
Microcotyle is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea. Species of Microcotyle are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.

Microcotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans. All the species in this family are parasitic on fish.

Microcotyle archosargi is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. It was first described by MacCallum in 1913 based on ten specimens. Hargis (1956) pointed out that the description and figures given by MacCallum were poor in details.
Microcotyle bassensis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle branchiostegi is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle longirostri is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle nemadactylus is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle neozealanica is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle helotes is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle cepolae is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle gimpo is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle sebastisci is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle victoriae is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle tanago is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Microcotyle pomatomi is a species of monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
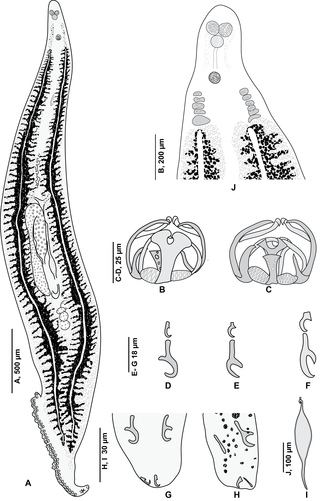
Pseudaxine is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; all its species are parasites of fish.

Microcotylinae is a subfamily within family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. This subfamily was created by Taschenberg in 1879.




