
Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds from the family Spheniscidae of the order Sphenisciformes. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adapted for life in the ocean water, penguins have countershaded dark and white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch with their bills and swallow whole while swimming. A penguin has a spiny tongue and powerful jaws to grip slippery prey.

Krill are small and exclusively marine crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word krill, meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish.

Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea, sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 33,000 species have been identified, grouped into 7 valid orders. They are small crustaceans, typically around 1 mm (0.04 in) in size, but varying from 0.2 to 30 mm in the case of the marine Gigantocypris. The largest known freshwater species is Megalocypris princeps, which reach 8mm in length. In most cases, their bodies are flattened from side to side and protected by a bivalve-like valve or "shell" made of chitin, and often calcium carbonate. The family Entocytheridae and many planktonic forms do not have calcium carbonate. The hinge of the two valves is in the upper (dorsal) region of the body. Ostracods are grouped together based on shell and soft part morphology. While early work indicated the group may not be monophyletic and early molecular phylogeny was ambiguous on this front, recent combined analyses of molecular and morphological data suggested monophyly in analyses with broadest taxon sampling, but this monophyly had no or very little support. They have a wide range of diets, and the class includes carnivores, herbivores, scavengers and filter feeders, but most ostracods are deposit feeders.

The Antarctic petrel is a boldly marked dark brown and white petrel, found in Antarctica, most commonly in the Ross and Weddell Seas. They eat Antarctic krill, fish, and small squid. They feed while swimming but can dive from both the surface and the air.
Traditionally, the Myodocopa and Podocopa have been classified as subclasses within the class Ostracoda, although there is some question about how closely related the two groups actually are. The Myodocopa are defined by possession of a poorly calcified carapace, and 8–9 articles in the exopod of the second antenna. The ventral margin of the carapace is not concave, and the valves do not overlap to a great extent.

Cylindroleberididae is a family of ostracods that shows remarkable morphological diversity. The defining feature is the possession of gills: 7–8 leaf-like pairs at the posterior of the body. Other features common to all species in the family include a "baleen-comb" on both the maxilla and the fifth limb, a sword-shaped coxal endite on the mandible, and the triaenid bristles on the basal endites of the mandible.

The Podocopida are an order of ostracods in the subclass Podocopa. It is the most diverse of the five orders of ostracods, and the only one with freshwater species. The group also has a rich fossil record.
Polycopidae is a family of marine ostracods. Its members are related to animals in the suborder Halocypridina, but are sufficiently distinct to be placed in the sub-order Cladocopina. There is even some speculation that a separate order may be warranted. The genera in the family differ from the other suborder, Halocypridina, in several features: the central adductor muscle scars are in a triangular or half-rosette pattern, they lack sixth and seventh limbs, and the maxilla has both an exopod and endopod.
Spelaeoecia is a genus of crustaceans in the family Thaumatocyprididae. One species, the Bermudan endemic S. bermudensis, is listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List. It contains the following species:

Gigantocypris, sometimes known as giant ostracod or giant seed shrimp, is a genus of ostracod crustaceans in family Cypridinidae, and among the most well-known members of the class Ostracoda. Its members are extremely large for ostracods, measuring up to 3.2 cm (1.3 in) across, have a globular shape, are typically semi-transparent orange or reddish, and have a large pair of mirror-like eyes that are used to locate their small animal prey. They are found worldwide in dark, deep and cold oceans.

Cypridinidae is a family of ostracods. About half of all known species are bioluminescent. Some use the light only for defence, others also for courtship displays. The lineages with sexually dimorphic bioluminescent displays have more species other lineages, which indicates that bioluminescent courtship could increase the diversification rates.

Mount Southwick is a mountain in Owen Ridge near the south end of the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica, located 9 nautical miles (17 km) south-southeast of Mount Craddock. The peak surmounts Bolgrad Glacier to the northwest, Kornicker Glacier to the east and Sirma Glacier to the southwest.

Thomas Glacier is a roughly Z-shaped glacier which drains the southeast slopes of Vinson Massif and flows for 17 nautical miles (31 km) through the south part of the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains, leaving the range between Doyran and Petvar Heights south of Johnson Spur.

Kornicker Glacier is a glacier draining northeastwards from the cirque bounded by Mount Liptak, Mount Southwick, Mount Milton and Mount Mullen in the southern Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The glacier flows along the northwestern side of Petvar Heights and merges with the terminus of the southeast-flowing Thomas Glacier as both glaciers emerge from the range.

Petvar Heights are the heights rising to 2492 m at Mount Mullen in southeast Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The heights occupy an oval shaped area with a diameter of 21 km, separated from the rest of Sentinel Range by Wessbecher Glacier to the southwest, Kasilag Pass to the west, and Kornicker Glacier to the northwest and north. Their interior is drained by Hudman, Carey, Razboyna, Gabare and Divdyadovo Glaciers.
Azygocypridina lowryi, colloquially known as the baked bean, is a species of ostracod crustacean or "seed shrimp" in the family Cypridinidae. It is found in deep waters off the east coast of Australia.
Azygocypridina is a genus of ostracods in the family Cypridinidae, which appears to be "the least derived living ostracod", having remained largely unchanged for 350 million years. It contains the following species:

Razboyna Glacier is the 3 nautical miles long and 1 nautical mile wide glacier in Petvar Heights on the southeast side of Sentinel Range in Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica situated north of Drama Glacier, east of Kornicker Glacier, and south of the lower course of Thomas Glacier. It is draining the north slopes of Bagra Peak, and flowing northeastwards to leave the range north of Long Peak.
Paul Tasch was an American paleontologist.
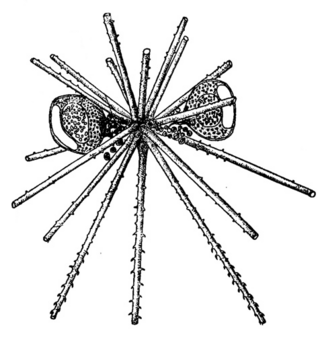
Astracantha is a genus of planktonic phaeodaria and the only member of the family Astracanthidae. They are an unusual family of marine protists, but can be found across all oceans, from tropical to Arctic and Antarctic waters.









