
The Westland Limousine was a 1920s British single-engined four-seat light transport aircraft built by Westland Aircraft.

The BAT F.K.23 Bantam was a British single-seat fighter biplane produced by British Aerial Transport Company Limited of London during World War I.

The BAT F.K.24 Baboon was a British two-seat training biplane produced by British Aerial Transport Company Limited of London during World War I.

The de Havilland DH.18 was a single-engined British biplane transport aircraft of the 1920s built by de Havilland.

The de Havilland DH.34 was a single engined British biplane airliner built by the de Havilland Aircraft Company in the 1920s. 12 were built, with the DH.34 serving with Imperial Airways and its predecessors for several years.

The Bristol Ten-seater and Bristol Brandon were British single-engine biplane transport aircraft built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company in the early 1920s. Only three were built, two of which were used as civil transports and one of which served with the Royal Air Force.

The Dorand AR.1 was a World War I French two-seat observation biplane aircraft used by the French Air Force, the American Expeditionary Force and, in small numbers, by Serbian Aviation.
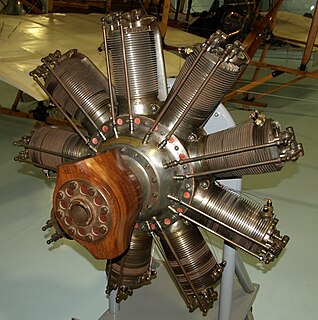
The Clerget 9B was a nine-cylinder rotary aircraft engine of the World War I era designed by Pierre Clerget. Manufactured in both France and Great Britain, it was used on such aircraft as the Sopwith Camel. The Clerget 9Bf was an increased stroke version.

The Kennedy Giant was a British biplane heavy bomber designed by Kennedy Aeroplanes Ltd. during the First World War. The design was an imitation of works by Igor Sikorsky, with whom the owner of Kennedy Aeroplanes Ltd., C. J. H. Mackenzie-Kennedy, had ostensibly worked prior to setting up the company. The aeroplane was a notorious failure; its size meant that construction had to take place in an open field as none of the hangars near Hayes, Middlesex, where the prototype was assembled, were large enough to house it. For its weight, the aircraft's four engines were inadequate, and the resulting under-powered aircraft could only fly in a straight line once airborne.

The Fiat R.2 was a reconnaissance aircraft produced in Italy shortly after World War I, and the first aircraft to be marketed under the Fiat brand,. It was a conventional two-bay biplane with equal-span, unstaggered wings and fixed tailskid undercarriage. The pilot and observer sat in tandem open cockpits. The design was a derivative of the SIA 7 and SIA 9 flown during the war, but was considerably revised by Rosatelli to correct ongoing problems with those types. A total of 129 were produced for the Air Corps of the Regio Esercito.

The Avro 533 Manchester was a First World War-era twin-engine biplane photo-reconnaissance and bomber aircraft designed and manufactured by Avro.
The Beardmore W.B.II was a British biplane fighter prototype of the 1910s.
The Westland Wagtail was a prototype British fighter aircraft of the First World War. A single-engined tractor biplane, the Wagtail was a failure owing to the unreliability of its engine, only five being built.

The BAT F.K.25 Basilisk was a prototype British fighter aircraft of the First World War. A single engined biplane intended to meet a requirement to replace the Sopwith Snipe, the Basilisk was unsuccessful, only three being built.

The Macchi M.15 was an Italian reconnaissance aircraft, bomber and trainer, designed by Alessandro Tonini and Piero Bergonzi and built by Macchi.
The Grahame-White G.W.E.7 was a British twin-engined transport biplane, designed by M Boudot and built by Grahame-White Aviation Company at Hendon.
The Clerget 11Eb was an 11-cylinder rotary aircraft engine of the World War I era designed by Pierre Clerget. Powering Sopwith types it was nominally rated at 200 horsepower (150 kW).

The Clerget 7Z was a seven-cylinder rotary aircraft engine of the World War I era designed by Pierre Clerget. First appearing in 1911 it was nominally rated at 80 horsepower (60 kW). 347 examples were jointly built in Britain by Gordon Watney & Co Ltd of Weybridge and Gwynnes Limited of Hammersmith.

The Paalson Type 1, (Pålson), was a Swedish single-seat sport aircraft built around 1920. It was of conventional single-seat biplane layout but had some unusual features such as girder type interplane struts, a novel main undercarriage axle mounting and a mechanism allowing adjustment of the angle of incidence of the upper wing.

The BAT F.K.27 was a two-seater sporting biplane designed by Frederick Koolhoven and built by the British Aerial Transport Company Limited (BAT) in 1918.
















