
The Cyrillic script is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia and is used as the national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia and East Asia.

The East Slavic languages constitute one of the three regional subgroups of Slavic languages, currently spoken throughout Eastern Europe, Northern Asia, and the Caucasus. It is the group with the largest numbers of speakers, far out-numbering the Western and Southern Slavic groups. The existing East Slavic languages are Belarusian, Russian and Ukrainian; Rusyn is considered to be either a separate language or a dialect of Ukrainian.

Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country located in Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, and from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Black and Caspian seas in the south. Russia covers 17,125,191 square kilometres (6,612,073 sq mi), spanning more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land area, stretching eleven time zones, and bordering 16 sovereign nations. Moscow is the country's capital and largest city; other major cities include Saint Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Kazan, Nizhny Novgorod, Chelyabinsk and Samara.

Russian is an East Slavic language native to the Russians in Eastern Europe. It is an official language in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, as well as being widely used throughout the Caucasus, Central Asia and to some extent in the Baltic states. Russian belongs to the family of Indo-European languages, one of the four living members of the East Slavic languages alongside, and part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. There is a high degree of mutual intelligibility between Russian, Belarusian and Ukrainian.

Siberia is an extensive geographical region spanning much of Eurasia and Northern Asia. Siberia has been part of modern Russia since the latter half of the 16th century.

The Volga is the longest river in Europe. Flowing through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea, it has a length of 3,531 km (2,194 mi) and a catchment area of 1,360,000 km2 (530,000 sq mi). It is also Europe's largest river in terms of discharge and drainage basin. It is widely regarded as the national river of Russia. The old Russian state, the Rus' Khaganate, arose around the Volga river. Historically, it was an important meeting place of Eurasian civilizations.

The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east.
The Gzhelian is an age in the ICS geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest stage of the Pennsylvanian, the youngest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Gzhelian lasted from 303.7 to 298.9 Ma. It follows the Kasimovian age/stage and is followed by the Asselian age/stage, the oldest subdivision of the Permian system.

The 2018 FIFA World Cup was an international football tournament contested by men's national teams and took place between 14 June and 15 July 2018 in Russia. It was the 21st FIFA World Cup, a worldwide football tournament held once every four years. It was the eleventh time the championships had been held in Europe, and the first time they were held in Eastern Europe. At an estimated cost of over $14.2 billion, it was the most expensive World Cup to date.
Eurasia is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as they have no clear physical separation between them; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data.

Vladivostok is the largest city and the administrative centre of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area of 331.16 square kilometres, with a population of 606,561 residents, up to 812,319 residents in the urban agglomeration. Vladivostok is the second-largest city in the Far Eastern Federal District, as well as the Russian Far East, after Khabarovsk.
Autophila pauli is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Charles Boursin in 1940. It is found in arid areas of Jordan, Israel, Sinai, and Egypt.
Autophila anaphanes is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Charles Boursin in 1940. It is found in the eastern part of the Mediterranean, including the Balkans, Cyprus, Turkey, Lebanon and Israel.
Autophila cerealis is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Otto Staudinger in 1871. It is found in the Near East and Middle East, from Turkey and the Levant to Central Asia and the Arabian Peninsula.
Autophila limbata is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Otto Staudinger in 1871. It is found in southern France, southern Italy, the Iberian Peninsula, Greece, the Crimea, the Near East, Iran, Transcaucasia and Turkmenistan.
Autophila libanotica is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Otto Staudinger in 1901. It is found from Turkey to Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan Iran, northern Greece, Lebanon and Israel.
Autophila einsleri is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Hans Georg Amsel in 1935. It is found in Turkey, Jordan, Cyprus, the Caucasus, Syria, Iraq, Iran, Lebanon, Israel, Turkmenistan and Oman.
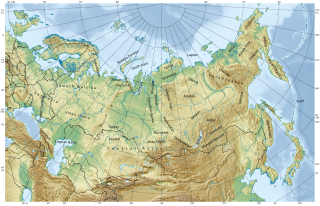
The geology of Russia, the world's largest country, which extends over much of northern Eurasia, consists of several stable cratons and sedimentary platforms bounded by orogenic (mountain) belts.

Somov Sea was a proposed name for part of the Southern Ocean. It would be located north of the easternmost part of the Antarctic subcontinent East Antarctica, north of Oates Coast, Victoria Land, and of George V Coast, between 150° and 170° East. West of it would be the D'Urville Sea. East of Cape Adare, at 170°14' East, is the Ross Sea.
Hans Georg Amsel was a German entomologist with four publications ranging from 1951 to 1962. His home town was Cologne, although he frequently was in Kiel. His original job was in the banking industry, and he later worked in a bookstore. After quitting his job as bookstore worker, he decided to follow his heart and transfer to zoology, where he became an entomologist. His specific profession was studying Lepidoptera. "Soon after he was appointed as Head of Department of Entomology at the Colonial and Overseas museum called to Bremen, then rendered military service and, worked as a private scholar, he came as entomologist at the State Collections of Natural History in Karlsruhe," states a letter for his 60th birthday from the Journal of the Entomological Society of Vienna. During Amsel's career, he authored about twenty-six different Lepidoptera species and genera, and published four books.











