
Tetraplegia, also known as quadriplegia, is defined as the dysfunction or loss of motor and/or sensory function in the cervical area of the spinal cord. A loss of motor function can present as either weakness or paralysis leading to partial or total loss of function in the arms, legs, trunk, and pelvis; paraplegia is similar but affects the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral segments of the spinal cord and arm function is spared. The paralysis may be flaccid or spastic. A loss of sensory function can present as an impairment or complete inability to sense light touch, pressure, heat, pinprick/pain, and proprioception. In these types of spinal cord injury, it is common to have a loss of both sensation and motor control.
The ankle jerk reflex, also known as the Achilles reflex, occurs when the Achilles tendon is tapped while the foot is dorsiflexed. It is a type of stretch reflex that tests the function of the gastrocnemius muscle and the nerve that supplies it. A positive result would be the jerking of the foot towards its plantar surface. Being a deep tendon reflex, it is monosynaptic. It is also a stretch reflex. These are monosynaptic spinal segmental reflexes. When they are intact, integrity of the following is confirmed: cutaneous innervation, motor supply, and cortical input to the corresponding spinal segment.
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.

A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex. In vertebrates, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This allows for faster reflex actions to occur by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of routing signals through the brain. The brain will receive the input while the reflex is being carried out and the analysis of the signal takes place after the reflex action.

Clonus is a set of involuntary and rhythmic muscular contractions and relaxations. Clonus is a sign of certain neurological conditions, particularly associated with upper motor neuron lesions involving descending motor pathways, and in many cases is accompanied by spasticity. Unlike small spontaneous twitches known as fasciculations, clonus causes large motions that are usually initiated by a reflex. Studies have shown clonus beat frequency to range from three to eight Hz on average, and may last a few seconds to several minutes depending on the patient’s condition.

The patellar reflex, also called the knee reflex or knee-jerk, is a stretch reflex which tests the L2, L3, and L4 segments of the spinal cord. Many animals, most significantly humans, have been seen to have the patellar reflex, including dogs, cats, horses, and other mammalian species.

The musculocutaneous nerve is a mixed branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus derived from cervical spinal nerves C5-C7. It arises opposite the lower border of the pectoralis major. It provides motor innervation to the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm: the coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, and brachialis. It provides sensory innervation to the lateral forearm. It courses through the anterior part of the arm, terminating 2 cm above elbow; after passing the lateral edge of the tendon of biceps brachii it is becomes known as the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm.

The triceps, or triceps brachii, is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of 3 parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. It is the muscle principally responsible for extension of the elbow joint.

An upper motor neuron lesion Is an injury or abnormality that occurs in the neural pathway above the anterior horn cell of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. Conversely, a lower motor neuron lesion affects nerve fibers traveling from the anterior horn of the spinal cord or the cranial motor nuclei to the relevant muscle(s).
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are motor neurons located in either the anterior grey column, anterior nerve roots or the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and cranial nerves with motor function. Many voluntary movements rely on spinal lower motor neurons, which innervate skeletal muscle fibers and act as a link between upper motor neurons and muscles. Cranial nerve lower motor neurons also control some voluntary movements of the eyes, face and tongue, and contribute to chewing, swallowing and vocalization. Damage to the lower motor neurons can lead to flaccid paralysis, absent deep tendon reflexes and muscle atrophy.
Tendon reflex may refer to:
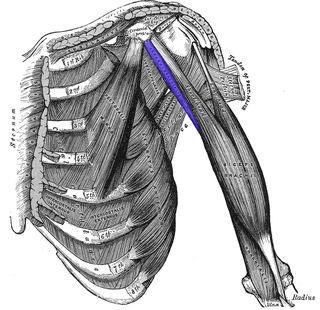
The coracobrachialis muscle is a muscle in the upper medial part of the arm. It is located within the anterior compartment of the arm. It originates from the coracoid process of the scapula; it inserts onto the middle of the medial aspect of the body of the humerus. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve. It acts to adduct and flex the arm.

The stretch reflex, or more accurately "muscle stretch reflex", is a muscle contraction in response to stretching a muscle. The function of the reflex is generally thought be maintaining the muscle at a constant length but the response is often coordinated across multiple muscles and even joints. The term deep tendon reflex is often wrongfully used by many health workers and students to refer to this reflex. "Tendons have little to do with the response, other than being responsible for mechanically transmitting the sudden stretch from the reflex hammer to the muscle spindle. In addition, some muscles with stretch reflexes have no tendons ".
Alpha (α) motor neurons (also called alpha motoneurons), are large, multipolar lower motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle and are directly responsible for initiating their contraction. Alpha motor neurons are distinct from gamma motor neurons, which innervate intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles.
The triceps reflex, a deep tendon reflex, is a reflex that elicits involuntary contraction of the triceps brachii muscle. It is sensed and transmitted by the radial nerve. The reflex is tested as part of the neurological examination to assess the sensory and motor pathways within the C7 and C8 spinal nerves.

A lower motor neuron lesion is a lesion which affects nerve fibers traveling from the lower motor neuron(s) in the anterior horn/anterior grey column of the spinal cord, or in the motor nuclei of the cranial nerves, to the relevant muscle(s).
The brachioradialis reflex is observed during a neurological exam by striking the brachioradialis tendon directly with a reflex hammer when the patient's arm is relaxing. This reflex is carried by the radial nerve
The Golgi tendon reflex (also called inverse stretch reflex, autogenic inhibition, tendon reflex) is an inhibitory effect on the muscle resulting from the muscle tension stimulating Golgi tendon organs (GTO) of the muscle, and hence it is self-induced. The reflex arc is a negative feedback mechanism preventing too much tension on the muscle and tendon. When the tension is extreme, the inhibition can be so great it overcomes the excitatory effects on the muscle's alpha motoneurons causing the muscle to suddenly relax. This reflex is also called the inverse myotatic reflex, because it is the inverse of the stretch reflex.

An upper limb neurological examination is part of the neurological examination, and is used to assess the motor and sensory neurons which supply the upper limbs. This assessment helps to detect any impairment of the nervous system, being used both as a screening and an investigative tool. The examination findings when combined with a detailed history of a patient, can help a doctor reach a specific or differential diagnosis. This would enable the doctor to commence treatment if a specific diagnosis has been made, or order further investigations if there are differential diagnoses.










