
George Hoyt Whipple was an American physician, pathologist, biomedical researcher, and medical school educator and administrator. Whipple shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1934 with George Richards Minot and William Parry Murphy "for their discoveries concerning liver therapy in cases of anemia". This makes Whipple the first of several Nobel laureates affiliated with the University of Rochester.

Hemolysis or haemolysis, also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid. Hemolysis may occur in vivo or in vitro.

Anemia or anaemia is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. The name is derived from Ancient Greek: ἀναιμία anaimia, meaning 'lack of blood', from ἀν- an-, 'not' and αἷμα haima, 'blood'. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe.

A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may include fatigue, shortness of breath, bleeding disorders, anemia, or frequent infections. Some types may develop into acute myeloid leukemia.
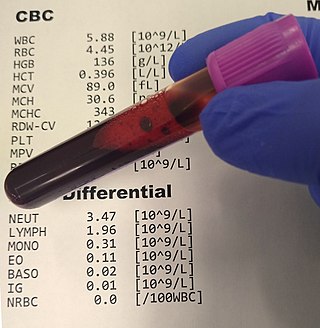
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, the concentration of hemoglobin, and the hematocrit. The red blood cell indices, which indicate the average size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells, are also reported, and a white blood cell differential, which counts the different types of white blood cells, may be included.

Babesiosis or piroplasmosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with a eukaryotic parasite in the order Piroplasmida, typically a Babesia or Theileria, in the phylum Apicomplexa. Human babesiosis transmission via tick bite is most common in the Northeastern and Midwestern United States and parts of Europe, and sporadic throughout the rest of the world. It occurs in warm weather. People can get infected with Babesia parasites by the bite of an infected tick, by getting a blood transfusion from an infected donor of blood products, or by congenital transmission . Ticks transmit the human strain of babesiosis, so it often presents with other tick-borne illnesses such as Lyme disease. After trypanosomes, Babesia is thought to be the second-most common blood parasite of mammals. They can have major adverse effects on the health of domestic animals in areas without severe winters. In cattle the disease is known as Texas cattle fever or redwater.

A blood smear, peripheral blood smear or blood film is a thin layer of blood smeared on a glass microscope slide and then stained in such a way as to allow the various blood cells to be examined microscopically. Blood smears are examined in the investigation of hematological (blood) disorders and are routinely employed to look for blood parasites, such as those of malaria and filariasis.

Pernicious anemia is a disease in which not enough red blood cells are produced due to a deficiency of vitamin B12. Those affected often have a gradual onset. The most common initial symptoms are feeling tired and weak. Other symptoms of anemia may include shortness of breath, lightheadedness, headaches, sore red tongue, cold hands and feet, pale or yellow skin, chest pain, and an irregular heartbeat. The digestive tract may also be disturbed giving symptoms that can include nausea and vomiting, heartburn, upset stomach and loss of appetite. Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency may include decreased ability to think, numbness in the hands and feet, memory problems, blurred vision, trouble walking, poor balance, muscle weakness, decreased smell and taste, poor reflexes, clumsiness, depression, and confusion. Without treatment, some of these problems may become permanent.

Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonly occurs within the spleen, but also can occur in the reticuloendothelial system or mechanically. Hemolytic anemia accounts for 5% of all existing anemias. It has numerous possible consequences, ranging from general symptoms to life-threatening systemic effects. The general classification of hemolytic anemia is either intrinsic or extrinsic. Treatment depends on the type and cause of the hemolytic anemia.

Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder of the enzyme pyruvate kinase which affects the survival of red blood cells. Both autosomal dominant and recessive inheritance have been observed with the disorder; classically, and more commonly, the inheritance is autosomal recessive. Pyruvate kinase deficiency is the second most common cause of enzyme-deficient hemolytic anemia, following G6PD deficiency.

Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. An anemia is a red blood cell defect that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic anemia results from inhibition of DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. When DNA synthesis is impaired, the cell cycle cannot progress from the G2 growth stage to the mitosis (M) stage. This leads to continuing cell growth without division, which presents as macrocytosis. Megaloblastic anemia has a rather slow onset, especially when compared to that of other anemias. The defect in red cell DNA synthesis is most often due to hypovitaminosis, specifically vitamin B12 deficiency or folate deficiency. Loss of micronutrients may also be a cause.
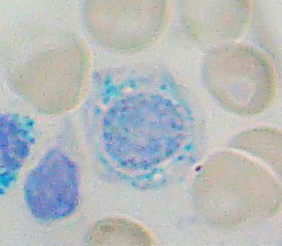
Sideroblastic anemia, or sideroachrestic anemia, is a form of anemia in which the bone marrow produces ringed sideroblasts rather than healthy red blood cells (erythrocytes). In sideroblastic anemia, the body has iron available but cannot incorporate it into hemoglobin, which red blood cells need in order to transport oxygen efficiently. The disorder may be caused either by a genetic disorder or indirectly as part of myelodysplastic syndrome, which can develop into hematological malignancies.

