
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

n-Butyllithium C4H9Li (abbreviated n-BuLi) is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS). Also, it is broadly employed as a strong base (superbase) in the synthesis of organic compounds as in the pharmaceutical industry.

1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (Ph2PCH2)2 (Ph = phenyl). It is a commonly used bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.

Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are chemical compounds with the general formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride Cl−Mg−CH3 and phenylmagnesium bromide (C6H5)−Mg−Br. They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds.
Organogermanium chemistry is the science of chemical species containing one or more C–Ge bonds. Germanium shares group 14 in the periodic table with carbon, silicon, tin and lead. Historically, organogermanes are considered as nucleophiles and the reactivity of them is between that of organosilicon and organotin compounds. Some organogermanes have enhanced reactivity compared with their organosilicon and organoboron analogues in some cross-coupling reactions.
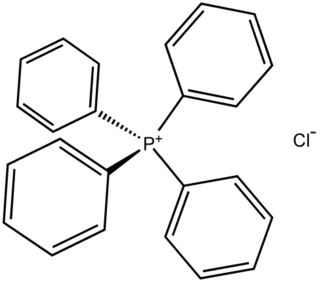
Tetraphenylphosphonium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [(C6H5)4P]Cl, abbreviated Ph4PCl or PPh4Cl or [PPh4]Cl, where Ph stands for phenyl. Tetraphenylphosphonium and especially tetraphenylarsonium salts were formerly of interest in gravimetric analysis of perchlorate and related oxyanions. This colourless salt is used to generate lipophilic salts from inorganic and organometallic anions. Thus, [Ph4P]+ is useful as a phase-transfer catalyst, again because it allows inorganic anions to dissolve in organic solvents.
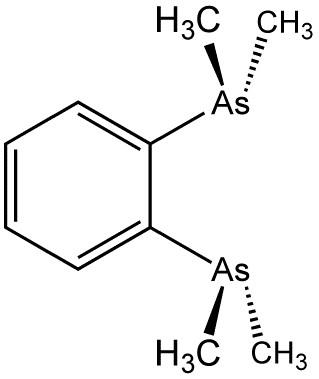
1,2-Bis(dimethylarsino)benzene (diars) is the organoarsenic compound with the formula C6H4(As(CH3)2)2. The molecule consists of two dimethylarsino groups attached to adjacent carbon centers of a benzene ring. It is a chelating ligand in coordination chemistry. This colourless oil is commonly abbreviated "diars."

Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts.

Chlorodiphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PCl, abbreviated Ph2PCl. It is a colourless oily liquid with a pungent odor that is often described as being garlic-like and detectable even in the ppb range. It is useful reagent for introducing the Ph2P group into molecules, which includes many ligands. Like other halophosphines, Ph2PCl is reactive with many nucleophiles such as water and easily oxidized even by air.
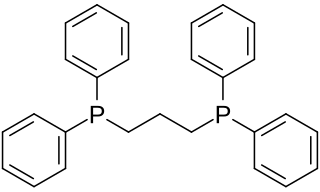
1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula Ph2P(CH2)3PPh2. The compound is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is slightly air-sensitive, degrading in air to the phosphine oxide. It is classified as a diphosphine ligand in coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.

Benzene-1,2-dithiol is the organosulfur compound with the formula C6H4(SH)2. This colourless viscous liquid consists of a benzene ring with a pair of adjacent thiol groups. The conjugate base of this diprotic compound serves as chelating agent in coordination chemistry and a building block for the synthesis of other organosulfur compounds.

Organocerium chemistry is the science of organometallic compounds that contain one or more chemical bond between carbon and cerium. These compounds comprise a subset of the organolanthanides. Most organocerium compounds feature Ce(III) but some Ce(IV) derivatives are known.

Metal amides (systematic name metal azanides) are a class of coordination compounds composed of a metal center with amide ligands of the form NR2−. Amido complexes of the parent amido ligand NH2− are rare compared to complexes with diorganylamido ligand, such as dimethylamido. Amide ligands have two electron pairs available for bonding.

POCOP is a type of pincer ligand. Pincer type ligands are tridentate ligands that bind three sites on one plane of a metal complex. POCOP forms complexes with one M-C(aryl) bond and two phosphinite ligands. The term POCOP is used both for the ligand, with formula C6H4(OPPh2)2, and its complexes, with formula C6H3(OPPh2)2]− (Ph = C6H5)

Phenylsodium C6H5Na is an organosodium compound. Solid phenylsodium was first isolated by Nef in 1903. Although the behavior of phenylsodium and phenyl magnesium bromide are similar, the organosodium compound is very rarely used.
In organophosphorus chemistry, an aminophosphine is a compound with the formula R3−nP(NR2)n where R = H or an organic substituent, and n = 0, 1, 2. At one extreme, the parents H2PNH2 and P(NH2)3 are lightly studied and fragile, but at the other extreme tris(dimethylamino)phosphine (P(NMe2)3) is commonly available. Intermediate members are known, such as Ph2PN(H)Ph. These compounds are typically colorless and reactive toward oxygen. They have pyramidal geometry at phosphorus.

Isopropylmagnesium chloride is an organometallic compound with the general formula (CH3)2HCMgCl. This highly flammable, colorless, and moisture sensitive material is the Grignard reagent derived from isopropyl chloride. It is commercially available, usually as a solution in tetrahydrofuran.

1,2-Bis(dichlorophosphino)benzene is an organophosphorus compound with the formula C6H4(PCl2)2. This viscous colorless liquid is a precursor to chelating diphosphines of the type C6H4(PR2)2. It is prepared from 1,2-dibromobenzene by sequential lithiation followed by treatment with (Et2N)2PCl (Et = ethyl), which affords C6H4[P(NEt2)2]2. This species is finally cleaved with hydrogen chloride:

In chemistry, a transition metal ether complex is a coordination complex consisting of a transition metal bonded to one or more ether ligand. The inventory of complexes is extensive. Common ether ligands are diethyl ether and tetrahydrofuran. Common chelating ether ligands include the glymes, dimethoxyethane (dme) and diglyme, and the crown ethers. Being lipophilic, metal-ether complexes often exhibit solubility in organic solvents, a property of interest in synthetic chemistry. In contrast, the di-ether 1,4-dioxane is generally a bridging ligand.


















