
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.
Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in speciality chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and drugs. The development of hydroformylation is one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.
In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis by a soluble catalyst in a solution. Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, principally in solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysis describes processes where the catalysts and substrate are in distinct phases, typically solid-gas, respectively. The term is used almost exclusively to describe solutions and implies catalysis by organometallic compounds. Homogeneous catalysis is established technology that continues to evolve. An illustrative major application is the production of acetic acid. Enzymes are examples of homogeneous catalysts.

Wilkinson's catalyst is the common name for chloridotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I), a coordination complex of rhodium with the formula [RhCl(PPh3)3] (Ph = phenyl). It is a red-brown colored solid that is soluble in hydrocarbon solvents such as benzene, and more so in tetrahydrofuran or chlorinated solvents such as dichloromethane. The compound is widely used as a catalyst for hydrogenation of alkenes. It is named after chemist and Nobel laureate Sir Geoffrey Wilkinson, who first popularized its use.

Crabtree's catalyst is an organoiridium compound with the formula [C8H12IrP(C6H11)3C5H5N]PF6. It is a homogeneous catalyst for hydrogenation and hydrogen-transfer reactions, developed by Robert H. Crabtree. This air stable orange solid is commercially available and known for its directed hydrogenation to give trans stereoselectivity with respective of directing group.
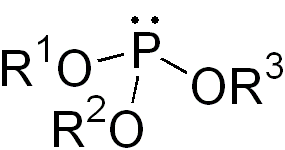
In chemistry a phosphite ester or organophosphite usually refers to an organophosphorous compound with the formula P(OR)3. They can be considered as esters of an unobserved tautomer phosphorous acid, H3PO3, with the simplest example being trimethylphosphite, P(OCH3)3. Some phosphites can be considered esters of the dominant tautomer of phosphorous acid (HP(O)(OH)2). The simplest representative is dimethylphosphite with the formula HP(O)(OCH3)2. Both classes of phosphites are usually colorless liquids.
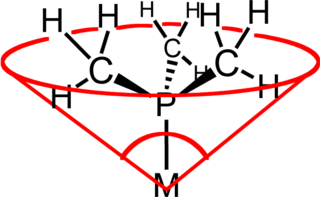
In coordination chemistry, the ligand cone angle is a measure of the steric bulk of a ligand in a transition metal coordination complex. It is defined as the solid angle formed with the metal at the vertex and the outermost edge of the van der Waals spheres of the ligand atoms at the perimeter of the cone. Tertiary phosphine ligands are commonly classified using this parameter, but the method can be applied to any ligand. The term cone angle was first introduced by Chadwick A. Tolman, a research chemist at DuPont. Tolman originally developed the method for phosphine ligands in nickel complexes, determining them from measurements of accurate physical models.

In coordination chemistry the bite angle is the ligand–metal–ligand bond angle of coordination complex containing a bidentate ligand. This geometric parameter is used to classify chelating ligands, including those in organometallic complexes. It is most often discussed in terms of catalysis, as changes in bite angle can affect not just the activity and selectivity of a catalytic reaction but even allow alternative reaction pathways to become accessible.
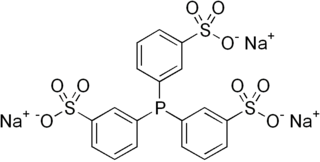
3,3′,3′′-Phosphanetriyltris(benzenesulfonic acid) trisodium salt (abbreviated TPPTS), is an organic compound that is also known as sodium triphenylphosphine trisulfonate. The compound has the formula P(C6H4SO3Na)3. This white solid is an unusual example of a water-soluble phosphine. Its complexes are also water-soluble. Its complex with rhodium is used in the industrial production of butyraldehyde.
Asymmetric hydrogenation is a chemical reaction that adds two atoms of hydrogen to a target (substrate) molecule with three-dimensional spatial selectivity. Critically, this selectivity does not come from the target molecule itself, but from other reagents or catalysts present in the reaction. This allows spatial information to transfer from one molecule to the target, forming the product as a single enantiomer. The chiral information is most commonly contained in a catalyst and, in this case, the information in a single molecule of catalyst may be transferred to many substrate molecules, amplifying the amount of chiral information present. Similar processes occur in nature, where a chiral molecule like an enzyme can catalyse the introduction of a chiral centre to give a product as a single enantiomer, such as amino acids, that a cell needs to function. By imitating this process, chemists can generate many novel synthetic molecules that interact with biological systems in specific ways, leading to new pharmaceutical agents and agrochemicals. The importance of asymmetric hydrogenation in both academia and industry contributed to two of its pioneers — William Standish Knowles and Ryōji Noyori — being awarded one half of the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
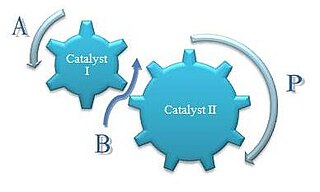
Concurrent tandem catalysis (CTC) is a technique in chemistry where multiple catalysts produce a product otherwise not accessible by a single catalyst. It is usually practiced as homogeneous catalysis. Scheme 1 illustrates this process. Molecule A enters this catalytic system to produce the comonomer, B, which along with A enters the next catalytic process to produce the final product, P. This one-pot approach can decrease product loss from isolation or purification of intermediates. Reactions with relatively unstable products can be generated as intermediates because they are only transient species and are immediately used in a consecutive reaction.

DuPhos is a class of organophosphorus compound that are used ligands for asymmetric synthesis. The name DuPhos is derived from (1) the chemical company that sponsored the research leading to this ligand's invention, DuPont and (2) the compound is a diphosphine ligand type. Specifically it is classified as a C2-symmetric ligand, consisting of two phospholanes rings affixed to a benzene ring.

Organorhodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a rhodium-carbon chemical bond, and the study of rhodium and rhodium compounds as catalysts in organic reactions.
In chemistry, metal-catalysed hydroboration is a reaction used in organic synthesis. It is one of several examples of homogeneous catalysis.

A metal-phosphine complex is a In coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0).
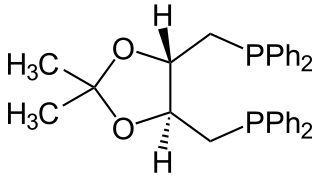
DIOP is an organophosphorus compound that is used as a chiral ligand in asymmetric catalysis. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
Clark Landis is an American chemist, whose research focuses on organic and inorganic chemistry. He is currently a Professor of Chemistry at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. He was awarded the ACS Award in Organometallic Chemistry in 2010, and is a fellow of the American Chemical Society and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
In chemistry, phosphorochloridites are a class of organophosphorus compound with the formula (RO)2PCl (R = organic substituent). They are pyramidal in shape, akin to regular phosphites (P(OR)3). They are usually colorless and sensitive toward hydrolysis and, to some extent, oxidation to the corresponding phosphorochloridates ((RO)2P(O)Cl).

2,2′-Biphenylene phosphorochloridite is the name for a polycyclic organophosphorus compound with the formula C12H8O2PCl. It is a precursor to diphosphite ligands such as BiPhePhos by reaction with suitable diols. 2,2′-Biphenylene phosphorochloridites, which is a white solid, is prepared from 2,2′-biphenol and phosphorus trichloride. It is prepared by the reaction of 2,2′-biphenol and phosphorus trichloride.

2,2′-Biphenol is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4OH)2. It is one of three symmetrical isomers of biphenol. A white solid, it is a precursor to diphosphite ligands that are used to support industrial hydroformylation catalysis.















