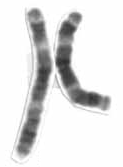
Chromosome 3 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 3 spans 201 million base pairs and represents about 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.

RING finger protein 38 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNF38 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase, Intestinal cell kinase or ICK is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ICK gene.

Zinc finger protein 44 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF44 gene.

Zinc finger protein 19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF19 gene.

Zinc finger protein 280D, also known as Suppressor Of Hairy Wing Homolog 4, SUWH4, Zinc Finger Protein 634, ZNF634, or KIAA1584, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF280D gene located on chromosome 15q21.3.

UPF0687 protein C20orf27 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C20orf27 gene. It is expressed in the majority of the human tissues. One study on this protein revealed its role in regulating cell cycle, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis via promoting the activation of NFĸB pathway.

Iroquois-class homeodomain protein IRX-1, also known as Iroquois homeobox protein 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IRX1 gene. All members of the Iroquois (IRO) family of proteins share two highly conserved features, encoding both a homeodomain and a characteristic IRO sequence motif. Members of this family are known to play numerous roles in early embryo patterning. IRX1 has also been shown to act as a tumor suppressor gene in several forms of cancer.

Transmembrane protein 242 (TMEM242) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM242 gene. The tmem242 gene is located on chromosome 6, on the long arm, in band 2 section 5.3. This protein is also commonly called C6orf35, BM033, and UPF0463 Transmembrane Protein C6orf35. The tmem242 gene is 35,238 base pairs long, and the protein is 141 amino acids in length. The tmem242 gene contains 4 exons. The function of this protein is not well understood by the scientific community. This protein contains a DUF1358 domain.

Zinc finger protein 184, also known as ZNF184, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF184 gene on chromosome 6. It was first identified by Goldwurm et al. in 1996.

WW and C2 domain containing 2 (WWC2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WWC2 gene (4q35.1). Though function of WWC2 remains unknown, it has been predicted that WWC2 may play a role in cancer.

Zinc finger protein 226 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF226 gene.

C8orf48 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C8orf48 gene. C8orf48 is a nuclear protein specifically predicted to be located in the nuclear lamina. C8orf48 has been found to interact with proteins that are involved in the regulation of various cellular responses like gene expression, protein secretion, cell proliferation, and inflammatory responses. This protein has been linked to breast cancer and papillary thyroid carcinoma.

Chromosome 3 open reading frame 67 or C3orf67 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the gene C3orf67. The function of C3orf67 is not yet fully understood.

C8orf34 is a protein that, in Homo sapiens, is encoded by the C8orf34 gene. Aliases for C8orf34 include vestibule-1 or VEST-1. Within the cell, C8orf34 is localized to the nucleus and nucleoli where it may play a role in the regulation of gene expression as well as the cell cycle.

Chromosome 1 Opening Reading Frame 94 or C1orf94 is a protein in human coded by the C1orf94 gene. The function of this protein is still poorly understood.

C11orf98 is a protein-encoding gene on chromosome 11 in humans of unknown function. It is otherwise known as c11orf48. The gene spans the chromosomal locus from 62,662,817-62,665,210. There are 4 exons. It spans across 2,394 base pairs of DNA and produces an mRNA that is 646 base pairs long.

C12orf29 is a protein that in humans is encoded by chromosome 12 open reading frame 29. The gene is ubiquitously expressed in various tissues. The protein has 325 amino acids. The biological process of C12orf29 has been annotated as hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation. The molecular and cellular functions of C12orf29 gene have not yet well understood by the scientific community.

Chromosome 12 Open Reading Frame 50 (C12orf50) is a protein-encoding gene which in humans encodes for the C12orf50 protein. The accession id for this gene is NM_152589. The location of C12orf50 is 12q21.32. It covers 55.42 kb, from 88429231 to 88373811, on the reverse strand. Some of the neighboring genes to C12orf50 are RPS4XP15, LOC107984542, and C12orf29. RPS4XP15 is upstream C12orf50 and is on the same strand. LOC107984542 and C12orf29 are both downstream. LOC107984542 is on the opposite strand while C12orf29 is on the same strand. C12orf50 has six isoforms. This page is focusing on isoform X1. C12orf50 isoform X1 is 1711 nucleotides long and has a protein with a length of 414 aa.

C2orf80 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the c2orf80 gene. The gene c2orf80 also goes by the alias GONDA1. In humans, c2orf80 is exclusively expressed in the brain. While relatively little is known about the function of c2orf80, medical studies have shown a strong association between variations in c2orf80 and IDH-mutant gliomas, 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis, and a possible association with blood pressure.



























