
Praseodymium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula PrCl3. Like other lanthanide trichlorides, it exists both in the anhydrous and hydrated forms. It is a blue-green solid that rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a light green heptahydrate.

In organic chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively-charged polyatomic ions of the structure [NR4]+, where R is an alkyl group, an aryl group or organyl group. Unlike the ammonium ion and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule.

Dysprosium(III) chloride (DyCl3), also known as dysprosium trichloride, is a compound of dysprosium and chlorine. It is a white to yellow solid which rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a hexahydrate, DyCl3·6H2O. Simple rapid heating of the hydrate causes partial hydrolysis to an oxychloride, DyOCl.

Ammonium fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula NH4F. It crystallizes as small colourless prisms, having a sharp saline taste, and is highly soluble in water. Like all fluoride salts, it is moderately toxic in both acute and chronic overdose.
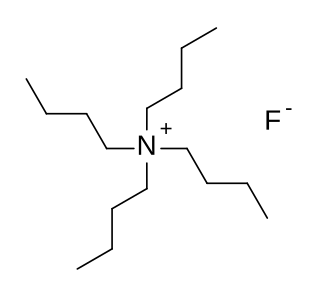
Tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride, commonly abbreviated to TBAF and n-Bu4NF, is a quaternary ammonium salt with the chemical formula (CH3CH2CH2CH2)4N+F−. It is commercially available as the white solid trihydrate and as a solution in tetrahydrofuran. TBAF is used as a source of fluoride ion in organic solvents.

Chromium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF3. It forms several hydrates. The compound CrF3 is a green crystalline solid that is insoluble in common solvents, but the hydrates [Cr(H2O)6]F3 (violet) and [Cr(H2O)6]F3·3H2O (green) are soluble in water. The anhydrous form sublimes at 1100–1200 °C.

Cobalt(II) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula (CoF2). It is a pink crystalline solid compound which is antiferromagnetic at low temperatures (TN=37.7 K) The formula is given for both the red tetragonal crystal, (CoF2), and the tetrahydrate red orthogonal crystal, (CoF2·4H2O). CoF2 is used in oxygen-sensitive fields, namely metal production. In low concentrations, it has public health uses. CoF2 is sparingly soluble in water. The compound can be dissolved in warm mineral acid, and will decompose in boiling water. Yet the hydrate is water-soluble, especially the di-hydrate CoF2·2H2O and tri-hydrate CoF2·3H2O forms of the compound. The hydrate will also decompose with heat.
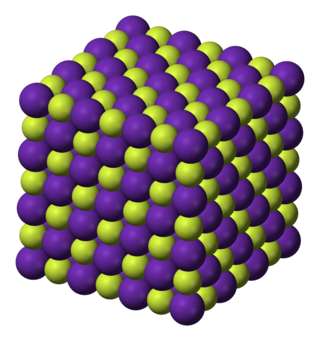
Rubidium fluoride (RbF) is the fluoride salt of rubidium. It is a cubic crystal with rock-salt structure.

Hexafluorosilicic acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H
2SiF
6. Aqueous solutions of hexafluorosilicic acid consist of salts of the cation and hexafluorosilicate anion. These salts and their aqueous solutions are colorless.

Aluminium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula AlF3. It forms hydrates AlF3·xH2O. Anhydrous AlF3 and its hydrates are all colorless solids. Anhydrous AlF3 is used in the production of aluminium metal. Several occur as minerals.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula (ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride' is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.

Tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH or TMAOH) is a quaternary ammonium salt with molecular formula N(CH3)4+ OH−. It is commonly encountered in form of concentrated solutions in water or methanol. TMAH in solid state and its aqueous solutions are all colorless, but may be yellowish if impure. Although TMAH has virtually no odor when pure, samples often have a strong fishy smell due to presence of trimethylamine which is a common impurity. TMAH has several diverse industrial and research applications.
In chemistry, an onium ion is a cation formally obtained by the protonation of mononuclear parent hydride of a pnictogen, chalcogen, or halogen. The oldest-known onium ion, and the namesake for the class, is ammonium, NH+4, the protonated derivative of ammonia, NH3.

The Sommelet–Hauser rearrangement (named after M. Sommelet and Charles R. Hauser) is a rearrangement reaction of certain benzyl quaternary ammonium salts. The reagent is sodium amide or another alkali metal amide and the reaction product a N,N-dialkylbenzylamine with a new alkyl group in the aromatic ortho position. For example, benzyltrimethylammonium iodide, [(C6H5CH2)N(CH3)3]I, rearranges in the presence of sodium amide to yield the o-methyl derivative of N,N-dimethylbenzylamine.
Charles Roy Hauser was an American chemist. Hauser was a member of the National Academy of Sciences and a professor of chemistry at Duke University.

Tetraethylammonium chloride (TEAC) is a quaternary ammonium compound with the chemical formula [N(CH2CH3)4]+Cl−, sometimes written as [NEt4]Cl. In appearance, it is a hygroscopic, colorless, crystalline solid. It has been used as the source of tetraethylammonium ions in pharmacological and physiological studies, but is also used in organic chemical synthesis.
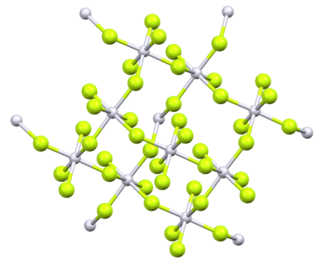
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.
Gadolinium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula GdF3.
Lutetium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of lutetium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Lu(NO3)3. The compound forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates. The compound is poisonous.

The hexafluoroarsenate anion is a chemical species with formula AsF−6. Hexafluoroarsenate is relatively inert, being the conjugate base of the notional superacid hexafluoroarsenic acid.

