Alpha-thalassemia is a form of thalassemia involving the genes HBA1 and HBA2. Thalassemias are a group of inherited blood conditions which result in the impaired production of hemoglobin, the molecule that carries oxygen in the blood. Normal hemoglobin consists of two alpha chains and two beta chains; in alpha-thalassemia, there is a quantitative decrease in the amount of alpha chains, resulting in fewer normal hemoglobin molecules. Furthermore, alpha-thalassemia leads to the production of unstable beta globin molecules which cause increased red blood cell destruction. The degree of impairment is based on which clinical phenotype is present.
Heinz bodies are inclusions within red blood cells composed of denatured hemoglobin. They are not visible with routine blood staining techniques, but can be seen with supravital staining. The presence of Heinz bodies represents damage to hemoglobin and is classically observed in G6PD deficiency, a genetic disorder that causes hemolytic anemia. In veterinary medicine, Heinz bodies may be seen following the consumption of foods containing thiosulfate and propylene glycol compounds by cats, dogs and certain primates.

Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have few or absent symptoms. In moderate deficiency, feeling tired, anemia, soreness of the tongue, mouth ulcers, breathlessness, feeling faint, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, pallor, hair loss, decreased ability to think and severe joint pain and the beginning of neurological symptoms, including abnormal sensations such as pins and needles, numbness and tinnitus may occur. Severe deficiency may include symptoms of reduced heart function as well as more severe neurological symptoms, including changes in reflexes, poor muscle function, memory problems, blurred vision, irritability, ataxia, decreased smell and taste, decreased level of consciousness, depression, anxiety, guilt and psychosis. If left untreated, some of these changes can become permanent. Temporary infertility reversible with treatment, may occur. In exclusively breastfed infants of vegetarian mothers who don't take B12 supplements as advised, undetected and untreated deficiency can lead to poor growth, poor development, and difficulties with movement.

Pappenheimer bodies are abnormal basophilic granules of iron found inside red blood cells on routine blood stain. They are a type of inclusion body composed of ferritin aggregates, or mitochondria or phagosomes containing aggregated ferritin. They appear as dense, blue-purple granules within the red blood cell and there are usually only one or two, located in the cell periphery. They stain on a Romanowsky stain because clumps of ribosomes are co‐precipitated with the iron‐containing organelles.

Elliptocytes, also known as ovalocytes or cigar cells, are abnormally shaped red blood cells that appear oval or elongated, from slightly egg-shaped to rod or pencil forms. They have normal central pallor with the hemoglobin appearing concentrated at the ends of the elongated cells when viewed through a light microscope. The ends of the cells are blunt and not sharp like sickle cells.

Polychromasia is a disorder where there is an abnormally high number of immature red blood cells found in the bloodstream as a result of being prematurely released from the bone marrow during blood formation These cells are often shades of grayish-blue. Polychromasia is usually a sign of bone marrow stress as well as immature red blood cells. 3 types are recognized, with types 1 and 2 being referred to as 'young red blood cells' and type 3 as 'old red blood cells'. Giemsa stain is used to distinguish all three types of blood smears. The young cells will generally stain gray or blue in the cytoplasm. These young red blood cells are commonly called reticulocytes. All polychromatophilic cells are reticulocytes, however, not all reticulocytes are polychromatophilic. In the old blood cells, the cytoplasm either stains a light orange or does not stain at all.
Hemoglobin H (Hb H)Disease, also called alpha-thalassemia intermedia, is a disease affecting hemoglobin, the oxygen carrying molecule within red blood cells. It is a form of Alpha-thalassemia which most commonly occurs due to deletion of 3 out of 4 of the α-globin genes.
Anemia is a condition in which blood has a lower-than-normal amount of red blood cells or hemoglobin. Anemia in pregnancy is a decrease in the total red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin in the blood during pregnancy. Anemia is an extremely common condition in pregnancy world-wide, conferring a number of health risks to mother and child. While anemia in pregnancy may be pathologic, in normal pregnancies, the increase in RBC mass is smaller than the increase in plasma volume, leading to a mild decrease in hemoglobin concentration referred to as physiologic anemia. Maternal signs and symptoms are usually non-specific, but can include: fatigue, pallor, dyspnea, palpitations, and dizziness. There are numerous well-known maternal consequences of anemia including: maternal cardiovascular strain, reduced physical and mental performance, reduced peripartum blood reserves, increased risk for peripartum blood product transfusion, and increased risk for maternal mortality.


















