
The thylacine, also commonly known as the Tasmanian tiger or Tasmanian wolf, is an extinct carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmania and New Guinea. The thylacine died out in New Guinea and mainland Australia around 3,600–3,200 years ago, prior to the arrival of Europeans, possibly because of the introduction of the dingo, whose earliest record dates to around the same time, but which never reached Tasmania. Prior to European settlement, around 5,000 remained in the wild on Tasmania. Beginning in the nineteenth century, they were perceived as a threat to the livestock of farmers and bounty hunting was introduced. The last known of its species died in 1936 at Hobart Zoo in Tasmania. The thylacine is widespread in popular culture and is a cultural icon in Australia.

Phascolarctos is a genus of marsupials with one extant species, the koala Phascolarctos cinereus, an iconic animal of Australia. Several extinct species of the genus are known from fossil material, these were also large tree dwellers that browsed on Eucalyptus leaves.

Thylacoleo is an extinct genus of carnivorous marsupials that lived in Australia from the late Pliocene to the Late Pleistocene, often known as marsupial lions. They were the largest and last members of the family Thylacoleonidae, occupying the position of apex predator within Australian ecosystems. The largest and last species, Thylacoleo carnifex, approached the weight of a lioness. The estimated average weight for the species ranges from 101 to 130 kg.

Chaeropus, known as the pig-footed bandicoots, is a genus of small marsupials that became extinct during the 20th century. They were the only members of the family Chaeropodidae in order Peramelemorphia, with unusually thin legs, yet were able to move rapidly. Two recognised species inhabited dense vegetation on the arid and semiarid plains of Australia. The genus' distribution range was later reduced to an inland desert region, where it was last recorded in the 1950s; it is now presumed extinct.
Yalkaparidon is an extinct genus of Australian marsupials, first described in 1988 and known only from the Oligo-Miocene deposits of Riversleigh, northwestern Queensland, Australia.

Perameles is a genus of marsupials of the order Peramelemorphia. They are referred to as long-nosed bandicoots or barred bandicoots.

Palorchestes is an extinct genus of large terrestrial, herbivorous Australian marsupial of the family Palorchestidae, living from the Miocene through to the Late Pleistocene. Like other palorchestids, it had highly retracted nasal region suggesting that it had a prehensile lip, as well as highly unusual clawed forelimbs that were used to grasp vegetation.

Paludirex is an extinct genus of mekosuchine crocodylian from the Pliocene and Pleistocene of Australia. A large and robust semi-aquatic ambush hunter capable of attaining lengths of up to 5 m (16 ft), it was likely the top predator of Australia's waterways prior to the appearance of modern saltwater crocodiles. Two species are known, the smaller Paludirex gracilis and the larger Paludirex vincenti. A third as of yet unnamed species may have also existed.

The northern or sandy nail-tail wallaby is a species of macropod found across northern Australia on arid and sparsely wooded plains. The largest species of the genus Onychogalea, it is a solitary and nocturnal herbivorous browser that selects its food from a wide variety of grasses and succulent plant material. Distinguished by a slender and long-limbed form that resembles the typical and well known kangaroos, although their standing height is shorter, around half of one metre, and their weight is less than nine kilograms. As with some medium to large kangaroo species, such as Osphranter rufus, they have an unusual pentapedal motion at slow speeds by stiffening the tail for a fifth limb. When fleeing a disturbance, they hop rapidly with the tail curled back and repeatedly utter the sound "wuluhwuluh". Their exceptionally long tail has a broad fingernail-like protuberance beneath a dark crest of hair at its end, a peculiarity of the genus that is much broader than the other species. The name unguifera, meaning claw, is a reference to this extraordinary attribute, the purpose of which is unknown.
The Ugi naked-tailed rat is a poorly known and possibly extinct species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is known from a single specimen collected on Ugi Island in the Solomon Islands.
The Nullarbor dwarf bettong, Bettongia pusilla, was a potoroine marsupial that occurred in Australia. The animal is only known from skeletons found in caves of the Nullarbor Plain and is now classified as recently extinct.

Propleopus is an extinct genus of marsupials. Three species are known: P. chillagoensis from the Plio-Pleistocene, and P. oscillans and P. wellingtonensis from the Pleistocene. In contrast to most other kangaroos, and similar to their small extant relative, the musky rat-kangaroo, they were probably omnivorous.
Blinasaurus is a name of an extinct genus of prehistoric brachyopid found in Triassic geological formations of Australia. The type species is Platyceps wilkinsonii Stephens, 1887. The genus was established by John W. Cosgriff in 1969 to incorporate the type, discovered in New South Wales, and the author's new fossil species, Blinasaurus henwoodi, describing type material found in Blina Shale in the Kimberley region of northwest Australia.

Platycepsion wilksoni is an extinct species of prehistoric amphibian, known from partial skeleton deposited in shale at the Gosford Quarry site of the Terrigal Formation in Australia. This specimen may represent a larval stage, as denoted by the presence of external gills, making it the first evidence of larval development in stereospondyls.

Dukecynus is an extinct genus of meat-eating metatherian belonging to the order Sparassodonta, which lived in South America during the Middle Miocene (Laventan), between about 13.8 and 11.8 million years ago. The name of the genus meaning "Duke dog", for Duke University and the Greek word cynos, dog, for the pretended similarity of this animal with dogs. A single species known so far, Dukecynus magnus. The species name "magnus" derives from Latin for big, to reflect their great size.

Thylacosmilidae is an extinct family of metatherian predators, related to the modern marsupials, which lived in South America between the Miocene and Pliocene epochs. Like other South American mammalian predators that lived prior to the Great American Biotic Interchange, these animals belonged to the order Sparassodonta, which occupied the ecological niche of many eutherian mammals of the order Carnivora from other continents. The family's most notable feature are the elongated, laterally flattened fangs, which is a remarkable evolutionary convergence with other saber-toothed mammals like Barbourofelis and Smilodon.
Ambassis marianus, commonly known as the estuary perchlet, Ramsay's glassfish, estuary glassfish or glass perchlet, is a species of fish in the family Ambassidae. It is native to coastal eastern Australia. It gains its common name from its transparent appearance.
Macropus pan is a species of marsupial that existed during the Pliocene in Australia, known only from fossils located at several sites across Australia. The species is recognised as allied to the modern grey kangaroos, the western Macropus fuliginosus and eastern Macropus giganteus, in a clade initially named as subgenus Macropus (Macropus) Dawson & Flannery. The first description was provided by Charles W. De Vis in 1895, emerging from the author's examination of fossil material held at the Queensland Museum. Fossil specimens of Quanbun local fauna, named for a site in Western Australia, were also identified as this species. The origin of the type specimen was not recorded, although based on comparisons to material with a known provenance it is assumed to have excavated at Chinchilla, Queensland. A larger macropod than any modern species, the standing height was estimated to be over two metres.
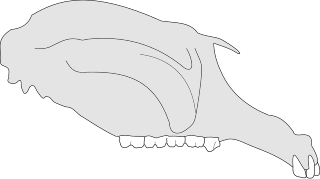
Propalorchestes is a fossil genus of palorchestid marsupial that existed in Australia during the Miocene epoch.

Peradectes is an extinct genus of small metatherian mammals known from the latest Cretaceous to Eocene of North and South America and Europe. The first discovered fossil of P. elegans, was one of 15 Peradectes specimens described in 1921 from the Mason pocket fossil beds in Colorado. The monophyly of the genus has been questioned.














