reproductive gametes, zoids can be either male or female depending on the species. For example, some brown alga (Phaeophyceae) reproduce by producing multi-flagellated male and female gametes that recombine to form the diploid sporangia. Zoids are primarily found in some protists, diatoms, green alga, brown alga, non-vascular plants, and a few vascular plants. The most common classification group that produces zoids is the heterokonts or stramenopiles. These include green alga, brown alga, oomycetes, and some protists. The term is generally not used to describe motile, flagellated sperm found in animals. Zoid is also commonly confused for zooid which is a single organism that is part of a colonial animal.

Thalassiosira pseudonana is a species of marine centric diatoms. It was chosen as the first eukaryotic marine phytoplankton for whole genome sequencing. T. pseudonana was selected for this study because it is a model for diatom physiology studies, belongs to a genus widely distributed throughout the world's oceans, and has a relatively small genome at 34 mega base pairs. Scientists are researching on diatom light absorption, using the marine diatom of Thalassiosira. The diatom requires a high enough concentration of CO2 in order to utilize C4 metabolism (Clement et al. 2015).

Chaetocerotaceae is a diatom family (Bacillariophyta). This family comprise the three genera Attheya T. West, Bacteriastrum Shadbolt and Chaetoceros Ehrenberg. Chaetoceros is perhaps the largest and most species rich genus of marine planktonic diatoms. The taxonomic status within Chaetocerotaceae at present is somewhat unclear.

Bolidophyceae is a class of photosynthetic heterokont picophytoplankton, and consist of less than 20 known species. They are distinguished by the angle of flagellar insertion and swimming patterns as well as recent molecular analyses. Bolidophyceae is the sister taxon to the diatoms (Bacillariophyceae). They lack the characteristic theca of the diatoms, and have been proposed as an intermediate group between the diatoms and all other heterokonts.
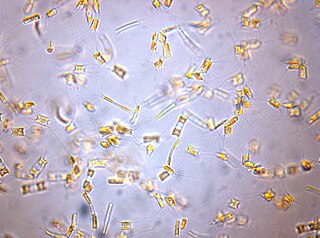
Attheya is a genus of small single celled diatoms. Some of these species were earlier regarded to belong to Chaetoceros, or to Gonioceros, the taxonomic status of some of these species are still debated.
Attheya arenicola is a diatom in the genus Attheya. Type material was collected from intertidal sand in Penbre, South Wales.
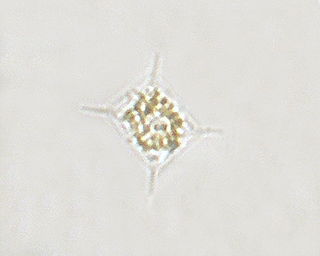
Attheya decora is a species of diatoms in the genus Attheya. Type material was collected from Cresswell sands, Northumberland by Mr. Atthey.
Attheya flexuosa is a species of diatoms in the genus Attheya. Type material was collected from Benllech, Gwynedd, North Wales in UK on intertidal sand.

Attheya longicornis is a species of diatoms in the genus Attheya. Type material was collected from Penberth, Cornwall in England.

Bacteriastrum is a genus of diatoms in family Chaetocerotaceae. There are more than 30 described species in genus Bacteriastrum, but many of these are not currently accepted, and new species are still added to the genus. The type species for the genus is Bacteriastrum furcatum Shadbolt.
Attheya gaussii is a species of diatoms in the genus Attheya.
Attheya septentrionalis is a species of diatoms in the genus Attheya.

Nitzschia is a common pennate marine diatom. In the scientific literature, this genus, named after Christian Ludwig Nitzsch, is sometimes referred to incorrectly as Nitzchia, and it has many species described, which all have a similar morphology. In its current circumscription, Nitzschia is paraphyletic.
Miracula is a genus of parasitic protists that parasite diatoms, containing the type species Miracula helgolandica. More recently, the species Miracula moenusica from the river Main in Frankfurt am Main, Miracula islandica from a shore in the north of Iceland, Miracula einbuarlaekurica from a streamlet in the north of Iceland, and Miracula blauvikensis from the shore at the research station Blávík in the east fjords of Iceland were added to the genus. It is the only genus in the family Miraculaceae, of uncertain taxonomic position within the Oomycetes. They're one of the most basal lineages in the phylogeny of Oomycetes.

Thalassiosira is a genus of centric diatoms, comprising over 100 marine and freshwater species. It is a diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotes that make up a vital part of marine and freshwater ecosystems, in which they are key primary producers and essential for carbon cycling
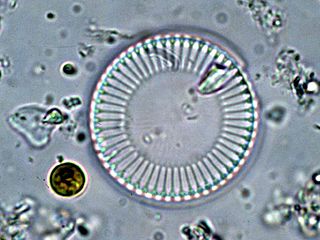
Cyclotella is a genus of diatoms often found in oligotrophic environments, both marine and fresh water. It is in the family Stephanodiscaceae and the order Thalassiosirales. The genus was first discovered in the mid-1800s and since then has become an umbrella genus for nearly 100 different species, the most well-studied and the best known being Cyclotella meneghiniana. Despite being among the most dominant genera in low-productivity environments, it is relatively understudied.

Diatoms belong to a large group called the heterokonts, which include both autotrophs such as golden algae and kelp; and heterotrophs such as water moulds. The classification of heterokonts is still unsettled: they may be designated a division, phylum, kingdom, or something intermediate to those. Consequently, diatoms are ranked anywhere from a class, usually called Diatomophyceae or Bacillariophyceae, to a division (=phylum), usually called Bacillariophyta, with corresponding changes in the ranks of their subgroups.











