
Mahonia aquifolium, the Oregon grape or holly-leaved barberry, is a species of flowering plant in the family Berberidaceae, native to western North America. It is an evergreen shrub growing 1–3 meters tall and 1.5 m (5 ft) wide, with pinnate leaves consisting of spiny leaflets, and dense clusters of yellow flowers in early spring, followed by dark bluish-black berries.

Mahonia is a genus of approximately 70 species of evergreen shrubs and, rarely, small trees in the family Berberidaceae, native to eastern Asia, the Himalaya, North and Central America. They are closely related to the genus Berberis and botanists disagree on whether to recognize a separate Mahonia. Many botanists prefer to classify Mahonia as a part of Berberis because several species in both genera are able to hybridize, and because there are no consistent morphological differences between the two groups other than the leaf pinnation. However, recent DNA-based phylogenetic studies retain the two separate genera, by clarifying that unifoliolate-leaved Berberis s.s. is derived from within a paraphyletic group of shrubs bearing imparipinnate evergreen leaves, which are then divided into three genera: Mahonia, Alloberberis, and Moranothamnus ; a broadly-circumscribed Berberis would also be monophyletic.

Berberis, commonly known as barberry, is a large genus of deciduous and evergreen shrubs from 1–5 m (3.3–16.4 ft) tall, found throughout temperate and subtropical regions of the world. Species diversity is greatest in South America and Asia; Europe, Africa and North America have native species as well. The best-known Berberis species is the European barberry, Berberis vulgaris, which is common in Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, and central Asia, and has been widely introduced in North America. Many of the species have spines on the shoots and all along the margins of the leaves.

The Berberidaceae are a family of 18 genera of flowering plants commonly called the barberry family. This family is in the order Ranunculales. The family contains about 700 known species, of which the majority are in Berberis. The species include trees, shrubs and perennial herbaceous plants.

Berberis microphylla, common name box-leaved barberry and Magellan barberry, in Spanish calafate and michay and other names, is an evergreen shrub, with simple, shiny box-like leaves. The calafate is native to southern Argentina and Chile and is a symbol of Patagonia.

Berberis darwinii, Darwin’s barberry, is a species of flowering plant in the family Berberidaceae, native to southern Chile and Argentina and naturalized elsewhere. Regional vernacular names include michay, calafate, and quelung. Growing to 3–4 m (9.8–13.1 ft) tall, it is an evergreen thorny shrub.

Apigenin (4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone), found in many plants, is a natural product belonging to the flavone class that is the aglycone of several naturally occurring glycosides. It is a yellow crystalline solid that has been used to dye wool.

Berberis vulgaris, also known as common barberry, European barberry or simply barberry, is a shrub in the genus Berberis native to the Old World. It produces edible but sharply acidic berries, which people in many countries eat as a tart and refreshing fruit.

Berberis thunbergii, the Japanese barberry, Thunberg's barberry, or red barberry, is a species of flowering plant in the barberry family Berberidaceae, native to Japan and eastern Asia, though widely naturalized in China and North America, where it has become a problematic invasive in many places, leading to declines in species diversity, increased tick habitat, and soil changes. Growing to 1 m tall by 2.5 m broad, it is a small deciduous shrub with green leaves turning red in the autumn, brilliant red fruits in autumn and pale yellow flowers in spring.

Flavones are a class of flavonoids based on the backbone of 2-phenylchromen-4-one (2-phenyl-1-benzopyran-4-one).
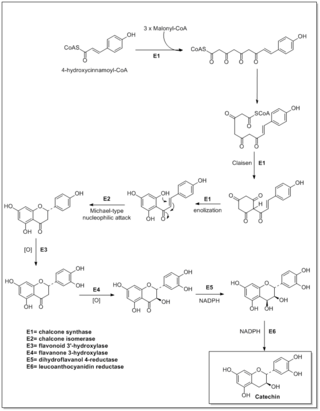
Flavonoids are synthesized by the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway in which the amino acid phenylalanine is used to produce 4-coumaroyl-CoA. This can be combined with malonyl-CoA to yield the true backbone of flavonoids, a group of compounds called chalcones, which contain two phenyl rings. Conjugate ring-closure of chalcones results in the familiar form of flavonoids, the three-ringed structure of a flavone. The metabolic pathway continues through a series of enzymatic modifications to yield flavanones → dihydroflavonols → anthocyanins. Along this pathway, many products can be formed, including the flavonols, flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins (tannins) and a host of other various polyphenolics.
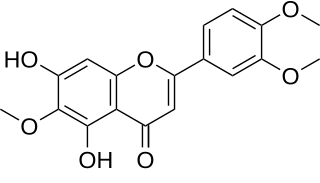
Eupatilin (5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4',6-trimethoxyflavone) is an O-methylated flavone, a type of flavonoids. It can be found in Artemisia asiatica (Asteraceae).
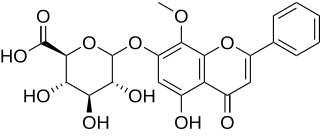
Oroxindin is a flavone, a type of phenolic chemical compound. It is a wogonoside, more accurately a wogonin glucuronide isolated from Oroxylum indicum (Bignoniaceae), Bacopa monnieri (Plantaginaceae) and Holmskioldia sanguinea.

Apiin is a natural flavonoid, a diglycoside of the flavone apigenin found in the winter-hardy plants parsley and celery, and in banana leaf. The glycoside moiety at carbon-7 of apigenin, O-β-D-apiofuranosyl(→)2-β-D-glucosyl, is carried by several other flavones in parsley plant and seed. The sugar apiose possibly play a role in winter hardiness of celery, duckweed and parsley.

6-Hydroxyflavone is a flavone, a type of chemical compound. It is one of the noncompetitive inhibitors of cytochrome P450 2C9. It is reported in Crocus and leaves of Barleria prionitis Linn. . 6-Hydroxyflavone may have a potential as a therapeutic drug capable for the treatment of anxiety-like disorders.

Rhoifolin is a chemical compound. It is first isolated from plant Rhus succedanea. The term "Rhoi" derived from generic name of plant Rhus. It is a flavone, a type of flavonoid isolated from Boehmeria nivea, China grass or ramie (leaf), from Citrus limon, Canton lemon (leaf), from Citrus x aurantium, the bigarade or bitter orange (plant), from Citrus x paradisi, the grapefruit (leaf), from Ononis campestris, the cammock (shoot) and from Sabal serratula, the serenoa or sabal fruit (plant).
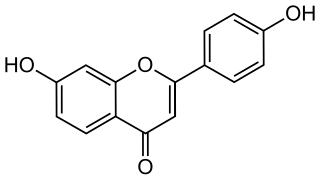
4′,7-Dihydroxyflavone is a flavone. It is found in Medicago truncatula in relation with the root nodulation symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti or in seeds of Sophora viciifolia.

Hispidulin is a naturally occurring flavone with potential antiepileptic activity in rats and gerbils. It is found in plants including Grindelia argentina, Arrabidaea chica, Saussurea involucrate, Crossostephium chinense, Artemisia, and Salvia.

The Ziarat Juniper Forest is a juniper forest in Ziarat, Balochistan, Pakistan.
















