Related Research Articles

Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea, sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 70,000 species have been identified, grouped into several orders. They are small crustaceans, typically around 1 mm (0.039 in) in size, but varying from 0.2 to 30 mm in the case of Gigantocypris. Their bodies are flattened from side to side and protected by a bivalve-like, chitinous or calcareous valve or "shell". The hinge of the two valves is in the upper (dorsal) region of the body. Ostracods are grouped together based on gross morphology. While early work indicated the group may not be monophyletic; and early molecular phylogeny was ambiguous on this front, recent combined analyses of molecular and morphological data found support for monophyly in analyses with broadest taxon sampling.

Gammaridea is one of the suborders of the order Amphipoda, comprising small, shrimp-like crustaceans. Until recently, in a traditional classification, it encompassed about 7,275 (92%) of the 7,900 species of amphipods described by then, in approximately 1,000 genera, divided among around 125 families. That concept of Gammaridea included almost all freshwater amphipods, while most of the members still were marine.
Traditionally, the Myodocopa and Podocopa have been classified as subclasses within the class Ostracoda, although there is some question about how closely related the two groups actually are. The Myodocopa are defined by possession of a poorly calcified carapace, and 8–9 articles in the exopod of the second antenna. The ventral margin of the carapace is not concave, and the valves do not overlap to a great extent.
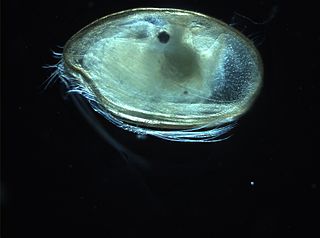
The Myodocopida is one of the two orders within the Myodocopa, in turn a subclass of the Ostracoda. The Myodocopida are distinguished by a worm-like seventh limb, and, usually, a rostrum above an incisure (notch) from which the antennae can protrude. Unlike other ostracods, many species of the Myodocopida have lateral compound eyes Over the last thirty years there has been much research into the morphology, behaviour and distribution of myodocopids. More recently, DNA sequences have been used to investigate the phylogeny of various groups.
Cylindroleberididae is a family of ostracods that shows remarkable morphological diversity. The defining feature is the possession of gills: 7–8 leaf-like pairs at the posterior of the body. Other features common to all species in the family include a "baleen-comb" on both the maxilla and the fifth limb, a sword-shaped coxal endite on the mandible, and the triaenid bristles on the basal endites of the mandible.

The starlet sea anemone is a species of small sea anemone in the family Edwardsiidae native to the east coast of the United States, with introduced populations along the coast of southeast England and the west coast of the United States. Populations have also been located in Nova Scotia, Canada. This sea anemone is found in the shallow brackish water of coastal lagoons and salt marshes where its slender column is usually buried in the mud and its tentacles exposed. Its genome has been sequenced and it is cultivated in the laboratory as a model organism, but the IUCN has listed it as being a "Vulnerable species" in the wild.
The Podocopida are an order of ostracods in the subclass Podocopa. It is divided into five suborders – Bairdiocopina, Cypridocopina, Cytherocopina, Darwinulocopina, and Sigilliocopina. It is the most diverse of the four orders of ostracods, and also has a rich fossil record.
Polycopidae is a family of marine ostracods. Its members are related to animals in the suborder Halocypridina, but are sufficiently distinct to be placed in their own sub-order, Cladocopina. There is speculation that a separate order may be warranted. The genera in the family differ from the other suborder, Halocypridina, in several features: the central adductor muscle scars are in a triangular or half-rosette pattern, they lack sixth and seventh limbs, and the maxilla has both an exopod and endopod.
Spelaeoecia is a genus of crustaceans in the family Thaumatocyprididae. One species, the Bermudan endemic S. bermudensis, is listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List. It contains the following species:

Gigantocypris is a genus of ostracod crustaceans in family Cypridinidae, and among the most well-known members of the class Ostracoda. Its members are extremely large for ostracods, measuring up to 3.2 cm (1.3 in) across, have a globular shape, are typically semi-transparent orange or reddish, and have relatively large mirror-like eyes that are used to locate their small animal prey. They are found worldwide in dark, deep and cold oceans.
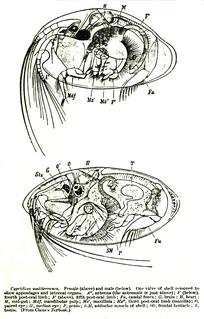
Cypridinidae is a family of ostracods, containing the following genera:
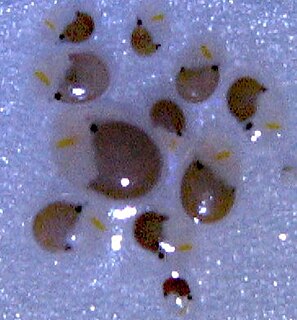
Vargula hilgendorfii, sometimes called the sea-firefly and one of three bioluminescent species known in Japan as umi-hotaru (海蛍), is a species of ostracod crustacean. It is the only member of genus Vargula to inhabit Japanese waters; all other members of its genus inhabit the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and waters off the coast of California. V. hilgendorfii was formerly more common, but its numbers have fallen significantly.

Luidia clathrata is a tropical species of starfish in the family Luidiidae. It is variously known as the slender-armed starfish, the gray sea star, or the lined sea star. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean.
Cypridocopina is a suborder of ostracods in the subclass Podocopa, order Podocopida. It is divided into three superfamilies – Cypridoidea, Macrocypridoidea and Pontocypridoidea.
Cypridoidea is a superfamily of ostracods in the suborder Cypridocopina. It is divided into four families: Candonidae, Cyprididae, Ilyocyprididae, and Notodromadidae.
Azygocypridina lowryi, colloquially known as the baked bean, is a species of ostracod crustacean or "seed shrimp" in the family Cypridinidae. It is found in deep waters off the east coast of Australia.

Kraussillichirus kraussi, commonly named the common sandprawn or pink prawn, is a species of ghost shrimp, an African crustacean in the family Callianassidae.
Paramoera walkeri is an amphipod of the genus Paramoera. It lives around Antarctica.
Thaumatocyprididae is a family of ostracods in the order Halocyprida which contains seven genera and one subfamily. It appeared in the Lopingian Epoch, 259.9 million years ago.
Vargula tsujii is a bioluminescent cypridinid ostracod found in southern California. It feeds on dead and decaying fish and invertebrates. Vargula tsujii is an important prey item of the plainfin midshipman fish, as it is the source of luciferin for the bioluminescence seen in the fish.
References
- ↑ Andrew R. Parker (2009). "Sub-micron structures causing reflection and antireflection in animals". In Stanislav Gorb (ed.). Functional Surfaces in Biology, Functional Surfaces in Biology. Springer. pp. 259–284. ISBN 9781402066979.
- ↑ David Horne (2012). Brandão SN, Angel MV, Karanovic I, Parker A, Perrier V, Sames B, Yasuhara M (eds.). "Azygocypridina Sylvester-Bradley, 1950". World Ostracoda Database. World Register of Marine Species . Retrieved December 6, 2012.
| | This Ostracod-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |