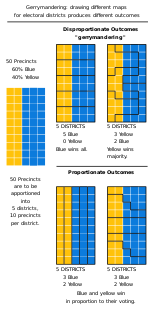
Gerrymandering is a practice intended to establish a political advantage for a particular party or group by manipulating district boundaries. The resulting district is known as a gerrymander ; however, that word is also a verb for the process. The term gerrymandering has negative connotations. Two principal tactics are used in gerrymandering: "cracking" and "packing". A third tactic, shown in the top-left diagram in the graphic to the right, is homogenization of all districts.
Norway elects its legislature on a national level. The parliament, the Storting, has 169 members elected for a four-year term by the proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies.

The 1931 United Kingdom general election was held on Tuesday 27 October 1931 and saw a landslide election victory for the National Government which had been formed two months previously after the collapse of the second Labour government. Collectively, the parties forming the National Government won 67% of the votes and 554 seats out of 615. The bulk of the National Government's support came from the Conservative Party, and the Conservatives won 470 seats. The Labour Party suffered its greatest defeat, losing four out of five seats compared with the previous election. The Liberal Party, split into three factions, continued to shrink and the Liberal National faction never reunited. Ivor Bulmer-Thomas said the results "were the most astonishing in the history of the British party system". It was the last election where one party received an absolute majority of the votes cast and the last UK general election not to take place on a Thursday, and would be the last election until 1997 in which a party won over 400 seats in the House of Commons.

The 1874 United Kingdom general election saw the incumbent Liberals, led by William Ewart Gladstone, lose decisively, even though it won a majority of the votes cast. Benjamin Disraeli's Conservatives won the majority of seats in the House of Commons, largely because they won a number of uncontested seats. It was the first Conservative victory in a general election since 1841. Gladstone's decision to call an election surprised his colleagues, for they were aware of large sectors of discontent in their coalition. For example, the nonconformists were upset with education policies; many working-class people disliked the new trade union laws and the restrictions on drinking. The Conservatives were making gains in the middle-class, Gladstone wanted to abolish the income tax, but failed to carry his own cabinet. The result was a disaster for the Liberals, who went from 387 MPs to only 242. Conservatives jumped from 271 to 350. For the first time the Irish Nationalists gained seats, returning 60. Gladstone himself noted: "We have been swept away in a torrent of gin and beer".
There are three types of elections in Denmark: elections to the national parliament, local elections and elections to the European Parliament. Referendums may also be called to consult the Danish citizenry directly on an issue of national concern.

Elections in Bangladesh gives information on election and election results in Bangladesh.
Elections in Hungary are held at two levels: general elections to elect the members of the National Assembly and local elections to elect local authorities. European Parliament elections are also held every 5 years.

The 1807 United Kingdom general election was the third general election to be held after the Union of Great Britain and Ireland.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 12 May 2007. The Independence Party remained the largest party in the Althing, winning 25 of the 63 seats.
General elections were held in India in 1991 to elect the members of the 10th Lok Sabha. The result of the election was that no party could get a majority, so a minority government was formed, resulting in a stable government for the next 5 years, under the new Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao.

Legislative elections in Portugal were held on 27 September 2009 to renew all 230 members of the Assembly of the Republic. The Socialist Party, led by incumbent Prime Minister José Sócrates, won the largest number of seats, but didn't repeat the overall majority they gained in 2005.

Partial general elections were held in Belgium on 8 June 1847. The result was a victory for the new Liberal Association, which had been formed the previous year. It won 33 seats to the Catholics' 21, as the latter were split into dogmatic and liberal groups. Voter turnout was 77%, although only 1% of the country's population was eligible to vote.

Partial general elections were held in Belgium on 10 June 1856. In the elections for the Chamber of Representatives the result was a victory for the Catholics, who won 63 of the 108 seats. Voter turnout was 60.6%, although only 43,573 people were eligible to vote.

General elections were held in Belgium on 10 December 1857, the first full general elections since 1848. The elections were called by royal order of 12 November 1857, dissolving the Chamber of Representatives that had convened in a new session only two days earlier.

General elections were held in Belgium on 11 August 1864, the first full general elections since 1857. Although the Catholics received the most votes for seats in the Chamber of Representatives, the result was a victory for the Liberal Party, which won 64 of the 116 seats. Voter turnout was 76.7%, although only 103,717 people were eligible to vote.

Partial general elections were held in Belgium on 13 June 1876. In the elections for the Chamber of Representatives the result was a victory for the Catholic Party, which won 67 of the 124 seats. Voter turnout was 67.5%, although only 63,278 people were eligible to vote.

Partial general elections were held in Belgium on 14 June 1859. The result was a victory for the Liberal Party, which won 69 of the 116 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 31 of the 58 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 55.9%, although only 49,672 people were eligible to vote.

Partial general elections were held in Belgium on 9 June 1874. The result was a victory for the Catholic Party, which won 68 of the 124 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 34 of the 62 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 64.1%, although only 52,074 people were eligible to vote.

Legislative elections were held in Belgium in June and July 1884, for partial Chamber and full Senate elections respectively. Voter turnout was 79.1% in the Chamber of Representatives elections, although only 69,276 people were eligible to vote.

General elections were held in Italy on 6 November 1904, with a second round of voting on 13 November. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc remained the largest in Parliament, winning 339 of the 508 seats. The papal ban on Catholics voting was relaxed for the first time, and three Catholics were elected.