
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration is a Washington, D.C.–based scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce, a United States federal government department. The agency is charged with forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charting the seas, conducting deep sea exploration, and managing fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone.
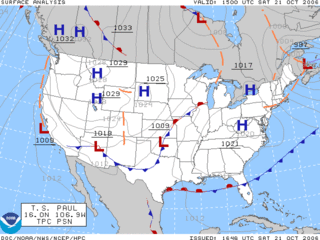
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations.

A tornado warning is a public warning that is issued by weather forecasting agencies to an area in the direct path of a tornado or a thunderstorm that is capable of producing a tornado. Modern weather surveillance technology such as Doppler weather radar allow for early detection of rotation in a thunderstorm, and for subsequent warnings to be issued before a tornado actually develops. It is nevertheless still not uncommon that warnings are issued based on reported visual sighting of a tornado, funnel cloud, or wall cloud, typically from weather spotters or the public, but also law enforcement or local emergency management. In particular, a tornado can develop in a gap of radar coverage, of which there are several known in the United States.

A tornado watch is a severe weather watch product of the National Weather Service that is issued by national weather forecasting agencies when meteorological conditions are favorable for the development of severe thunderstorms capable of producing tornadoes. In addition to the potential for tornado development, thunderstorms that develop within the watch area may contain large hail, straight-line winds, intense rainfall and/or flooding that pose a similar damage risk as the attendant tornado threat. A tornado watch does not mean a tornado is active or will appear, just that favorable conditions increases the likelihood of such happening. A watch must not be confused with a tornado warning.

A severe thunderstorm watch is a statement issued by weather forecasting agencies to advise the public that atmospheric conditions in a given region may lead to the development of severe thunderstorms within the region over several hours. The criteria for issuing a watch varies from country to country and may also include torrential rainfall and tornadoes. A watch may also be issued several hours ahead of the arrival of a mature and organized complex of storms, such as a mesoscale convective system.

The National Weather Service (NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the purposes of protection, safety, and general information. It is a part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) branch of the Department of Commerce, and is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland, within the Washington metropolitan area. The agency was known as the United States Weather Bureau from 1890 until it adopted its current name in 1970.

NEXRAD or Nexrad is a network of 159 high-resolution S-band Doppler weather radars operated by the National Weather Service (NWS), an agency of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) within the United States Department of Commerce, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) within the Department of Transportation, and the U.S. Air Force within the Department of Defense. Its technical name is WSR-88D.

A weather map, also known as synoptic weather chart, displays various meteorological features across a particular area at a particular point in time and has various symbols which all have specific meanings. Such maps have been in use since the mid-19th century and are used for research and weather forecasting purposes. Maps using isotherms show temperature gradients, which can help locate weather fronts. Isotach maps, analyzing lines of equal wind speed, on a constant pressure surface of 300 or 250 hPa show where the jet stream is located. Use of constant pressure charts at the 700 and 500 hPa level can indicate tropical cyclone motion. Two-dimensional streamlines based on wind speeds at various levels show areas of convergence and divergence in the wind field, which are helpful in determining the location of features within the wind pattern. A popular type of surface weather map is the surface weather analysis, which plots isobars to depict areas of high pressure and low pressure. Cloud codes are translated into symbols and plotted on these maps along with other meteorological data that are included in synoptic reports sent by professionally trained observers.

In meteorology, a downburst is a strong downward and outward gushing wind system that emanates from a point source above and blows radially, that is, in straight lines in all directions from the area of impact at surface level. Capable of producing damaging winds, it may sometimes be confused with a tornado, where high-velocity winds circle a central area, and air moves inward and upward. These usually last for seconds to minutes. Downbursts are particularly strong downdrafts within thunderstorms.

The Weather Prediction Center (WPC), located in College Park, Maryland, is one of nine service centers under the umbrella of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), a part of the National Weather Service (NWS), which in turn is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) of the U.S. Government. Until March 5, 2013 the Weather Prediction Center was known as the Hydrometeorological Prediction Center (HPC). The Weather Prediction Center serves as a center for quantitative precipitation forecasting, medium range forecasting, and the interpretation of numerical weather prediction computer models.
This article describes severe weather terminology used by the National Weather Service (NWS) in the United States. The NWS, a government agency operating as an arm of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) branch of the United States Department of Commerce (DoC), defines precise meanings for nearly all of its weather terms.
A pilot report or PIREP is a report of actual flight or ground conditions encountered by an aircraft. Reports commonly include information about atmospheric conditions or airport conditions. This information is usually relayed by radio to the nearest ground station, but other options also exist in some regions. The message would then be encoded and relayed to other weather offices and air traffic service units.
Logan County Airport is a public use airport located 2.2 nautical miles northeast of the central business district of Lincoln, a city in Logan County, Illinois, United States. It is owned by the Logan County Board. The airport is also the site of the National Weather Service Central Illinois.
An AIRMET, or Airmen's Meteorological Information, is a concise description of weather phenomena that are occurring or may occur (forecast) along an air route that may affect aircraft safety. Compared to SIGMETs, AIRMETs cover less severe weather: moderate turbulence and icing, sustained surface winds of 30 knots or more, or widespread restricted visibility.
The tornado outbreak of January 1–2, 2006, was one of the largest tornado outbreaks ever recorded in the month of January. The outbreak affected much of the Central and Southern United States and produced 20 tornadoes. The tornadoes caused considerable damage in the states of Kentucky and Georgia. There were no tornado related fatalities and only minor injuries were reported.

Ormond Beach Airport, also known as Ormond Beach Municipal Airport, is a general aviation airport located 3 miles (4.8 km) to the northwest of the city of Ormond Beach in Volusia County, Florida, United States.

Surface weather observations are the fundamental data used for safety as well as climatological reasons to forecast weather and issue warnings worldwide. They can be taken manually, by a weather observer, by computer through the use of automated weather stations, or in a hybrid scheme using weather observers to augment the otherwise automated weather station. The ICAO defines the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA), which is the model of the standard variation of pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity with altitude in the Earth's atmosphere, and is used to reduce a station pressure to sea level pressure. Airport observations can be transmitted worldwide through the use of the METAR observing code. Personal weather stations taking automated observations can transmit their data to the United States mesonet through the Citizen Weather Observer Program (CWOP), the UK Met Office through their Weather Observations Website (WOW), or internationally through the Weather Underground Internet site. A thirty-year average of a location's weather observations is traditionally used to determine the station's climate. In the US a network of Cooperative Observers make a daily record of summary weather and sometimes water level information.

The Ocean Prediction Center (OPC), established in 1995, is one of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction's (NCEP's) original six service centers. Until 2003, the name of the organization was the Marine Prediction Center. Its origins are traced back to the sinking of the RMS Titanic in 1912. The OPC issues forecasts up to five days in advance for ocean areas north of 31° north latitude and west of 35° west longitude in the Atlantic, and across the northeast Pacific north of 30° north latitude and east of 160° east longitude. Until recently, the OPC provided forecast points for tropical cyclones north of 20° north latitude and east of the 60° west longitude to the National Hurricane Center. OPC is composed of two branches: the Ocean Forecast Branch and the Ocean Applications Branch.

National Weather Service - Shreveport, LA (SHV) is one of 122 weather forecast offices around the United States. It is responsible for issuing public and aviation forecasts and warning for South Central and Southwestern Arkansas, Southeastern Oklahoma, and Eastern and Northeastern Texas Counties, as well as for North Central and Northwestern Louisiana Parishes. It is co-located with a weather radar (KSHV) of the NEXRAD network and an upper air sounding facility. It controls the issuance of weather information and bulletins on a certain number of NOAA Weather Radio.













