The Gulf of Saint Lawrence is the outlet of the North American Great Lakes via the Saint Lawrence River into the Atlantic Ocean. The gulf is a semienclosed sea, covering an area of about 226,000 square kilometres (87,000 sq mi) and containing about 34,500 cubic kilometres (8,300 cu mi) of water, which results in an average depth of 152 metres (499 ft).

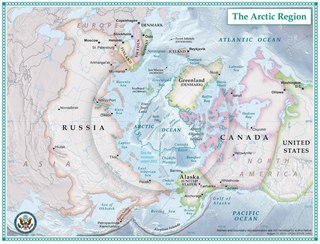
Banks Island is one of the larger members of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Situated in the Inuvik Region, and part of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region, of the Northwest Territories, it is separated from Victoria Island to its east by the Prince of Wales Strait and from the mainland by Amundsen Gulf to its south. The Beaufort Sea lies to its west, and to its northeast M'Clure Strait separates the island from Prince Patrick Island and Melville Island.

The Gulf of California is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately 4,000 km (2,500 mi). Rivers which flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado, Fuerte, Mayo, Sinaloa, Sonora, and the Yaqui. The gulf's surface area is about 160,000 km2 (62,000 sq mi). Depth soundings in the gulf have ranged from fording depth at the estuary near Yuma, Arizona, to in excess of 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) in the deepest parts.

Hailuoto is an island and a municipality in Northern Ostrobothnia region, Finland. The population of Hailuoto is 976 and the municipality covers an area of 200.53 km2 (77.43 sq mi) of which 1.70 km2 (0.66 sq mi) is inland water. The population density is 4.87/km2 (12.6/sq mi).

Amundsen Gulf is a gulf located in the Northwest Territories, Canada, between Banks Island and Victoria Island and the mainland. It is approximately 250 mi (400 km) in length and about 93 mi (150 km) across where it meets the Beaufort Sea.

Akpatok Island is one of the uninhabited Canadian Arctic islands in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is the largest island in Ungava Bay on the northern coast of Quebec. The island is named for the Akpat, the thick-billed murre, which live on ledges along the limestone cliffs surrounding the island.
Jenny Lind Island is a small island 420 km2 (160 sq mi) in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. The island is located in the Queen Maud Gulf, about 120 km (75 mi) southeast of Cambridge Bay.
Crown Prince Frederik Island is an island in Nunavut, Canada. It is located off the southern coast of western Baffin Island, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region's side of the Gulf of Boothia. It has an area of 401 km2 (155 sq mi).
The Twin Islands are similarly shaped Arctic islands in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. They are located in central James Bay, 56 km (35 mi) north east of Akimiski Island, and 58 km (36 mi) west of Quebec. The group includes North Twin and South Twin islands.

South Tweedsmuir Island is one of the Canadian arctic islands located in Foxe Basin, off the southwest coast of Baffin Island, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. Foley Island is to the north, North Tweedsmuir Island is to the northwest, Prince Charles Island is to the west, and Air Force Island is to the south.
The Minto Islands are a Canadian Arctic island group in the Nunavut Territory. The islands lie in the western portion of Queen Maud Gulf, between Kent Peninsula on Nunavut's mainland, and Melbourne Island. Back Point, Victoria Island is approximately 47.9 km (29.8 mi) to the north.
Berlinguet Inlet is a body of water within the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It runs west-east at Admiralty Inlet's southern end, separated from Berlinguet Bay, which opens into the Gulf of Boothia, by a 1.5 km (0.93 mi) isthmus. Baffin Island's Brodeur Peninsula is to the north.
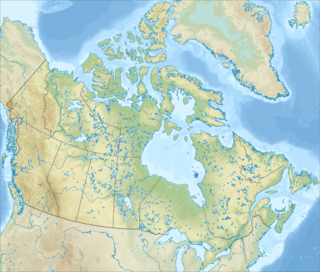
The Queen Maud Gulf Migratory Bird Sanctuary is Canada's largest federally owned protected area, encompassing some 61,765 km2 (23,848 sq mi) of the Arctic Circle coastline. 6,710 km2 (2,590 sq mi) are marine, and 55,055 km2 (21,257 sq mi) are terrestrial.

Baillarge Bay is an Arctic waterway in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is the second waterway to press eastward from Admiralty Inlet into Baffin Island. The southern point of its mouth is named Ship Point.
Boatswain Bay is an uninhabited waterway in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It extends eastward from James Bay into the headland, a part of Quebec.
Cape Liddon is an uninhabited headland on Devon Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located on the southwestern coast of the island at Radstock Bay.
Cape Vera is an uninhabited headland on Devon Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. Protruding off the island's northwestern Colin Archer Peninsula, it faces Jones Sound. Often, a polynya forms in the Cardigan Strait, a waterway that separates the cape from North Kent Island.
The uninhabited Cheyne Islands are members of the Queen Elizabeth Islands and the Canadian Arctic Archipelago in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. The group is made up of three islands known as North Island, Middle Island, and South Island. Located approximately 5 km (3.1 mi) off eastern Bathurst Island, they are situated near Reindeer Bay within western Penny Strait.
Cape Parry is a headland in Canada's Northwest Territories. Located at the northern tip of the Parry Peninsula, it projects into Amundsen Gulf. The nearest settlement is Paulatuk, 100 km (62 mi) to the south, and Fiji Island is located 9 km (5.6 mi) to the west. Cape Parry was formerly accessible through Cape Parry Airport that was located at the Distant Early Warning Line. The airport was listed as abandoned after the closure of the DEW line site.
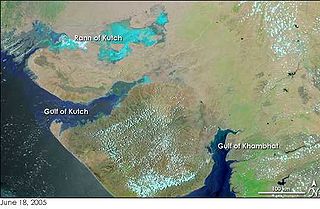
The Gulf of Khambhat, also known as the Gulf of Cambay, is a bay on the Arabian Sea coast of India, bordering the state of Gujarat. The Gulf of Khambhat is about 200 km (120 mi) long, about 20 km (12 mi) wide in the north and up to 70 km (43 mi) wide in the south. Major rivers draining Gujarat are the Narmada, Tapti, Mahi and Sabarmati that form estuaries in the gulf.