
Begonia is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Begoniaceae. The genus contains more than 2,000 different plant species. The Begonias are native to moist subtropical and tropical climates. Some species are commonly grown indoors as ornamental houseplants in cooler climates. In cooler climates some species are cultivated outside in summertime for their bright colorful flowers, which have sepals but no petals.

Bouteloua curtipendula, commonly known as sideoats grama, is a perennial, short prairie grass that is native throughout the temperate and tropical Western Hemisphere, from Canada south to Argentina.

Begoniaceae is a family of flowering plants with two genera and about 2040 species occurring in the subtropics and tropics of both the New World and Old World. All but one of the species are in the genus Begonia. There have been many recent discoveries of species in the genus Begonia, such as Begonia truncatifolia which is endemic to San Vincente, Palawan. B. truncatifolia is smaller than other species of the genus Begonia and this new species is proposed Critically Endangered by standards set by the IUCN. The only other genus in the family, Hillebrandia, is endemic to the Hawaiian Islands and has a single species. Phylogenetic work supports Hillebrandia as the sister taxon to the rest of the family. The genus Symbegonia was reduced to a section of Begonia in 2003, as molecular phylogenies had shown it to be derived from within that genus. Members of the genus Begonia are well-known and popular houseplants.

Rapana venosa, common name the veined rapa whelk or Asian rapa whelk, is a species of large predatory sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc or whelk, in the family Muricidae, the rock shells.

Viola purpurea is a species of violet with yellow flowers and the common name goosefoot violet.

Begonia sutherlandii, known as the Sutherland begonia and as iwozya in Kimalila, Tanzania, is a tuberous flowering perennial plant in the family Begoniaceae, growing to 0.5 metres (20 in) with fleshy pink stems from 10 to 80 centimetres long. Leaves are commonly dark green and veined with red and covered with short hairs on the underside. They are asymmetrical in shape and the margin is toothed. Flowers, produced in pendent panicles throughout summer, are 20–26 millimetres (0.8–1.0 in) in diameter, and are usually orange or orange–red with yellow anthers.

Notelaea venosa is a very common shrub or small tree in eastern Australia. Occurring in or adjacent to rainforest from Lakes Entrance, Victoria to Cunninghams Gap in south eastern Queensland. Common names include veined mock-olive, smooth mock-olive, large-leaved mock-olive and large mock-olive. Often seen in the bushland areas in Sydney.
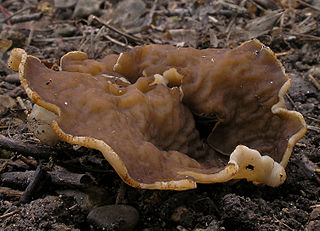
Disciotis venosa, commonly known as the bleach cup, veiny cup fungus, or the cup morel is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae. Fruiting from April, they are often difficult to locate because of their nondescript brown color.

Monardella douglasii is a species of flowering plant in the mint family known by the common name Douglas' monardella.

Abantis venosa, the veined skipper or veined paradise skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Zululand, Eswatini, Transvaal, Zimbabwe, Kenya and Uganda.
Lysimachia venosa is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Primulaceae known by the common name veined yellow loosestrife. It is endemic to Hawaii, where it is known only from the island of Kauai. The plant was only collected twice, last in 1911, but in 1991, a branch was discovered that had broken off the steep cliffs above the headwaters of the Wailua River. The branch was from a plant of this species and may have fallen from the summit of Mount Waialeale. No more specimens have been found since and the plant may be extinct, but some experts believe it may still exist in unsurveyed parts of the habitat. It was federally listed as an endangered species of the United States in 2010.

Haworthiopsis venosa, formerly Haworthia venosa, known in Afrikaans as venstertjie, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Haworthiopsis belonging to the family Asphodelaceae, native to Namibia and South Africa.

Thelymitra cyanea, commonly known as the veined sun orchid in Australia and as the swamp sun orchid or striped sun orchid in New Zealand, is a species of orchid which is native to New Zealand and south-eastern Australia. It has a single erect, fleshy, channelled leaf and up to five bright blue flowers with darker blue veins. It is usually found growing in swamps, sphagnum bogs, and subalpine herbfields, often in clonal colonies.

Ctenucha venosa, the veined ctenucha moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in the US from southern Nevada and Arizona to Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma and Texas, as well as in Mexico, Guatemala, Panama and Venezuela.

Onobrychis venosa, veined sainfoin is a perennial, spreading or suberect herb 10–25 cm high, with a short stem. Leaves alternate, compound, imparipinnate, leaflets ovoid to suborbicular 10-40 x 5–30 mm with characteristic bronze venation, hairy only along margins. Zygomorphic flowers with yellow petals with conspicuous dark-red nerves in axillary racemes. Flowers from February to May. The fruit is a circular flattened hairy pod.
Diospyros venosa is a tree in the family Ebenaceae. It is native to Southeast Asia, from the Maluku Islands to Myanmar. It provides raw material for handicrafts, traditional medicine and fuel.
Venosa is a town and comune in Italy.

Diuris venosa, commonly known as the veined doubletail is a species of orchid which is endemic to New South Wales. It has a few thin, erect leaves and up to four white to lilac-coloured flowers with deep red to purple blotches and lines.

Thelymitra venosa, commonly known as the large veined sun orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to New South Wales. It has a single fleshy, channelled leaf and up to six relatively large, bright-blue flowers with darker veins. The arms on the side of the column are twisted and yellow, but not toothed at the tip. Unlike most other thelymitras, the flowers do not usually close on cloudy days.

Begonia rex, the king begonia, is a species of flowering plant in the family Begoniaceae. It is found from Arunachal Pradesh to southeast China, and has been introduced to Bangladesh, Cuba, and Hispaniola. It is a parent to over 500 cultivars in the Begonia Rex Cultorum Group of houseplants. Other parents in the multitude of crosses made during the creation of the Group include Begonia annulata, B. cathayana, B. decora, B. diadema, B. dregei, B. grandis, B. hatacoa, B. palmata, and B. xanthina.


















