
Neurospora crassa is a type of red bread mold of the phylum Ascomycota. The genus name, meaning 'nerve spore' in Greek, refers to the characteristic striations on the spores. The first published account of this fungus was from an infestation of French bakeries in 1843.

Byrsonima crassifolia is a species of flowering plant in the family Malpighiaceae, native to tropical America. Common names used in English include nance, maricao cimun, craboo, and golden spoon. In Jamaica it is called hogberry.

Malpighia is a genus of flowering plants in the nance family, Malpighiaceae. It contains 108 species of shrubs or small trees, all of which are native to the American tropics, ranging from Texas through Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean to Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador. The generic name honours Marcello Malpighi, a 17th-century Italian physician and botanist. The species grow to 1–6 m (3.3–19.7 ft) tall, with a dense, often thorny crown. The leaves are evergreen, simple, 0.5–15 cm (0.20–5.91 in) long, with an entire or serrated margin. The flowers are solitary or in umbels of two to several together, each flower 1–2 cm (0.39–0.79 in) diameter, with five white, pink, red, or purple petals. The fruit is a red, orange, or purple drupe, containing two or three hard seeds. M. emarginata, the acerola, is cultivated for its sweet and juicy fruits, which are very rich in vitamin C.

Malpighiaceae is a family of flowering plants in the order Malpighiales. It comprises about 73 genera and 1315 species, all of which are native to the tropics and subtropics. About 80% of the genera and 90% of the species occur in the New World and the rest in the Old World.
HomoloGene, a tool of the United States National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), is a system for automated detection of homologs among the annotated genes of several completely sequenced eukaryotic genomes.

Byrsonima is one of about 75 genera in the Malpighiaceae, a family of flowering plants in the order Malpighiales. In particular in American English, they are known as locustberries. Another widely seen common name is serrets or serrettes.
Byrsonima horneana is a species of plant in the Malpighiaceae family. It is endemic to Puerto Rico.
Byrsonima ophiticola is a species of plant in the Malpighiaceae family. It is endemic to Puerto Rico.

Crassa unitella is a moth of the family Oecophoridae. It is known from most of Europe.
Coleophora crassa is a moth of the family Coleophoridae.

Allocasuarina crassa, commonly known as Cape Pillar sheoak, is a species of flowering plant in the family Casuarinaceae and is endemic to a small area in far south-eastern Tasmania. It is a low shrub to small tree that is monoecious or dioecious, with spreading to erect branchlets up to 170 mm (6.7 in) long, the leaves reduced to scales in whorls of seven to ten, the fruiting cones 15–34 mm (0.6–1 in) long containing winged seeds (samaras) 5–8 mm (0.2–0.3 in) long.
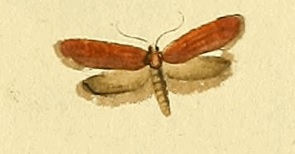
Crassa tinctella, the tinted tubic, is a moth of the family Oecophoridae. It was described by Jacob Hübner in 1796. It is found in most of Europe, except Ireland, the Iberian Peninsula and most of the Balkan Peninsula.

Byrsonima lucida is a species of plant in the Malpighiaceae family. It is endemic to islands in the Caribbean and to the U.S. state of Florida. It is a shrub or small tree, and produces pink flowers. Its natural habitat is hammocks in dry limestone rocklands, and in sandy pine-palm woods.

Byrsonima intermedia is a species of plant in the Malpighiaceae family. It is found in Brazil and Paraguay.

Byrsonima basiloba is a species of plant in the Malpighiaceae family. It is found in Brazil.

Byrsonima coccolobifolia is a species of plant in the Malpighiaceae family. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela.

Byrsonima sericea is a species of semi-deciduous tree native to Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Guyana, and French Guiana.
Byrsonima wadsworthii is a rare plant known only to the Luquillo Mountains and the Cordillera Central in Northeastern Puerto Rico. First described by botanist Elbert Luther Little, the plant was named in 1953 in honor of Dr. Frank H. Wadsworth, former supervisor of the Caribbean National Forest and first director of the International Institute of Tropical Forestry. The first recorded botanical collection was by Claud L. Horn of the Forest Service in 1934.












