Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair.
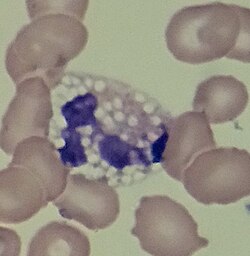
Neutropenia is an abnormally low concentration of neutrophils in the blood. Neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells and serve as the primary defense against infections by destroying bacteria, bacterial fragments and immunoglobulin-bound viruses in the blood. People with neutropenia are more susceptible to bacterial infections and, without prompt medical attention, the condition may become life-threatening.

Neutrophilia is leukocytosis of neutrophils, that is, a high number of neutrophils in the blood. Because neutrophils are the main type of granulocytes, mentions of granulocytosis often overlap in meaning with neutrophilia.
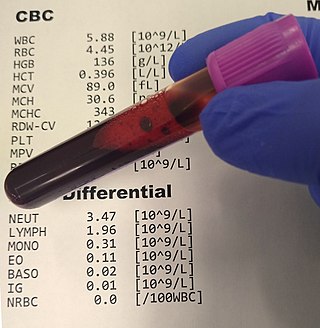
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, the concentration of hemoglobin, and the hematocrit. The red blood cell indices, which indicate the average size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells, are also reported, and a white blood cell differential, which counts the different types of white blood cells, may be included.

Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals.

Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, also known as colony-stimulating factor 3, is a glycoprotein that stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells and release them into the bloodstream.

Granulocytes are cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear. They have varying shapes (morphology) of the nucleus ; and are referred to as polymorphonuclear leukocytes. In common terms, polymorphonuclear granulocyte refers specifically to "neutrophil granulocytes", the most abundant of the granulocytes; the other types have varying morphology. Granulocytes are produced via granulopoiesis in the bone marrow.
Leukocytosis is a condition in which the white cell is above the normal range in the blood. It is frequently a sign of an inflammatory response, most commonly the result of infection, but may also occur following certain parasitic infections or bone tumors as well as leukemia. It may also occur after strenuous exercise, convulsions such as epilepsy, emotional stress, pregnancy and labor, anesthesia, as a side effect of medication, and epinephrine administration. There are five principal types of leukocytosis:
- Neutrophilia
- Lymphocytosis
- Monocytosis
- Eosinophilia
- Basophilia
Döhle bodies are light blue-gray, oval, basophilic, leukocyte inclusions located in the peripheral cytoplasm of neutrophils. They measure 1-3 μm in diameter. Not much is known about their formation, but they are thought to be remnants of the rough endoplasmic reticulum.

Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 2 (CSF2), is a monomeric glycoprotein secreted by macrophages, T cells, mast cells, natural killer cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts that functions as a cytokine. The pharmaceutical analogs of naturally occurring GM-CSF are called sargramostim and molgramostim.

Integrin alpha M (ITGAM) is one protein subunit that forms heterodimeric integrin alpha-M beta-2 (αMβ2) molecule, also known as macrophage-1 antigen (Mac-1) or complement receptor 3 (CR3). ITGAM is also known as CR3A, and cluster of differentiation molecule 11B (CD11B). The second chain of αMβ2 is the common integrin β2 subunit known as CD18, and integrin αMβ2 thus belongs to the β2 subfamily integrins.

Granulopoiesis is a part of haematopoiesis, that leads to the production of granulocytes. A granulocyte, also referred to as a polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN), is a type of white blood cell that has multi lobed nuclei, usually containing three lobes, and has a significant amount of cytoplasmic granules within the cell. Granulopoiesis takes place in the bone marrow. It leads to the production of three types of mature granulocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils.

Toxic granulation refers to dark coarse granules found in granulocytes, particularly neutrophils, in patients with inflammatory conditions.

White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. White blood cells include three main subtypes; granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes.
Leukocyte apheresis is a medical device therapy for the treatment of inflammation of the colon. It works by removing from the blood a group of white blood cells called activated leukocytes that play a key role in the inflammatory stages of ulcerative colitis (UC). Selectively reducing these cells in the blood helps to reduce inflammation in the colon. Leukocyte apheresis can help UC patients with chronic, grumbling disease who are either unsuitable for, intolerant of, or failing on medicines described above.

Jordans' anomaly is a familial abnormality of white blood cell morphology. Individuals with this condition exhibit persistent vacuolation of granulocytes and monocytes in the peripheral blood and bone marrow. Jordans' anomaly is associated with neutral lipid storage diseases.

A white blood cell differential is a medical laboratory test that provides information about the types and amounts of white blood cells in a person's blood. The test, which is usually ordered as part of a complete blood count (CBC), measures the amounts of the five normal white blood cell types – neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and basophils – as well as abnormal cell types if they are present. These results are reported as percentages and absolute values, and compared against reference ranges to determine whether the values are normal, low, or high. Changes in the amounts of white blood cells can aid in the diagnosis of many health conditions, including viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections and blood disorders such as leukemia.
Alder–Reilly anomaly, or Alder anomaly, is an inherited abnormality of white blood cells associated with mucopolysaccharidosis. When blood smears and bone marrow preparations from patients with Alder–Reilly anomaly are stained and examined microscopically, large, coarse granules may be seen in their neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes. The condition may be mistaken for toxic granulation, a type of abnormal granulation in neutrophils that occurs transiently in inflammatory conditions.
A granulocyte transfusion is a medical procedure in which granulocytes are infused into a person's blood. Granulocyte transfusions were historically used to prevent and treat infections in people with neutropenia, but the practice declined in popularity in the 1980s. Interest in the procedure increased in the 1990s due to the development of more effective methods for harvesting granulocytes and a growing population of people with severe neutropenia from chemotherapy. However, the treatment's efficacy remains poorly understood and its use is controversial.

Artificial white blood cells are typically membrane bound vesicles designed to mimic the immunomodulatory behavior of naturally produced leukocytes. While extensive research has been done with regards to artificial red blood cells and platelets for use in emergency blood transfusions, research into artificial white blood cells has been focused on increasing the immunogenic response within a host to treat cancer or deliver drugs in a more favorable fashion. While certain limitations have prevented leukocyte mimicking particles from becoming widely used and FDA approved, more research is being allocated to this area of synthetic blood which has the potential for producing a new form of treatment for cancer and other diseases.