
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column, derived from the notochord. This includes all animals apart from the chordate subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelid, and cnidarians.

The Sipuncula or Sipunculida is a class containing about 162 species of unsegmented marine annelid worms. The name Sipuncula is from the genus name Sipunculus, and comes from the Latin siphunculus meaning a "small tube".

The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into segments, but echiurans have secondarily lost their segmentation. The majority of echiurans live in burrows in soft sediment in shallow water, but some live in rock crevices or under boulders, and there are also deep sea forms. More than 230 species have been described. Spoon worms are cylindrical, soft-bodied animals usually possessing a non-retractable proboscis which can be rolled into a scoop-shape to feed. In some species the proboscis is ribbon-like, longer than the trunk and may have a forked tip. Spoon worms vary in size from less than a centimetre in length to more than a metre.
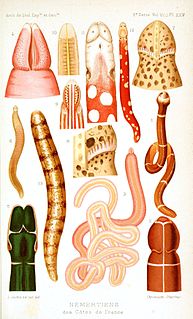
Nemertea is a phylum of animals also known as ribbon worms or proboscis worms. Most ribbon worms are very slim, usually only a few millimeters wide, although a few have relatively short but wide bodies. Many have patterns of yellow, orange, red and green coloration. The foregut, stomach and intestine run a little below the midline of the body, the anus is at the tip of the tail, and the mouth is under the front. A little above the gut is the rhynchocoel, a cavity which mostly runs above the midline and ends a little short of the rear of the body. All species have a proboscis which lies in the rhynchocoel when inactive but everts to emerge just above the mouth to capture the animal's prey with venom. A highly extensible muscle in the back of the rhynchocoel pulls the proboscis in when an attack ends. A few species with stubby bodies filter feed and have suckers at the front and back ends, with which they attach to a host.

The Polychaeta, also known as the bristle worms or polychaetes, are a paraphyletic class of annelid worms, generally marine. Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm and the sandworm or clam worm Alitta.

A larva is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.

The semipalmated sandpiper is a very small shorebird. The genus name is from Ancient Greek kalidris or skalidris, a term used by Aristotle for some grey-coloured waterside birds. The specific pusilla is Latin for "very small".

The Clitellata are a class of annelid worms, characterized by having a clitellum - the 'collar' that forms a reproductive cocoon during part of their life cycles. The clitellates comprise around 8,000 species. Unlike the class of Polychaeta, they do not have parapodia and their heads are less developed.

Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land, as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water, and amphibians, which rely on a combination of aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Some groups of insects are terrestrial, such as ants, butterflies, earwigs, cockroaches, grasshoppers and many others, while other groups are partially aquatic, such as mosquitoes and dragonflies, which pass their larval stages in water.

Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from 8.5 micrometres (0.00033 in) to 33.6 metres (110 ft). They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology.

The Anisakidae are a family of intestinal nematodes (roundworms). The larvae of these worms can cause anisakiasis when ingested by humans, in raw or insufficiently cooked fish.

Pupa is a genus of small sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Acteonidae.

Euspira is a genus of medium-sized sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the subfamily Polinicinae of the family Naticidae, the moon snails.

Tectonatica pusilla is a species of predatory sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Naticidae, the moon snails.
Aeolosoma is a genus of minute annelid worms, variously attributed either to oligochaetes or polychaetes. Unlike most polychaetes, they reside in freshwater environments in various parts of the world.

The annelids, also known as the ringed worms or segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments.
The Aeolosomatidae is a family of very small, aquatic annelid worms, between 0.3 and 10 mm in length and 0.04-0.06 mm in diameter. About 30 species have been described in three genera. These worms are known as suction-feeding worms and occupy freshwater, brackish, and saltwater habitats. They are bottom and sediment dwellers, inhabiting spaces around aquatic plants and the detritus-rich sands and sediments of freshwater habitats (microfauna)

Semimytilus algosus is a species of mussels. A common name for this species is Bisexual mussel, or Dwarf mussel. It is the first species where trioecy was reported in the phylum Mollusca.

Salvatoria clavata is a species of Annelida in the family Syllidae.The species is similar to Brania pusilla but is a bit longer measuring in about 2mm to 3mm, individuals in this species can even grow to 10 mm. They have parental care. It has an acrosome shaped like a beaker.

Aepophilus is a monotypic genus of bugs, containing the species Aepophilus bonnairei in the monotypic subfamily Aepophilinae in the monotypic family Aepophilidae of the infraorder Leptopodomorpha. It is found on the Atlantic coast of Europe.

















