Bass fishing is the activity of angling for the North American gamefish known colloquially as the black bass. There are numerous black bass species considered as gamefish in North America, including largemouth bass, smallmouth bass, spotted bass or Kentucky bass, and Guadalupe bass. Black bass are members of the sunfish (Centrarchidae) family.

The Lehigh River, a tributary of the Delaware River, is a 109-mile-long (175 km) river located in eastern Pennsylvania, in the United States. Part of the Lehigh, along with a number of its tributaries, is designated a Pennsylvania Scenic River by the state's Department of Conservation and Natural Resources. "Lehigh" is an Anglicization of the Lenape name for the river, Lechewuekink, meaning "where there are forks".

Rice Lake is a lake located in Northumberland and Peterborough counties in south-eastern Ontario. The lake is located south of the city of Peterborough, and the Kawartha Lakes and north of Cobourg. It is part of the Trent-Severn Waterway, which flows into the lake by the Otonabee and out via the Trent. The lake is 28 kilometres (17 mi) long and 5 km wide. Its maximum depth is 10m, with a surface water level at 187 m above sea level, raised to its present height by the Hastings Dam, built in the 19th century as part of the Trent-Severn canal system. Natives called it Pemadashdakota or "lake of the burning plains".

Lake Scugog is an artificially flooded lake in Scugog, Regional Municipality of Durham and the unitary city of Kawartha Lakes in central Ontario, Canada. It lies between the communities of Port Perry and Lindsay. The lake has been raised and lowered several times over its history. Though not technically part of the Kawartha lakes due to its shallow depths, it is often geographically linked to them. Its sole outflow, the Scugog River, connects to Sturgeon Lake. Lake Scugog is in the Great Lakes Basin and forms part of the Trent–Severn Waterway.

Lake Doré is a freshwater lake in the township of North Algona-Wilberforce, Renfrew County, Ontario, Canada, about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) north of the community of Eganville in the neighbouring township of Bonnechere Valley.

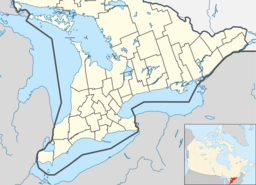
Balsam Lake is a lake in the City of Kawartha Lakes in Central Ontario, Canada. It is in the Great Lakes Basin, is one of the lakes of the Kawartha Lakes, and is at the summit of the Trent–Severn Waterway.
Tangamong Lake is a lake in the Lake Ontario drainage basin in the township of Wollaston, Hastings County in eastern Ontario, Canada, at the easternmost end of the Kawartha Lakes chain. It is also part of area of responsibility of the Crowe Valley Conservation Authority.

Salerno Lake, formerly Devil's Lake, is a lake in the municipalities of Highlands East and Minden Hills in Haliburton County in Central Ontario, Canada. The lake is part of the Kawartha Lakes, and lies in the Great Lakes Basin. It is part of cottage country approximately a 2 1⁄2-hour drive away from Toronto.

The Queen Elizabeth II Wildlands Provincial Park is a provincial park in south-central Ontario, Canada, between Gravenhurst and Minden. The park, named for Elizabeth II, Queen of Canada, is 33,505 hectares in size, making it the second largest park south of Algonquin Park, but it has a fragmented shape as a result of many private lands within its boundary.

Burnt River is a hamlet located in the middle of the former Township of Somerville, in the City of Kawartha Lakes, Ontario, Canada. The community is on the Burnt River.

Stony Lake is a lake in Peterborough County in Central Ontario, Canada. There are three interconnected lakes which together are known as Stony or Stoney Lake. Stoney Lake forms the eastern end of the Kawartha lakes region. It is primarily a summer cottage area but there are many permanent residences on the lakes.
The Indian Lake Chain is a tourism designation given to a series of interconnected lakes located northwest of the community of Vermilion Bay in Kenora District, Ontario, Canada. The designation takes its name from Indian Lake that is part of the series. According to maps published by resorts located on the lakes, the Indian Lake Chain consists of ten lakes: Little Boulder Lake, Boulder Lake, Cobble Lake, Bladder Lake, Big Moose Lake, Little Moose Lake, Whitney Lake, Edward Lake, Indian Lake and Forrest Lake. However, the Atlas of Canada shows only seven lakes, as Little Boulder, Boulder, Cobble and Bladder Lakes are all simply designated "Cobble Lake". The surface elevation of the lakes is approximately 377 metres (1,237 ft), and the water level is maintained by the Forest Lake Dam..
Spednic Lake is a mesotrophic lake in the Chiputneticook Lakes chain along the Canada–United States border between the state of Maine and the province of New Brunswick that is best known for its bass fishing. Sometimes it is viewed as the headwaters of the St. Croix River, sometimes a lake further up the chain is considered the headwaters. The international border runs through the lake. A northeastern arm of the lake, located entirely in Canada, retains the name Palfrey Lake. Prior to dam construction that expanded Spednic Lake they were separate lakes, but now they are hydrologically and ecologically a single combined lake.
Eels Lake is a lake located between the Kawartha Lakes and Haliburton Highlands region of Ontario, Canada.

Four Mile Lake is a lake in the city of Kawartha Lakes in Central Ontario, Canada. The lake is 3.56 kilometres (2.21 mi) northeast of Coboconk, Ontario and 2.08 kilometres (1.29 mi) west of Burnt River. It is one of the Kawartha Lakes series of lakes and is in the Great Lakes Basin.

Pigeon Lake is a lake in Ontario, Canada. It is one of a group of lakes called the Kawartha lakes, which are the namesake of the city of Kawartha Lakes, and the Trent-Severn Waterway. Pigeon Lake is 27 km long and up to 3 km wide.

Victoria Road is an unincorporated community in the Canadian province of Ontario, located within the single-tier municipality of Kawartha Lakes. The village was built around a station on the Toronto and Nipissing Railway, which was constructed in 1872. The station — the second last on the line — served the community and area until the last train passed through in 1965, after which the tracks were lifted.

Canal Lake is a lake of Ontario, Canada, situated in the City of Kawartha Lakes. The lake is triangular, roughly 8.4 kilometres (5.2 mi) long and 2.6 kilometres (1.6 mi) at its widest point, with an area of 2,136 acres (864 ha). The depth ranges from 4.44 feet (1.35 m) to a max depth of 15 feet (4.6 m). Canal Lake is a medium size lake with a large diversity of fishing spots.