METAR is a format for reporting weather information. A METAR weather report is predominantly used by aircraft pilots, and by meteorologists, who use aggregated METAR information to assist in weather forecasting. Today, according to the advancement of technology in civil aviation, the METAR is sent as IWXXM model.
A winter weather advisory is a hazardous weather statement issued by local Weather Forecast Offices (WFO) of the National Weather Service in the United States when one or more types of winter precipitation—snow, rain and snow mixed, freezing rain, sleet, graupel, etc.—presenting a hazard, but not expected to produce accumulations meeting storm warning criteria, are forecast within 36 hours of the expected onset of precipitation or are occurring in the advisory's coverage area.
SYNOP is a numerical code used for reporting weather observations made by staffed and automated weather stations. SYNOP reports are typically sent every six hours by Deutscher Wetterdienst on shortwave and low frequency using RTTY. A report consists of groups of numbers describing general weather information, such as the temperature, barometric pressure and visibility at a weather station. It can be decoded by open-source software such as seaTTY, metaf2xml or Fldigi.
In aviation meteorology, a trend type forecast (TTF), also known simply as a trend, is a weather forecast written by a person on location at a major airport or military base. A TTF is a professionally considered forecast for weather over a two-hour period, and is based on an actual weather report, such as a METAR or SPECI and appended to the end of it. A TTF is similar to or sometimes in addition to a TAF, a terminal aerodrome forecast, but during the TTF's validity period is considered superior to a TAF.
SIGMET, or Significant Meteorological Information, is a severe weather advisory that contains meteorological information concerning the safety of all aircraft. Compared to AIRMETs, SIGMETs cover more severe weather. Today, according to the advancement of technology in civil aviation, the SIGMET is sent as IWXXM model.
An AIRMET, or Airmen's Meteorological Information, is a concise description of weather phenomena that are occurring or may occur (forecast) along an air route that may affect aircraft safety. Compared to SIGMETs, AIRMETs cover less severe weather: moderate turbulence and icing, sustained surface winds of 30 knots or more, or widespread restricted visibility. Today, according to the advancement of technology in civil aviation, the AIRMET is sent as IWXXM model.
MAFOR, an abbreviation of MArine FORecast, is a North American code used in the transmission of marine weather forecasts to compress a volume of meteorological and marine information into shorter code for convenience during radio broadcasting. The MAFOR forecast usually supplies the period of validity for the forecast, future wind speed and direction, weather, visibility and 'state of sea.'
China Southern Airlines Flight 3456 (CZ3456/CSN3456) was a scheduled domestic passenger flight from Chongqing Jiangbei International Airport to Shenzhen Huangtian Airport. On 8 May 1997, the Boeing 737 performing this route crashed during the second attempt to land in a thunderstorm. The flight number 3456 is still used by China Southern and for the Chongqing-Shenzhen route but now with the Airbus A320 family or Boeing 737 Next Generation aircraft.
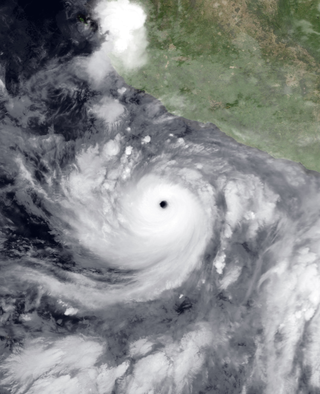
Hurricane Carlotta was the most powerful hurricane of the 2000 Pacific hurricane season. The third tropical cyclone of the season, Carlotta developed from a tropical wave on June 18 about 270 miles (430 km) southeast off the coast of Mexico. With favorable conditions for development, it strengthened steadily at first, followed by a period of rapid deepening to peak winds of 155 mph (249 km/h) on June 22. Cooler waters caused Carlotta to gradually weaken, and on June 25 it degenerated into a remnant area of low pressure while located about 260 miles (420 km) west-southwest of Cabo San Lucas.

TAP Flight 425 was a regular flight from Brussels, Belgium, to Santa Catarina Airport, Portugal, with an intermediate scheduled stop in Lisbon. On 19 November 1977, the Boeing 727 operating the service overran the airport's runway before crashing onto the nearby beach and exploding, killing 131 of the 164 people on board.

Airport weather stations are automated sensor suites which are designed to serve aviation and meteorological operations, weather forecasting and climatology. Automated airport weather stations have become part of the backbone of weather observing in the United States and Canada and are becoming increasingly more prevalent worldwide due to their efficiency and cost-savings.

