| Blue nevus | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Blue neuronevus, dermal melanocytoma, nevus coeruleus, nevus bleu [1] |
 | |
| Blue nevus | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Single well-defined blue-black bump [2] |
| Complications | Rarely malignant transformation [3] |
| Types | Dendritic, cellular [2] |
| Causes | Unclear [3] |
| Diagnostic method | Visualisation, dermoscopy [4] |
| Differential diagnosis | Dermatofibroma, melanoma [3] [5] |
| Treatment | Monitoring, excision [3] |
| Prognosis | Good [3] |
| Frequency | Female>male [2] |
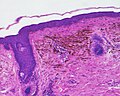
A blue nevus is a type of coloured mole, typically a single well-defined blue-black bump. [1] [2]
Contents
The blue colour is caused by the pigment being deep in the skin. [4]
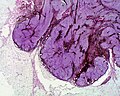
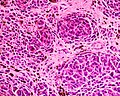
Diagnosis is by visualisation and dermoscopy. [4] A biopsy is sometimes performed, or the whole lesion surgically removed. [3] The outcome is generally good but there is a small chance of cancerous transformation. [3] Differential diagnosis includes dermatofibroma and melanoma. [3]
Blue nevi are more common in females than males. [2] It was first studied in 1906 by Tièche, a student of Josef Jadassohn. [6]