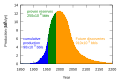
The Hubbert curve is an approximation of the production rate of a resource over time. It is a symmetric logistic distribution curve, often confused with the "normal" gaussian function. It first appeared in "Nuclear Energy and the Fossil Fuels," geologist M. King Hubbert's 1956 presentation to the American Petroleum Institute, as an idealized symmetric curve, during his tenure at the Shell Oil Company. It has gained a high degree of popularity in the scientific community for predicting the depletion of various natural resources. The curve is the main component of Hubbert peak theory, which has led to the rise of peak oil concerns. Basing his calculations on the peak of oil well discovery in 1948, Hubbert used his model in 1956 to create a curve which predicted that oil production in the contiguous United States would peak around 1970.

Marion King Hubbert was an American geologist and geophysicist. He worked at the Shell research lab in Houston, Texas. He made several important contributions to geology, geophysics, and petroleum geology, most notably the Hubbert curve and Hubbert peak theory, with important political ramifications. He was often referred to as "M. King Hubbert" or "King Hubbert".

The Hubbert peak theory says that for any given geographical area, from an individual oil-producing region to the planet as a whole, the rate of petroleum production tends to follow a bell-shaped curve. It is one of the primary theories on peak oil.
An energy carrier is a substance (fuel) or sometimes a phenomenon that contains energy that can be later converted to other forms such as mechanical work or heat or to operate chemical or physical processes.

Peak oil is the theorized point in time when the maximum rate of global oil production will occur, after which oil production will begin an irreversible decline. The primary concern of peak oil is that global transportation heavily relies upon the use of gasoline and diesel fuel. Switching transportation to electric vehicles, biofuels, or more fuel-efficient forms of travel may help reduce oil demand.
Kenneth S. Deffeyes was a geologist who worked with M. King Hubbert, the creator of the Hubbert peak theory, at the Shell Oil Company research laboratory in Houston, Texas. He claimed Chickasaw ancestry.

Colin J. Campbell was a British petroleum geologist who predicted that oil production would peak by 2007. He claimed the consequences of this are uncertain but drastic, due to the world's dependency on fossil fuels for the vast majority of its energy. His theories have received wide attention but are disputed and have not significantly changed governmental energy policies at this time. To deal with declining global oil production, he proposed the Rimini protocol.
The Hirsch report, the commonly referred to name for the report Peaking of World Oil Production: Impacts, Mitigation, and Risk Management, was created by request for the US Department of Energy and published in February 2005. Some information was updated in 2007. It examined the time frame for the occurrence of peak oil, the necessary mitigating actions, and the likely impacts based on the timeliness of those actions.
Oil depletion is the decline in oil production of a well, oil field, or geographic area. The Hubbert peak theory makes predictions of production rates based on prior discovery rates and anticipated production rates. Hubbert curves predict that the production curves of non-renewing resources approximate a bell curve. Thus, according to this theory, when the peak of production is passed, production rates enter an irreversible decline.
Renewable Fuels are fuels produced from renewable resources. Examples include: biofuels, Hydrogen fuel, and fully synthetic fuel produced from ambient carbon dioxide and water. This is in contrast to non-renewable fuels such as natural gas, LPG (propane), petroleum and other fossil fuels and nuclear energy. Renewable fuels can include fuels that are synthesized from renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar. Renewable fuels have gained in popularity due to their sustainability, low contributions to the carbon cycle, and in some cases lower amounts of greenhouse gases. The geo-political ramifications of these fuels are also of interest, particularly to industrialized economies which desire independence from Middle Eastern oil.
World energy resources are the estimated maximum capacity for energy production given all available resources on Earth. They can be divided by type into fossil fuel, nuclear fuel and renewable resources.

The Hubbert linearization is a way to plot production data to estimate two important parameters of a Hubbert curve, the approximated production rate of a nonrenewable resource following a logistic distribution:
Peak gas is the point in time when the maximum global natural gas production rate will be reached, after which the rate of production will enter its terminal decline. Although demand is peaking in the United States and Europe, it continues to rise globally due to consumers in Asia, especially China. Natural gas is a fossil fuel formed from plant matter over the course of millions of years. Natural gas derived from fossil fuels is a non-renewable energy source; however, methane can be renewable in other forms such as biogas. Peak coal was in 2013, and peak oil is forecast to occur before peak gas. One forecast is for natural gas demand to peak in 2035.

Peak oil is the point at which oil production, sometimes including unconventional oil sources, hits its maximum. Predicting the timing of peak oil involves estimation of future production from existing oil fields as well as future discoveries. The most influential production model is Hubbert peak theory, first proposed in the 1950s. The effect of peak oil on the world economy remains controversial.

Out of Gas: The End of the Age of Oil is a 2004 book written by David Goodstein. It describes peak oil and the future of civilization.

The End of Oil: On the Edge of a Perilous New World is a non-fiction book by American journalist and author Paul Roberts. Published in 2004, it is Roberts' book-length debut. It provides an analysis of the various problems associated with humanity's reliance on oil and other fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas.
The reserves-to-production ratio is the remaining amount of a non-renewable resource, expressed in time. While applicable to all natural resources, the RPR is most commonly applied to fossil fuels, particularly petroleum and natural gas. The reserve portion (numerator) of the ratio is the amount of a resource known to exist in an area and to be economically recoverable. The production portion (denominator) of the ratio is the amount of resource produced in one year at the current rate.

Sustainability measurement is a set of frameworks or indicators to measure how sustainable something is. This includes processes, products, services and businesses. Sustainability is difficult to quantify. It may even be impossible to measure. To measure sustainability, the indicators consider environmental, social and economic domains. The metrics are still evolving. They include indicators, benchmarks and audits. They include sustainability standards and certification systems like Fairtrade and Organic. They also involve indices and accounting. And they can include assessment, appraisal and other reporting systems. These metrics are used over a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. Sustainability measures include corporate sustainability reporting, Triple Bottom Line accounting. They include estimates of the quality of sustainability governance for individual countries. These use the Environmental Sustainability Index and Environmental Performance Index. Some methods let us track sustainable development. These include the UN Human Development Index and ecological footprints.

A Thousand Barrels a Second: The Coming Oil Break Point and the Challenges Facing an Energy Dependent World is a 2007 book by Canadian energy economist and columnist Peter Tertzakian that describes the multiple pressures forcing an upending of oil's dominant role in the global energy supply mix and conjectures about how economic, social and technological innovation will drive the inevitable adjustment process.

Unconventional reservoirs, or unconventional resources are accumulations where oil & gas phases are tightly bound to the rock fabric by strong capillary forces, requiring specialised measures for evaluation and extraction.