
Bacillus is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum Bacillota, with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural Bacilli is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. Bacillus species can be either obligate aerobes which are dependent on oxygen, or facultative anaerobes which can survive in the absence of oxygen. Cultured Bacillus species test positive for the enzyme catalase if oxygen has been used or is present.

Bacillus subtilis, known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus Bacillus, B. subtilis is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. B. subtilis has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. B. subtilis is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies.

Subtilisin is a protease initially obtained from Bacillus subtilis.

Bacillus virus Φ29 is a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) bacteriophage with a prolate icosahedral head and a short tail that belongs to the genus Salasvirus, order Caudovirales, and family Salasmaviridae. They are in the same order as phages PZA, Φ15, BS32, B103, M2Y (M2), Nf, and GA-1. First discovered in 1965, the Φ29 phage is the smallest Bacillus phage isolated to date and is among the smallest known dsDNA phages.
An origin of transfer (oriT) is a short sequence ranging from 40-500 base pairs in length that is necessary for the transfer of DNA from a gram-negative bacterial donor to recipient during bacterial conjugation. The transfer of DNA is a critical component for antimicrobial resistance within bacterial cells and the oriT structure and mechanism within plasmid DNA is complementary to its function in bacterial conjugation. The first oriT to be identified and cloned was on the RK2 (IncP) conjugative plasmid, which was done by Guiney and Helinski in 1979.
Spore photoproduct lyase is a radical SAM enzyme that repairs DNA cross linking of thymine bases caused by UV-radiation. There are several types of thymine cross linking, but SPL specifically targets 5-thyminyl-5,6-dihydrothymine, which is also called spore photoproduct (SP). Spore photoproduct is the predominant type of thymine crosslinking in germinating endospores, which is why SPL is unique to organisms that produce endospores, such as Bacillus subtilis. Other types of thymine crosslinking, such as cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD) and pyrimidine (6-4) pyrimidone photoproducts (6-4PPs), are less commonly formed in endospores. These differences in DNA crosslinking are a function of differing DNA structure. Spore genomic DNA features many DNA binding proteins called small acid soluble proteins, which changes the DNA from the traditional B-form conformation to an A-from conformation. This difference in conformation is believed to be the reason why dormant spores predominantly accumulate SP in response to UV-radiation, rather than other forms of cross linking. Spores cannot repair cross-linking while dormant, instead the SPs are repaired during germination to allow the vegetative cell to function normally. When not repaired, spore photoproduct and other types of crosslinking can cause mutations by blocking transcription and replication past the point of the crosslinking. The repair mechanism utilizing spore photoproduct lyase is one of the reasons for the resilience of certain bacterial spores.

L-form bacteria, also known as L-phase bacteria, L-phase variants or cell wall-deficient (CWD) bacteria, are growth forms derived from different bacteria. They lack cell walls. Peptidoglycan (murein) is absent. Two types of L-forms are distinguished: unstable L-forms, spheroplasts that are capable of dividing, but can revert to the original morphology, and stable L-forms, L-forms that are unable to revert to the original bacteria.
Roberto Kolter is Professor of Microbiology, Emeritus at Harvard Medical School, an author, and past president of the American Society for Microbiology. Kolter has been a professor at Harvard Medical School since 1983 and was Co-director of Harvard's Microbial Sciences Initiative from 2003-2018. During the 35-year term of the Kolter laboratory from 1983 to 2018, more than 130 graduate student and postdoctoral trainees explored an eclectic mix of topics gravitating around the study of microbes. Kolter is a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and of the American Academy of Microbiology.
Bacillus atrophaeus is a species of black-pigmented bacteria. Its type strain is NRRL NRS-213. B. atrophaeus strains have been used extensively in biomedicine as indicator strains for heat- and chemical-based decontamination regimens. Most of the strains in use are derivatives of a lineage of B. atrophaeus that originated at Camp Detrick in the 1950s, where many modern biocontainment procedures were developed. B. atrophaeus has historically been known by several other names, including B. globigii and B. subtilis var. niger. Modern phylogenetic analyses using multiple genetic methods have placed B. atrophaeus close to B. subtilis. Its original and still most prominent use is as a surrogate organism for pathogenic B. anthracis, beginning in the U.S. bio-weapons program, as its pigmentation readily facilitated discrimination from non-pigmented background organisms in environmental samples. Subsequent genomic and phenotypic analysis of strains derived from the Camp Detrick isolates revealed that they had been deliberately selected for strains that exhibited elevated rates of sporulation.
Bacillolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Bacillus vallismortis is a species of bacteria, with type strain DV1-F-3.
DnaD is a 232 amino acid long protein that is part of the primosome involved in prokaryotic DNA replication. In Bacillus subtilis, genetic analysis has revealed three primosomal proteins, DnaB, DnaD, and DnaI, that have no obvious homologues in E. coli. They are involved in primosome function both at arrested replication forks and at the chromosomal origin.
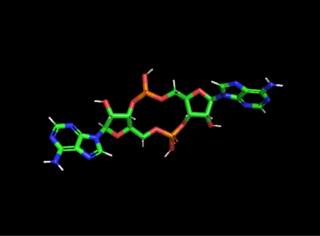
Cyclic di-AMP is a second messenger used in signal transduction in bacteria and archaea. It is present in many Gram-positive bacteria, some Gram-negative species, and archaea of the phylum euryarchaeota.
The Citrate-Mg2+:H+ (CitM) / Citrate-Ca2+:H+ (CitH) Symporter (CitMHS) Family (TC# 2.A.11) is a family of transport proteins belonging to the Ion transporter superfamily. Members of this family are found in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, archaea and possibly eukaryotes. These proteins all probably arose by an internal gene duplication event. Lensbouer & Doyle (2010) have reviewed these systems, classifying the porters with three superfamilies, according to ion-preference:
The NhaC family belongs to the Ion Transporter (IT) Superfamily. A representative list of proteins belonging to the NhaC family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
In bacteriology, minicells are bacterial cells that are smaller than usual. The first minicells reported were from a strain of Escherichia coli that had a mutation in the Min System that lead to mis-localization of the septum during cell division and the production of cells of random sizes.
John Howard Mueller was an American biochemist, pathologist, and bacteriologist. He is known as the discoverer of the amino acid methionine in 1921, and as the co-developer, with Jane Hinton, of the eponymous Mueller–Hinton agar.
Niallia is a genus of Gram-Positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae from the order Bacillales. The type species of this genus is Niallia circulans.
Sutcliffiella is a genus of Gram-Positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae from the order Bacillales. The type species of this genus is Sutcliffiella cohnii.
Alkalicoccus is a genus of Gram-Positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae from the order Bacillales. The type species of this genus is Alkalicoccus saliphilus.





