
Bacillus is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum Bacillota, with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural Bacilli is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. Bacillus species can be either obligate aerobes which are dependent on oxygen, or facultative anaerobes which can survive in the absence of oxygen. Cultured Bacillus species test positive for the enzyme catalase if oxygen has been used or is present.

Bacillus subtilis, known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus Bacillus, B. subtilis is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. B. subtilis has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. B. subtilis is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies.

Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is a species of bacterium in the genus Bacillus that is the source of the BamHI restriction enzyme. It also synthesizes a natural antibiotic protein barnase, a widely studied ribonuclease that forms a famously tight complex with its intracellular inhibitor barstar, and plantazolicin, an antibiotic with selective activity against Bacillus anthracis.
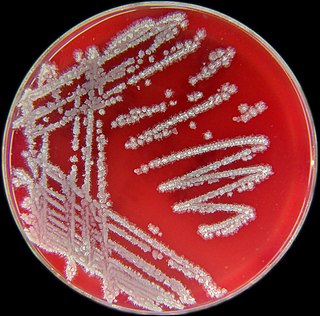
Bacillus licheniformis is a bacterium commonly found in the soil. It is found on bird feathers, especially chest and back plumage, and most often in ground-dwelling birds and aquatic species.

Bacillus megaterium is a rod-like, Gram-positive, mainly aerobic, spore forming bacterium found in widely diverse habitats. It has a cell length up to 4 µm and a diameter of 1.5 µm, which is quite large for bacteria. The cells often occur in pairs and chains, where the cells are joined together by polysaccharides on the cell walls.

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.

Nattokinase is an enzyme extracted and purified from a Japanese food called nattō. Nattō is produced by fermentation by adding the bacterium Bacillus natto, which also produces the enzyme, to boiled soybeans. While other soy foods contain enzymes, it is only the nattō preparation that contains the specific nattokinase enzyme.
Bacillus atrophaeus is a species of black-pigmented bacteria. Its type strain is NRRL NRS-213. B. atrophaeus strains have been used extensively in biomedicine as indicator strains for heat- and chemical-based decontamination regimens. Most of the strains in use are derivatives of a lineage of B. atrophaeus that originated at Camp Detrick in the 1950s, where many modern biocontainment procedures were developed. B. atrophaeus has historically been known by several other names, including B. globigii and B. subtilis var. niger. Modern phylogenetic analyses using multiple genetic methods have placed B. atrophaeus close to B. subtilis. Its original and still most prominent use is as a surrogate organism for pathogenic B. anthracis, beginning in the U.S. bio-weapons program, as its pigmentation readily facilitated discrimination from non-pigmented background organisms in environmental samples. Subsequent genomic and phenotypic analysis of strains derived from the Camp Detrick isolates revealed that they had been deliberately selected for strains that exhibited elevated rates of sporulation.
Unsaturated rhamnogalacturonyl hydrolase (EC 3.2.1.172, YteR, YesR) is an enzyme with systematic name 2-O-(4-deoxy-beta-L-threo-hex-4-enopyranuronosyl)-alpha-L-rhamnopyranose hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Bacillus mojavensis is a bacterium. Bacillus axarquiensis and Bacillus malacitensis are considered later heterotypic synonyms of B. mojavensis. It is named after the Mojave Desert.
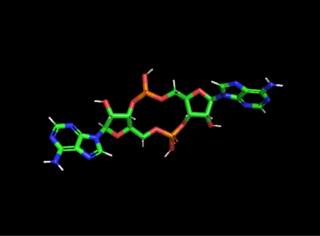
Cyclic di-AMP is a second messenger used in signal transduction in bacteria and archaea. It is present in many Gram-positive bacteria, some Gram-negative species, and archaea of the phylum euryarchaeota.

Protein Arginine Phosphatase (PAPs), also known as Phosphoarginine Phosphatase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the dephosphorylation of phosphoarginine residues in proteins. Protein phosphatases (PPs) are "obligatory heteromers" made up of two maximum catalytic subunits attached to a non-catalytic subunit. Arginine modification is a post-translational protein modification in gram-positive bacteria. McsB and YwIE were recently identified as phosphorylating enzymes in Bacillus Subtilis (B.Subtilis). YwIE was thought to be a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase, and McsB a tyrosine-kinase, however in 2012 Elsholz et al. showed that McsB is a protein-arginine-kinase (PAK) and YwlE is a phosphatase-arginine-phosphatase (PAP).
Alkalihalobacillus is a genus of gram-positive or gram-variable rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae from the order Bacillales. The type species of this genus is Alkalihalobacillus alcalophilus.
Metabacillus is a genus of rod-shaped bacteria exhibiting Gram-positive or Gram-variable staining in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Metabacillus fastidiosus.
Neobacillus is a genus of rod-shaped bacteria that show Gram-positive or Gram-variable staining. This genus belongs under the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species of Neobacillus is Neobacillus niacini.
Cytobacillus is a genus of rod-shaped bacteria that stain either Gram-positive or Gram-variable in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Cytobacillus firmus.
Heyndrickxia is a genus of gram-positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Heyndrickxia oleronia.

Lederbergia is a genus of gram-positive or Gram-variable, rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Lederbergia galactosidilyticus.
Litchfieldia is a genus of Gram-positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Bacillaceae within the order Bacillales. The type species for this genus is Litchfieldia alkalitelluris.

Petrobactin is a bis-catechol siderophore produced by M. hydrocarbonoclasticus, A. macleodii, and the anthrax-producing B. anthracis. Like other siderophores petrobactin is a highly specific iron(III) transport ligand, contributing to the marine microbial uptake of environmental iron.











