
Cynthia Ann Parker, Naduah, Narua, or Preloch, was a woman who was captured, aged around nine, by a Comanche band during the Fort Parker massacre in 1836, where several of her relatives were killed. She was taken with several of her family members, including her younger brother John Richard Parker. Parker was later adopted into the tribe and had three children with a chief. Twenty-four years later she was relocated and taken captive by Texas Rangers, aged approximately 33, and unwillingly forced to separate from her sons and conform to European-American society. Her Comanche name means "was found" or "someone found."
The Killough massacre is believed to have been both the largest and last Native American attack on white settlers in East Texas. The massacre took place on October 5, 1838, near Larissa, Texas, in the northwestern part of Cherokee County. There were eighteen victims, including Isaac Killough, Sr., and his extended family. They had immigrated to the Republic of Texas from Talladega County, Alabama, in 1837.

The Comanche Wars were a series of armed conflicts fought between Comanche peoples and Spanish, Mexican, and American militaries and civilians in the United States and Mexico from as early as 1706 until at least the mid-1870s. The Comanche were the Native American inhabitants of a large area known as Comancheria, which stretched across much of the southern Great Plains from Colorado and Kansas in the north through Oklahoma, Texas, and eastern New Mexico and into the Mexican state of Chihuahua in the south. For more than 150 years, the Comanche were the dominant native tribe in the region, known as “the Lords of the Southern Plains”, though they also shared parts of Comancheria with the Wichita, Kiowa, and Kiowa Apache and, after 1840, the southern Cheyenne and Arapaho.

The First Battle of Adobe Walls took place between the United States Army and Native Americans. The Kiowa, Comanche and Plains Apache tribes drove from the battlefield a United States column that was responding to attacks on white settlers moving into the Southwest. The battle on November 25, 1864, resulted in light casualties on both sides.

The Kichai tribe was a Native American Southern Plains tribe that lived in Texas, Louisiana, and Oklahoma. Their name for themselves was K'itaish.
Bird's Fort was a community north of present-day Arlington, Texas (USA). In 1841, when John Neely Bryan established Dallas, he invited the settlers at Bird's Fort to come live in his proposed city.

