
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

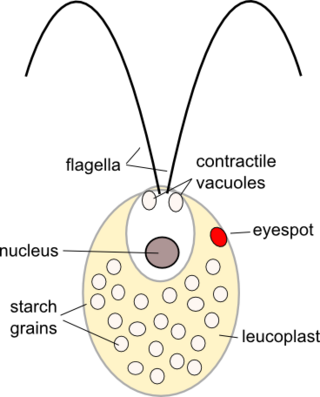
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 species of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.
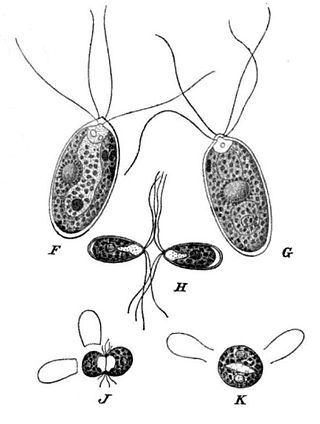
Polytoma is a genus of flagellates in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. Algae are similar to the genus Chlamydomonas, but lack chlorophyll and are colorless. Although they are not photosynthetic, they are grouped with the green algae because they are phylogenetically related to, and derived from, flagellate green algae.

Chlamydomonadaceae is a family of algae within the order Chlamydomonadales. Traditionally, it has been defined as containing single-celled flagellates with a cell wall.

Asterococcus is a genus of green algae in the order Chlamydomonadales. It is planktonic in freshwater ponds and lakes, or benthic within mires and swamps. It is a common and widespread genus, but is rarely abundant.
Asteromonas is a genus of green algae in the family Asteromonadaceae. It has been described from saline, marine, and brackish environments. It is closely related to the genus Dunaliella, another genus common in saline waters.
Carteria is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. Carteria are similar in morphology to the common genus Chlamydomonas and differ by having four, rather than two, flagella at the vegetative stage.
Characiochloris is a genus of green algae in the family Characiochloridaceae. Characiochloris is epiphytic on freshwater algae, or found in soil.

Characium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is very commonly found in freshwater habitats, where it is attached to phytoplankton or zooplankton.

Chlamydocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae.

Chloromonas is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. It is closely related to the model green algae, Chlamydomonas, and traditionally has been distinguished mainly through the absence of a pyrenoid.
Lobocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiosiphonaceae. It contains the single species Lobocharacium coloradoense. It has been isolated from a pond in Colorado, United States.

Lobomonas is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae, found in freshwater habitats. Although it is widely distributed, it is a rare genus.
Palmellopsis is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Palmellopsidaceae. They are either planktonic or attached to substrates in fresh water, or in aeroterrestrial habitats.

Sorastrum is a genus of green algae in the family Hydrodictyaceae. It is a component of the phytoplankton of freshwater ponds, lakes, and ditches. Sorastrum is common in tropical to temperate regions of the world, but due to its small size it is often overlooked.

Stephanosphaera is a genus of green algae in the family Haematococcaceae, containing the single species Stephanosphaera pluvialis. It forms colonies of flagellated cells. Although it was once placed in the family Volvocaceae, it is not closely related to them; its sister is the unicellular genus Balticola. The name comes from the Greek roots stephanos, meaning "crown", and sphaira, meaning "ball".
Vitreochlamys is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. It is sometimes known by the name Sphaerellopsis, published by Aleksandr Arkadievich Korshikov. However, that name is an illegitimate later homonym, preceded by SphaerellopsisM.C.Cooke. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats.
Follicularia is a genus of green algae, in the family Schizochlamydaceae. It is found in terrestrial habitats, mainly soil.
Korshikoviella is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae.

Apiocystis is a genus of algae belonging to the family Tetrasporaceae. It is found attached to freshwater aquatic algae or plants. The species of this genus are found in Europe and Northern America, and are widespread but generally uncommon.













