Paul Ehrlich was a Nobel Prize-winning German physician and scientist who worked in the fields of hematology, immunology and antimicrobial chemotherapy. Among his foremost achievements were finding a cure for syphilis in 1909 and inventing the precursor technique to Gram staining bacteria. The methods he developed for staining tissue made it possible to distinguish between different types of blood cells, which led to the ability to diagnose numerous blood diseases.

A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities.

Ethidium bromide is an intercalating agent commonly used as a fluorescent tag in molecular biology laboratories for techniques such as agarose gel electrophoresis. It is commonly abbreviated as EtBr, which is also an abbreviation for bromoethane. To avoid confusion, some laboratories have used the abbreviation EthBr for this salt. When exposed to ultraviolet light, it will fluoresce with an orange colour, intensifying almost 20-fold after binding to DNA. Under the name homidium, it has been commonly used since the 1950s in veterinary medicine to treat trypanosomiasis in cattle. The high incidence of antimicrobial resistance makes this treatment impractical in some areas, where the related isometamidium chloride is used instead. Despite its reputation as a mutagen, tests have shown it to have low mutagenicity without metabolic activation.

Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology, in cytology, and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues, cell populations, or organelles within individual cells.

Histopathology is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments.

A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. "Fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image.
Sex selection is the attempt to control the sex of the offspring to achieve a desired sex. It can be accomplished in several ways, both pre- and post-implantation of an embryo, as well as at childbirth. It has been marketed under the title family balancing.
DAPI, or 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, is a fluorescent stain that binds strongly to adenine–thymine-rich regions in DNA. It is used extensively in fluorescence microscopy. As DAPI can pass through an intact cell membrane, it can be used to stain both live and fixed cells, though it passes through the membrane less efficiently in live cells and therefore provides a marker for membrane viability.

Hoechst stains are part of a family of blue fluorescent dyes used to stain DNA. These bis-benzimides were originally developed by Hoechst AG, which numbered all their compounds so that the dye Hoechst 33342 is the 33,342nd compound made by the company. There are three related Hoechst stains: Hoechst 33258, Hoechst 33342, and Hoechst 34580. The dyes Hoechst 33258 and Hoechst 33342 are the ones most commonly used and they have similar excitation–emission spectra.
In pathology, silver staining is the use of silver to selectively alter the appearance of a target in microscopy of histological sections; in temperature gradient gel electrophoresis; and in polyacrylamide gels.
Hoechst, Hochst, or Höchst may refer to:
Bismarck brown Y also called C.I. 21000 and C.I. Basic Brown 1, is a diazo dye with the idealized formula [(H2N)2C6H3N2]2C6H4. The dye is a mixture of closely related compounds. It was one of the earliest azo dyes, being described in 1863 by German chemist Carl Alexander von Martius. It is used in histology for staining tissues.
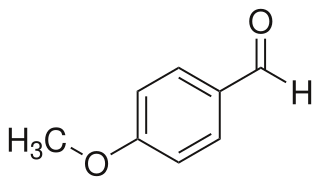
4-Anisaldehyde, or p-Anisaldehyde, is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4CHO. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with a formyl and a methoxy group. It is a colorless liquid with a strong aroma. It provides sweet, floral and strong aniseed odor. Two isomers of 4-anisaldehyde are known, ortho-anisaldehyde and meta-anisaldehyde. They are less commonly encountered.

Acridine orange is an organic compound that serves as a nucleic acid-selective fluorescent dye with cationic properties useful for cell cycle determination. Acridine orange is cell-permeable, which allows the dye to interact with DNA by intercalation, or RNA via electrostatic attractions. When bound to DNA, acridine orange is very similar spectrally to an organic compound known as fluorescein. Acridine orange and fluorescein have a maximum excitation at 502nm and 525 nm (green). When acridine orange associates with RNA, the fluorescent dye experiences a maximum excitation shift from 525 nm (green) to 460 nm (blue). The shift in maximum excitation also produces a maximum emission of 650 nm (red). Acridine orange is able to withstand low pH environments, allowing the fluorescent dye to penetrate acidic organelles such as lysosomes and phagolysosomes that are membrane-bound organelles essential for acid hydrolysis or for producing products of phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Acridine orange is used in epifluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. The ability to penetrate the cell membranes of acidic organelles and cationic properties of acridine orange allows the dye to differentiate between various types of cells. The shift in maximum excitation and emission wavelengths provides a foundation to predict the wavelength at which the cells will stain.
A side population (SP) in flow cytometry is a sub-population of cells that is distinct from the main population on the basis of the markers employed. By definition, cells in a side population have distinguishing biological characteristics, but the exact nature of this distinction depends on the markers used in identifying the side population.

SYBR Green I (SG) is an asymmetrical cyanine dye used as a nucleic acid stain in molecular biology. The SYBR family of dyes is produced by Molecular Probes Inc., now owned by Thermo Fisher Scientific. SYBR Green I binds to DNA. The resulting DNA-dye-complex best absorbs 497 nanometer blue light and emits green light. The stain preferentially binds to double-stranded DNA, but will stain single-stranded (ss) DNA with lower performance. SYBR Green can also stain RNA with a lower performance than ssDNA.

7-Aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD) is a fluorescent chemical compound with a strong affinity for DNA. It is used as a fluorescent marker for DNA in fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. It intercalates in double-stranded DNA, with a high affinity for GC-rich regions, making it useful for chromosome banding studies.
Cell synchronization is a process by which cells in a culture at different stages of the cell cycle are brought to the same phase. Cell synchrony is a vital process in the study of cells progressing through the cell cycle as it allows population-wide data to be collected rather than relying solely on single-cell experiments. The types of synchronization are broadly categorized into two groups; physical fractionization and chemical blockade.
Sperm sorting is a means of choosing what type of sperm cell is to fertilize the egg cell. Several conventional techniques of centrifugation or swim-up. Newly applied methods such as flow cytometry expand the possibilities of sperm sorting and new techniques of sperm sorting are being developed.
Cell cycle analysis by DNA content measurement is a method that most frequently employs flow cytometry to distinguish cells in different phases of the cell cycle. Before analysis, the cells are usually permeabilised and treated with a fluorescent dye that stains DNA quantitatively, such as propidium iodide (PI) or 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). The fluorescence intensity of the stained cells correlates with the amount of DNA they contain. As the DNA content doubles during the S phase, the DNA content (and thereby intensity of fluorescence) of cells in the G0 phase and G1 phase (before S), in the S phase, and in the G2 phase and M phase (after S) identifies the cell cycle phase position in the major phases (G0/G1 versus S versus G2/M phase) of the cell cycle. The cellular DNA content of individual cells is often plotted as their frequency histogram to provide information about relative frequency (percentage) of cells in the major phases of the cell cycle.