The Dawson massacre, also called the Dawson expedition, was an incident in which 36 Texian militiamen were killed by Mexican soldiers on September 17, 1842 near San Antonio de Bexar. The event occurred during the Battle of Salado Creek, which ended with a Texian victory. This was among numerous armed conflicts over the area between the Rio Grande and Nueces rivers, which the Republic of Texas tried to control after achieving independence in 1836.
The Texas–Indian wars were a series of conflicts between settlers in Texas and the Southern Plains Indians during the 19th-century. Conflict between the Plains Indians and the Spanish began before other European and Anglo-American settlers were encouraged—first by Spain and then by the newly Independent Mexican government—to colonize Texas in order to provide a protective-settlement buffer in Texas between the Plains Indians and the rest of Mexico. As a consequence, conflict between Anglo-American settlers and Plains Indians occurred during the Texas colonial period as part of Mexico. The conflicts continued after Texas secured its independence from Mexico in 1836 and did not end until 30 years after Texas became a state of the United States, when in 1875 the last free band of Plains Indians, the Comanches led by Quahadi warrior Quanah Parker, surrendered and moved to the Fort Sill reservation in Oklahoma.
The Battle of the Neches, the main engagement of the Cherokee War of 1838–1839, took place on 15–16 July in 1839 in what is now the Redland community. It resulted from the Córdova Rebellion and Texas President Mirabeau Bonaparte Lamar's determination to remove the Cherokee people from Texas. Many Cherokee had migrated there from the American Southeast to avoid being forced to Indian Territory.
The Yowani were a historical group of Choctaw people who lived in Texas. Yowani was also the name of a preremoval Choctaw village.
The Bowl ; John Watts Bowles was one of the leaders of the Chickamauga Cherokee during the Cherokee–American wars, served as a Principal Chief of the Cherokee Nation–West, and was a leader of the Texas Cherokees.
Preston, also known as Preston Bend, is an unincorporated community and census-designated place located on the Red River in Grayson County, Texas, United States. It grew in the 19th century at the intersection of several military and trade roads and was an important crossing on the Shawnee cattle trail. Preston lost prominence after the MK&T railroad bypassed the town to the east, leading to a decline in traveler and cattle drive traffic. Much of its former town site is submerged beneath the waters of Lake Texoma. Its population was 2,096 as of the 2010 census.
The Battle of the San Gabriels was an 1839 skirmish in the Texas–Indian wars.
The Córdova Rebellion, in 1838, was an uprising instigated in and around Nacogdoches, Texas. Alcalde Vicente Córdova and other leaders supported the Texas Revolution as long as it espoused a return to the Constitution of 1824.
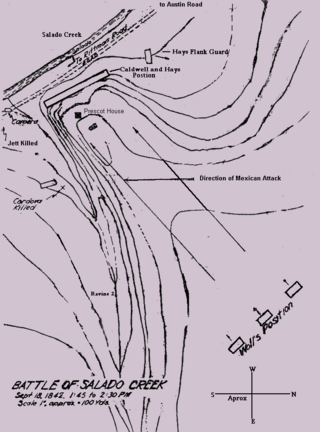
The Battle of the Salado was a decisive engagement in 1842 which repulsed the final Mexican invasion of the Republic of Texas. Colonel Mathew Caldwell of the Texas Rangers led just over 200 militia against an army of 1,600 Mexican Army soldiers and Cherokee warriors, and defeated them outside of San Antonio de Bexar along Salado Creek. As a result of this action, French-Mexican commander General Adrián Woll retreated south and back into Mexico.
The Battle of Echoee, or Etchoe Pass, was a battle on June 27, 1760 during the French and Indian War, between the British and colonial force under Archibald Montgomerie and a force of Cherokee warriors under Seroweh. It took place near the present-day municipality of Otto, in Macon County, North Carolina.
The Battle of Village Creek, also known as the Village Creek Massacre, occurred on May 24, 1841, on the embankments of Village Creek in what was then the Republic of Texas. The site of the massacre is now located in Tarrant County, Texas, named for Edward H. Tarrant, who commanded the Texan forces in the massacre. Tarrant rallied a volunteer militia of 69 men, including Captain John B. Denton, who would be the Texans’ only fatality and who would also go on to have a North Texas county bear his name. The Texans used information from a Native American man they had captured to locate the villages, after which they launched a surprise attack which evolved into a running gunfight between the Republic of Texas militia and the Cherokee, Muscogee/Creek, Seminole, Waco, Caddo, Kickapoo, Tonkawa, Wichita, Shawnee, and Anadarko villagers who inhabited Village Creek. Texans used the occurrence of increased Native American raids on Anglo settlements in the Red River counties as justification for the massacre, which was a part of the larger pattern in the Republic of Texas, under the leadership of President Mirabeau B. Lamar, to wage an “exterminating war” on Native peoples, calling for “their total extinction or total expulsion.”
Larissa is an unincorporated community in Cherokee County, Texas, United States. Larissa lies west of U.S. Highway 69, off Farm to Market Road 855 and approximately halfway between Jacksonville and Bullard. Larissa is about 20 miles (32 km) northwest of the county seat of Rusk.

Edward H. Tarrant was an American politician and general. He served in the Texas House of Representatives during both periods. Tarrant County, whose county seat is Fort Worth, was named after him.

Sam Houston had a diverse relationship with Native Americans, particularly the Cherokee from Tennessee. He was an adopted son, and he was a negotiator, strategist, and creator of fair public policy for Native Americans as a legislator, governor and president of the Republic of Texas. He left his widowed mother's home around 1808 and was taken in by John Jolly, a leader of the Cherokee. Houston lived in Jolly's village for three years. He adopted Cherokee customs and traditions, which stressed the importance of being honest and fair, and he learned to speak the Cherokee language. He felt that Cherokees and other indigenous people had been short-changed during negotiation of treaties with United States government, the realization influenced his decisions as a military officer, treaty negotiator, and in his roles as governor of the states of Tennessee and Texas, and president of the Republic of Texas.









