
Bosistoa is a genus of four species of tree in the family Rutaceae endemic to eastern Australia. They have simple or compound leaves arranged in opposite pairs and bisexual flowers arranged in panicles, each flower with five sepals, five white petals and ten stamens.

Acradenia euodiiformis, commonly known as yellow satinheart or bonewood, is a species of tree that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has mostly trifoliate leaves, the leaflets narrow elliptic to lance-shaped, with prominent oil glands, and panicles of white flowers. It grows in and near rainforest.

Karrabina benthamiana is a species of rainforest trees, growing naturally in north–eastern New South Wales and south–eastern Queensland, Australia. They have common names including red carabeen, leather jacket, brush mahogany, red bean, pink marara and brush mararie. This species used to be placed in the genus Geissois as Geissois benthamiana.

Bulbophyllum elisae, commonly known as the pineapple orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has crowded, wrinkled, pale green or yellowish clump-forming pseudobulbs, stiff, pale green to yellowish leaves and between three and twelve pale green to dark green flowers with a dark red to purple labellum. It usually grows in the tops of rainforest trees, on cliff faces or boulders.

Bosistoa floydii, commonly known as the five-leaf bosistoa or five-leaved bonewood, is a species of small rainforest tree that is endemic to north-eastern New South Wales. It has pinnate leaves usually with five elliptic leaflets, and panicles of tiny, creamy white flowers.

Bosistoa transversa, commonly known as the yellow satinheart, or three-leaved bosistoa, is a species of small to medium-sized rainforest tree that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has mostly pinnate leaves, usually with three leaflets and panicles of small white flowers.

Bosistoa pentacocca, commmonly known as ferny-leaf bosistoa, native almond or union nut, is a species of tree that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has pinnate leaves arranged in opposite pairs with between three and thirteen leaflets and panicles of small flowers arranged in leaf axils or on the ends of branches. It grows along streams in rainforest.

Caldcluvia paniculosa, known as the soft corkwood, is a rainforest tree of eastern Australia. It occurs from Ourimbah, Central Coast at 33° S to Eungella National Park in tropical Queensland. Other common names include corkwood, rose-leaf marara, brown alder and sugarbark. The generic placement of the species varies between sources, some preferring Ackama paniculosa.

Hakea rhombales, commonly known as walukara, is a shrub in the family Proteacea. It has red, pink or purple flowers and is endemic to Western Australia and the Northern Territory.

Corymbia torelliana, commonly known as cadaghi or cadaga, is a species of tree that is endemic to north Queensland. It has smooth, greenish grey to white bark, rough at the base of older trees, egg-shaped, heart-shaped or lance-shaped adult leaves, flower buds in groups of three or seven, white flowers and urn-shaped or shortened spherical fruit.

Zieria adenodonta, commonly known as the Wollumbin zieria, is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a dense, bushy shrub with leaves composed of three leaflets which are warty on the upper surface. In winter and early spring it has groups of five to eight flowers, each with four white petals, the groups usually shorter than the leaves.
Nervilia uniflora, commonly known as the red shield orchid, is a small terrestrial orchid found in northern Queensland. It has a single short-lived, pink or mauve flower. A dark green, heart-shaped leaf emerges at the base of the flowering stem after flowering.

Eulophia venosa, commonly known as the pointed corduroy orchid, is a plant in the orchid family and is native to India, parts of Southeast Asia as well as New Guinea and northern Australia. It is a deciduous, terrestrial orchid with one large and one small leaf and between six and twenty pale green or yellowish flowers with purple markings. It grows in rainforest and grassy forests.

Dendrobium baileyi, commonly known as the blotched gemini orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae and has arching stems and flowering stems with one or two spidery, yellow flowers with dark purple spots emerging from leaf axis. It grows in tropical North Queensland, New Guinea and the Solomon Islands.

Pomatocalpa macphersonii, commonly known as the blotched bladder orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid with thick, cord-like roots, between two and eight dark green, leathery leaves and up to thirty cup-shaped, yellow flowers with red blotches and a white labellum with red blotches. It usually grows on rainforest trees and is found in New Guinea and tropical North Queensland, Australia.
Saccolabiopsis armitii, commonly known as the spotted pitcher orchid, is an epiphytic orchid from the family Orchidaceae. It has a short stem, coarse, wiry roots, between three and six crowded, curved leaves and up to fifty yellowish green flowers with red markings and a white labellum. It usually grows in coastal scrub to rainforest in New Guinea and tropical North Queensland, Australia.

Sarcochilus ceciliae, commonly known as fairy bells, is a lithophytic orchid endemic to eastern Australia. It has up to ten channelled, spotted linear leaves and up to twenty pink flowers with a hairy labellum.

Boronia filifolia, commonly known as the slender boronia, is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It is a slender shrub with simple or pinnate leaves and pale to deep pink four-petalled flowers.

Boronia heterophylla, commonly known as red boronia or Kalgan boronia, is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, slender shrub with trifoliate leaves and deep pink to red, four-petalled flowers arranged singly in leaf axils.
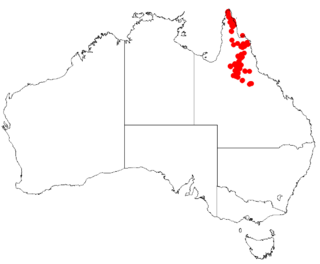
Boronia bowmanii is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to Queensland. It is an erect shrub with pinnate leaves and four-petalled flowers.


















