
Stahleck Castle is a 12th-century fortified castle in the Upper Middle Rhine Valley at Bacharach in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It stands on a crag approximately 160 metres (520 ft) above sea level on the left bank of the river at the mouth of the Steeg valley, approximately 50 kilometres (31 mi) south of Koblenz, and offers a commanding view of the Lorelei valley. Its name means "impregnable castle on a crag", from the Middle High German words stahel (steel) and ecke. It has a water-filled partial moat, a rarity in Germany. Built on the orders of the Archbishop of Cologne, it was destroyed in the late 17th century but rebuilt in the 20th and is now a hostel.

The Rhine Gorge is a popular name for the Upper Middle Rhine Valley, a 65 km section of the Rhine between Koblenz and Rüdesheim in the states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse in Germany. It was added to the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites in June 2002 because of its beauty as a cultural landscape, its importance as a route of transport across Europe, and the unique adaptations of the buildings and terraces to the steep slopes of the gorge.

Sankt Goar is a town on the west bank of the Middle Rhine in the Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis (district) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Hunsrück-Mittelrhein, whose seat is in Emmelshausen.

Rüdesheim am Rhein is a German winemaking town in the Rhine Gorge, and part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site in this region. It lies in the Rheingau-Taunus-Kreis district in the Regierungsbezirk of Darmstadt, Hessen. Known as Rüdesheim, it is officially Rüdesheim am Rhein, to distinguish it from Rüdesheim an der Nahe. It is a major tourist attraction, especially for foreign visitors.

Boppard, formerly also spelled Boppart, is a town and municipality in the Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis (district) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, lying in the Rhine Gorge, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The town is also a state-recognized tourism resort (Fremdenverkehrsort) and is a winegrowing centre.

Middle Rhine is the section of the Rhine between Bingen and Bonn in Germany. It flows through the Rhine Gorge, a formation created by erosion, which happened at about the same rate as an uplift in the region, leaving the river at about its original level, and the surrounding lands raised. This gorge is quite deep, about 130 metres (430 ft) from the top of the rocks down to the average water-line.

Kaub is a town in Germany, state Rhineland-Palatinate, district Rhein-Lahn-Kreis. It is part of the municipality (Verbandsgemeinde) Loreley. It is located on the right bank of the Rhine, approx. 50 km west from Wiesbaden. It is connected to Wiesbaden and Koblenz by railway. It has a Roman Catholic and an Evangelical church, and a statue of General Blücher. Historically, trade mainly consisted of the wines of the district.

Rheinböllen is a town in the Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis (district) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Simmern-Rheinböllen, whose seat is in Simmern. It was the seat of the former Verbandsgemeinde Rheinböllen.

Oberwesel is a town on the Middle Rhine in the Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis (district) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Hunsrück-Mittelrhein, whose seat is in Emmelshausen.

Pfalzgrafenstein Castle is a toll castle located on Falkenau island in the Rhine River, near the bank close to Kaub, Germany. Also known as "the Pfalz", Pfalzgrafenstein Castle has never been destroyed since being established in 1326/27.
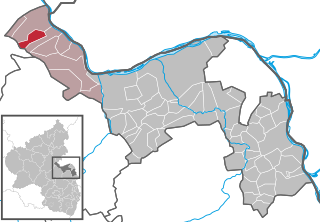
Manubach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Mainz-Bingen district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.

Oberdiebach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Mainz-Bingen district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.

Trechtingshausen is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Mainz-Bingen district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.

Schnorbach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis (district) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Simmern-Rheinböllen, whose seat is in Simmern.

Rhine Castle trail - Rheinburgenweg, follows the left side of the Rhine from Bingen to Remagen-Rolandseck and the right side takes the route of the Rheinsteig from Rüdesheim am Rhein to Koblenz.

Werner of Oberwesel was a 16-year-old boy whose unexplained death was blamed on Jews, leading to revenge killings of Jews across Europe. He was venerated as a Christian saint, and his memorial day was 19 April.

Klopp Castle is a castle in the town of Bingen am Rhein in the Upper Middle Rhine Valley in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. In the nineteenth century, the bergfried from the original medieval fortified castle was restored and a new building added which houses the town's administration.

The Rhine romanticism was the interpretation of the landscape conditions and history of the Rhine Valley in the cultural-historical period of the romanticism, by the end of the 18th century until the late 19th century and was continued in all forms of art expression.

A toll castle is a castle that, in the Middle Ages and the Early Modern Era, guarded a customs post and was intended to control it. They were typically found in the Holy Roman Empire. Toll castles always stood in the vicinity of an important long-distance trade route over, for example, the Alpine passes or the Middle Rhine. Such castles were usually placed at strategic locations, such as border crossings, river crossings or mountain passes, and were manned by armed guards. The actual toll-collecting point lay below at the road or river and was often linked by walls to the castle itself.

















































