
Armadillos are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. Nine extinct genera and 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of different environments.
Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses, in biology. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also called binominal nomenclature or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name or a scientific name; more informally it is also called a Latin name.

The family Psittacidae is one of three families of true parrots. It comprises the roughly 10 species of subfamily Psittacinae and 157 of subfamily Arinae, as well as several species that have gone extinct in recent centuries. Some of the most iconic birds in the world are represented here, such as the blue-and-gold macaw among the New World parrots and the grey parrot among the Old World parrots.

The opossum is a marsupial of the order Didelphimorphia endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 110+ species in 19 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North America in the Great American Interchange following the connection of the two continents. Their unspecialized biology, flexible diet, and reproductive habits make them successful colonizers and survivors in diverse locations and conditions.

The Accipitridae, one of the three families within the order Accipitriformes, are a family of small to large birds with strongly hooked bills and variable morphology based on diet. They feed on a range of prey items from insects to medium-sized mammals, with a number feeding on carrion and a few feeding on fruit. The Accipitridae have a cosmopolitan distribution, being found on all the world's continents and a number of oceanic island groups. Some species are migratory.

Laridae is a family of seabirds in the order Charadriiformes that includes the gulls, terns and skimmers. It includes around 100 species arranged into 22 genera. They are an adaptable group of mostly aerial birds found worldwide.

Bandicoots are a group of more than 20 species of small to medium-sized, terrestrial marsupial omnivores in the order Peramelemorphia. They are endemic to the Australia–New Guinea region, including the Bismarck Archipelago and, marginally, in Indonesia (Seram).

Opisthocomidae is a family of birds, the only named family within the order Opisthocomiformes. The only living representative is the hoatzin which lives in the Amazon and the Orinoco delta in South America. Several fossil species have been identified, including one from Africa and one from Europe.

In biology, a type is a particular specimen of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralize the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage, a type was a taxon rather than a specimen.
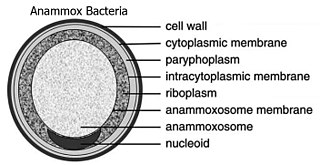
Planctomycetes are a phylum of aquatic bacteria and are found in samples of brackish, and marine and fresh water. They reproduce by budding. In structure, the organisms of this group are ovoid and have a holdfast, at the tip of a thin cylindrical extension from the cell body called the stalk, at the nonreproductive end that helps them to attach to each other during budding.

Croton is an extensive flowering plant genus in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. The plants of this genus were described and introduced to Europeans by Georg Eberhard Rumphius. The common names for this genus are rushfoil and croton, but the latter also refers to Codiaeum variegatum. The generic name comes from the Greek κρότος, which means "tick" and refers to the shape of the seeds of certain species.

Tapejara is a genus of Brazilian pterosaur from the Cretaceous Period. Tapejara crests consisted of a semicircular crest over the snout, and a bony prong which extended back behind the head.

Emys is a small genus of turtles in the family Emydidae. The genus is endemic to Europe and North America.

Tube-dwelling anemones or ceriantharians look very similar to sea anemones but belong to an entirely different subclass of anthozoans. They are solitary, living buried in soft sediments. Tube anemones live inside and can withdraw into tubes, which are composed of a fibrous material made from secreted mucus and threads of nematocyst-like organelles known as ptychocysts. Within the tubes of these ceriantharians, more than one polyp is present, which is an exceptional trait because species that create tube systems usually contain only one polyp per tube. Ceriantharians were formerly classified in the taxon Ceriantipatharia along with the black corals but have since been moved to their own subclass, Ceriantharia.

Aeolosaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now South America. Like most sauropods, it would have been a quadrupedal herbivore with a long neck and tail. Aeolosaurus is well known for a titanosaur, as it is represented by the remains of several individuals belonging to at least three species. However, like most titanosaurs, no remains of the skull are known. The holotype of Aeolosaurus rionegrinus consists of a series of seven tail vertebrae, as well as parts of both forelimbs and the right hindlimb. It was discovered in the Angostura Colorada Formation in Argentina, which dates from the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, about 83 to 74 million years ago.
Gondwanatitan was a titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur. Gondwanatitan was found in Brazil, at the time part of the southern supercontinent Gondwana, in the late Cretaceous Period. Like some other sauropods, Gondwanatitan was tall and ate tough shoots and leaves off of the tops of trees. G. faustoi's closest relative was Aeolosaurus.

Inga is a genus of small tropical, tough-leaved, nitrogen-fixing trees and shrubs, subfamily Mimosoideae. Inga's leaves are pinnate, and flowers are generally white. Many of the hundreds of species are used ornamentally.

Corallimorpharia is an order of marine cnidarians closely related to stony or reef building corals (Scleractinia). They occur in both temperate and tropical climates, although they are mostly tropical. Temperate forms tend to be very robust, with wide and long columns, whereas tropical forms tend to have very short columns with a wide oral disc and very short tentacles. The tentacles are usually arranged in rows radiating from the mouth. Many species occur together in large groups, although there are recorded instances of individuals. In many respects, they resemble the stony corals, except for the absence of a stony skeleton. Morphological and molecular evidence suggests that they are very closely related to stony corals.

The Solanaceae, or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and ornamentals. Many members of the family contain potent alkaloids, and some are highly toxic, but many—including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, bell and chili peppers—are used as food. The family belongs to the order Solanales, in the asterid group and class Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons). The Solanaceae consists of about 98 genera and some 2,700 species, with a great diversity of habitats, morphology and ecology.

















