Bromelain is an enzyme extract derived from the stems of pineapples, although it exists in all parts of the fresh plant and fruit. The extract has a history of folk medicine use. As a culinary ingredient, it may be used as a meat tenderizer.
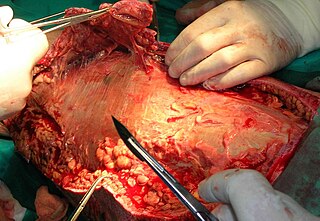
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira and others, is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug and monoclonal antibody used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and uveitis. It is administered by subcutaneous injection. It works by inactivating tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα).

Imiquimod, sold under the brand name Aldara among others, is a medication that acts as an immune response modifier that is used to treat genital warts, superficial basal cell carcinoma, and actinic keratosis.
Mepolizumab, sold under the brand name Nucala by GlaxoSmithKline, is a humanized monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of severe eosinophilic asthma, eosinophilic granulomatosis, and hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES). It recognizes and blocks interleukin-5 (IL-5), a signalling protein of the immune system.
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product that is almost an identical copy of an original product that is manufactured by a different company. Biosimilars are officially approved versions of original "innovator" products and can be manufactured when the original product's patent expires. Reference to the innovator product is an integral component of the approval.

Rilpivirine, sold under the brand names Edurant and Rekambys, is a medication, developed by Tibotec, used for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is a second-generation non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) with higher potency, longer half-life and reduced side-effect profile compared with older NNRTIs such as efavirenz.

Pradofloxacin, sold under the brand name Veraflox among others, is a third-generation enhanced spectrum veterinary antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone class. It was developed by Elanco Animal Health GmbH and received approval from the European Commission in April 2011, for prescription-only use in veterinary medicine for the treatment of bacterial infections in dogs and cats.
Proteases are in use, or have been proposed or tried, for a number of purposes related to medicine or surgery. Some preparations involving protease have undergone successful clinical trials and have regulatory authorization; and some further ones have shown apparently useful effects in experimental medical studies. Proteases have also been used by proponents of alternative therapies, or identified in materials of traditional or folk medicine. A serine protease of human origin, activated protein C, was produced in recombinant form and marketed as Drotrecogin alfa and licensed for intensive-care treatment of severe sepsis. It was voluntarily withdrawn by the manufacturer in 2011 after being shown to be ineffective.

Ingenol mebutate, sold under the brand name Picato, is a substance that is found in the sap of the plant Euphorbia peplus, commonly known as petty spurge, and is an inducer of cell death. This compound was isolated first from this plant in 2000. A gel formulation of the drug has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the topical treatment of actinic keratosis. Two different strengths of the gel have been approved for use on either the face and scalp (0.015%) or the trunk and extremities (0.05%), respectively. In 2020 the drug was withdrawn from the market in the EU.

Dabrafenib, sold under the brand name Tafinlar among others, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of cancers associated with a mutated version of the gene BRAF. Dabrafenib acts as an inhibitor of the associated enzyme B-Raf, which plays a role in the regulation of cell growth.

Cabotegravir, sold under the brand name Vocabria among others, is a antiretroviral medication used for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is available in the form of tablets and as an intramuscular injection, as well as in an injectable combination with rilpivirine under the brand name Cabenuva.
Asfotase alfa, sold under the brand name Strensiq, is a medication used in the treatment of people with perinatal/infantile- and juvenile-onset hypophosphatasia.

Ertugliflozin, sold under the brand name Steglatro, is a medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Atazanavir/cobicistat, sold under the brand name Evotaz, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS. It contains atazanavir and cobicistat. Atazanavir is an HIV protease inhibitor and cobicistat is an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes of the CYP3A family.
Bempedoic acid, sold under the brand name Nexletol among others, is a medication for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia.
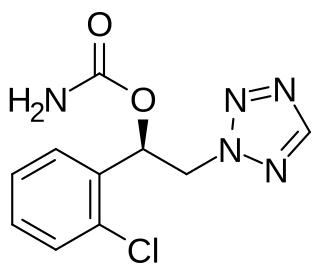
Cenobamate, sold under the brand names Xcopri (US) and Ontozry (EU), is a medication used for the treatment of partial-onset seizures, a kind of epilepsy, in adults. It is taken by mouth.
Avalglucosidase alfa, sold under the brand name Nexviazyme, is an enzyme replacement therapy medication used for the treatment of glycogen storage disease type II.
Spesolimab, sold under the brand name Spevigo, is a monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP). It is an interleukin-36 receptor (IL-36R) antagonist. It is given via injection into a vein.

Birch triterpenes, sold under the brand name Filsuvez, is an extract of birch bark used as a topical medication for the treatment of epidermolysis bullosa. The active ingredients are triterpenes extracted from the outer bark of silver birch and downy birch.