Surface weather observations are the fundamental data used for safety as well as climatological reasons to forecast weather and issue warnings worldwide. They can be taken manually, by a weather observer, by computer through the use of automated weather stations, or in a hybrid scheme using weather observers to augment the otherwise automated weather station. The ICAO defines the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA), which is the model of the standard variation of pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity with altitude in the Earth's atmosphere, and is used to reduce a station pressure to sea level pressure. Airport observations can be transmitted worldwide through the use of the METAR observing code. Personal weather stations taking automated observations can transmit their data to the United States mesonet through the Citizen Weather Observer Program (CWOP), the UK Met Office through their Weather Observations Website (WOW), or internationally through the Weather Underground Internet site. A thirty-year average of a location's weather observations is traditionally used to determine the station's climate. In the US a network of Cooperative Observers make a daily record of summary weather and sometimes water level information.

Tropical Cyclone Tam was the first named storm of the 2005–06 South Pacific cyclone season. Forming out of a tropical depression on January 6, the storm gradually intensified, becoming a tropical cyclone on January 12 and receiving the name Tam. Although it was traveling at a quick pace, the storm gained organization and reached its peak intensity with winds of 85 km/h (53 mph) the following day. However, the increasing forward motion of the storm, combined with strengthening wind shear, caused Tam to rapidly weaken on January 14. Around that time, it entered the Tropical Cyclone Warning Centre in Wellington, New Zealand's area of responsibility. Shortly thereafter, the storm transitioned into an extratropical cyclone and dissipated early the next day. Cyclone Tam produced heavy rainfall and strong winds over American Samoa upon being named. The precipitation caused several mudslides and flooding, which inflicted $26,000 in damage. The storm also had minor effects on Niue, Tonga, and Futuna.

Aria Air Flight 1525 was a scheduled Iranian domestic flight which crashed on landing at Mashhad International Airport, Mashhad, Iran, on 24 July 2009.

Bangkok Airways Flight 266 was a scheduled domestic passenger flight from Krabi Airport to Samui Airport, Thailand. On 4 August 2009, the aircraft skidded off the runway on landing and crashed into an old and unmanned control tower. One pilot died and 41 other people were injured.

On 26 August 2009, an Antonov An-12 crashed into a cemetery near Brazzaville, Congo.

AeroUnion Flight 302, operated by an Airbus A300B4-203F cargo aircraft, crashed in poor weather on final approach at General Mariano Escobedo International Airport, Monterrey, Mexico around 23:18 CDT on 13 April 2010, after a flight from Mexico City. All five people on board were killed, as well as one on the ground.

Swiss International Air Lines Flight 850 was an international scheduled passenger flight from Basel, Switzerland, to Hamburg, Germany. On 10 July 2002, the flight was unable to land at Fuhlsbüttel Airport due to weather. Attempts were made to divert to other airports at Berlin and Eberswalde before the crew decided to land at Werneuchen. On landing, the aircraft struck an earth bank which ripped off all three undercarriage legs, and came to rest on its belly with an engine on fire. One of the sixteen passengers suffered minor injuries. The aircraft was written off.

On 4 April 2011, Georgian Airways Flight 834, a Bombardier CRJ100 passenger jet of Georgian Airways operating a domestic flight from Kisangani to Kinshasa in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) crashed while attempting to land at Kinshasa Airport. The aircraft, which was chartered by the United Nations, was trying to land during a thunderstorm. Of the 33 people on board, only one person survived. The incident remains as the United Nations' deadliest aviation disaster. It is also the third-deadliest air disaster involving the CRJ100/200, behind Comair Flight 5191 and China Eastern Airlines Flight 5210.

The 2019–20 Australian region cyclone season was a below average tropical cyclone season for the waters surrounding Australia between longitudes 90°E and 160°E. The season officially began on 1 November 2019 and ended on 30 April 2020; however, tropical cyclones can form at any time of year, as evidenced by Tropical Cyclone Mangga during May 2020. As such, any system existing between 1 July 2019 and 30 June 2020 would count towards the season total. The season featured the region's second-latest start on record, with the formation of the first tropical low only occurring on 4 January 2020. A total of eight tropical cyclones formed during the season, which represents the region's least active season since the 2016–17 season. Three systems intensified further into severe tropical cyclones, and three systems made landfall within the region at tropical cyclone intensity. A total of 28 fatalities were caused, either directly or indirectly, as a result of impacts from the season's systems. Cyclone Ferdinand was the strongest of the season reaching Category 4 in late February 2020. However, it was the second-strongest storm, Cyclone Damien, that was the most damaging. Damien was the strongest tropical cyclone to strike Western Australia's Pilbara Region since Cyclone Christine in 2013, making landfall directly over the town of Dampier.











