In mathematics, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions that produces a third function that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term convolution refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function.
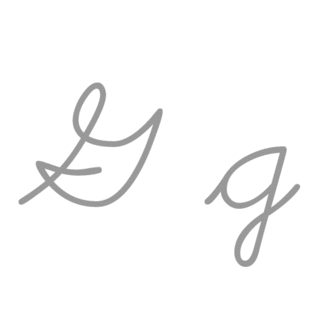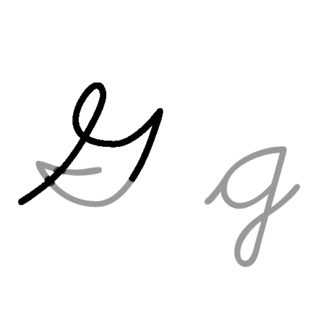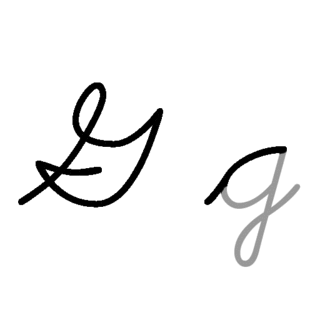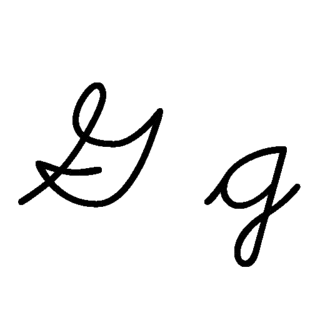
G, or g, is the seventh letter of the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is gee, plural gees.

In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes. The same amount of work is done by the body when decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest. Formally, a kinetic energy is any term in a system's Lagrangian which includes a derivative with respect to time.
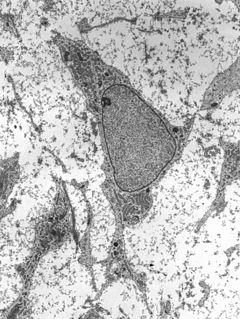
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type.

The tiger is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus Panthera. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on ungulates, such as deer and wild boar. It is territorial and generally a solitary but social predator, requiring large contiguous areas of habitat to support its requirements for prey and rearing of its offspring. Tiger cubs stay with their mother for about two years and then become independent, leaving their mother's home range to establish their own.
Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a family of notations invented by Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation. The letter O was chosen by Bachmann to stand for Ordnung, meaning the order of approximation.

A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions depending on space or time into functions depending on spatial frequency or temporal frequency. That process is also called analysis. An example application would be decomposing the waveform of a musical chord into terms of the intensity of its constituent pitches. The term Fourier transform refers to both the frequency domain representation and the mathematical operation that associates the frequency domain representation to a function of space or time.

Christopher George Latore Wallace, better known by his stage names the Notorious B.I.G., Biggie Smalls, or simply Biggie, was an American rapper and songwriter. Rooted in East Coast hip hop and particularly gangsta rap, he is widely considered one of the greatest rappers of all time. Wallace became known for his distinctive laid-back lyrical delivery, offsetting the lyrics' often grim content. His music was often semi-autobiographical, telling of hardship and criminality, but also of debauchery and celebration.

In mathematics, a function from a set X to a set Y assigns to each element of X exactly one element of Y. The set X is called the domain of the function and the set Y is called the codomain of the function.

The Group of Seven (G7) is an inter-governmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States. In addition, the European Union is a 'non-enumerated member'. Its members are the world's largest IMF advanced economies and liberal democracies; the group is officially organized around shared values of pluralism and representative government. As of 2020, the collective group accounts for over 50 percent of global net wealth, 32 to 46 percent of global gross domestic product, and approximately 770 million people or 10 percent of the world's population. Members are great powers in global affairs and maintain mutually close political, economic, social, legal, environmental, military, religious, cultural, and diplomatic relations. From 2022, Germany has taken over the rotating presidency of the G7, following the presidency of the United Kingdom.

The iPhone is a line of smartphones designed and marketed by Apple Inc. These devices use Apple's iOS mobile operating system. The first-generation iPhone was announced by then-Apple CEO Steve Jobs on January 9, 2007. Since then, Apple has annually released new iPhone models and iOS updates. As of November 1, 2018, more than 2.2 billion iPhones had been sold.

In telecommunications, 5G is the fifth-generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the planned successor to the 4G networks which provide connectivity to most current cellphones. 5G networks are predicted to have more than 1.7 billion subscribers and account for 25% of the worldwide mobile technology market by 2025, according to the GSM Association and Statista.

Caeneressa marcescoides is a moth in the family Erebidae. It is found in Borneo, Papua New Guinea and Thailand.
Caeneressa brithyris is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Herbert Druce in 1898. It is found on Borneo and Sumatra.
Caeneressa longipennis is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1862. It is found on Borneo. The habitat consists of lowland areas.
Caeneressa lutosa is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Jeremy Daniel Holloway in 1976. It is found on Borneo.

Caeneressa robusta is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Jeremy Daniel Holloway in 1976. It is found on Borneo.
Caeneressa sexpuncta is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Rothschild in 1912. It is found on Borneo. The habitat consists of lowland forests.
Caeneressa syntomoides is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Rothschild in 1912. It is found on Borneo. The habitat consists of lowland forests.
Crocidophora tienmushana is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Aristide Caradja and Edward Meyrick in 1935. It is found in Zhejiang, China.