Scuticaria okinawae is a moray eel found in the Pacific and Indian Oceans. It is commonly known as the shorttailed snake moray, shorttail moray, Seale's moray eel, or the Bennett's moray.

Callechelys is a genus of eels in the snake eel family Ophichthidae. It currently contains the following fifteen species:
Nichols's worm eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Edgar Ravenswood Waite in 1904, originally under the genus Muraenichthys.

The sharpsnout snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Max Carl Wilhelm Weber in 1913. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific, including East Africa, the Marshall Islands, and the Hawaiian Islands. It dwells at a depth range of 10 to 25 metres, and lives in congregations in confined regions of sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 40 centimetres (16 in).

The reptilian snake eel, also known as Henshaw's snake eel, the Hawaiian crocodile eel or the crocodile snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and John Otterbein Snyder in 1904.
Callechelys bilinearis, the twostripe snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1952. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and southeastern Atlantic Ocean, including Bermuda, the West Indies, Lesser Antilles, St. Helena Island and Ascension Island. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 22 metres, most often at around 0 to 5 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 172.4 centimetres (67.9 in).
Callechelys bitaeniata is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Wilhelm Peters in 1877. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the western Indian Ocean, including Kenya, Mozambique and Seychelles. Males can reach a maximum total length of 82 centimetres.
Callechelys catostoma, the black-striped snake eel or dark band snake eel,) is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Johann Gottlob Theaenus Schneider and Johann Reinhold Forster in 1801. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific, including the Red Sea, East Africa, the Society Islands, the Ryukyu Islands, and Lord Howe Island. It dwells at a depth range of 1–32 metres, and inhabits reefs. It burrows into loose gravel and sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 85 centimetres (33 in).
Callechelys cliffi, the sandy ridgefin eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by James Erwin Böhlke and John Carmon Briggs in 1954. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Mexico and Panama. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 30 metres, and inhabits sand sediments. Males can reach a maximum standard length of 45.5 centimetres (17.9 in).
Callechelys eristigma, the spotted ridgefin eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker and Richard Heinrich Rosenblatt in 1972. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Costa Rica, Mexico, and Panama. It dwells at a depth range of 5 to 25 metres, and inhabits benthic sediments of rock and sand. Males can reach a maximum standard length of 113 centimetres (44 in).
Callechelys galapagensis, the Galapagos ridgefin eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker and Richard Heinrich Rosenblatt in 1972. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from four specimens collected from the Galapagos Islands, in the southeastern Pacific Ocean. It inhabits coral, sand and rock.
Callechelys guineensis, the shorttail snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Balthazar Osório in 1893, originally under the genus Ophichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Florida, USA, Puerto Rico, Venezuela, the Bahamas, Saint Barthélemy, Senegal, Lesser Antilles, and Cape Verde. It dwells at a depth range of 4 to 35 metres, and inhabits the continental shelf, where it forms burrows in sand and mud. Males can reach a maximum total length of 108 centimetres (43 in).
Callechelys leucoptera is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Jean Cadenat in 1954. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Senegal to Côte d'Ivoire. It is known to dwell at a depth of 45 metres. It inhabits shallow waters where it forms burrows in the sand, which are sometimes exposed during low tide. Males can reach a maximum total length of 73 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 50 centimetres.

Callechelys muraena, the blotched snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Barton Warren Evermann in 1887. It is a rare tropical, marine eel which is known from the western and northwestern Atlantic Ocean, including the United States, the Gulf of Mexico, the Yucatan Peninsula, and Canada. It dwells at a depth range of 27–115 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 60 centimetres.
Callechelys papulosa, the blistered snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker in 1998. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from Papua New Guinea, in the western central Pacific Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 10 metres, and to inhabit regions of sand and grass. Males can reach a maximum total length of 55.1 centimetres.
Callechelys randalli is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John E. McCosker in 1998. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Marquesan Islands, in the eastern central Pacific Ocean. It is known to inhabit sand at a depth of 35 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 46.4 centimetres.
Callechelys springeri, the ridgefin eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Isaac Ginsburg in 1951, originally under the genus Gordiichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern Gulf of Mexico, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 22 to 36 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 80.1 centimeters (31.5 in).
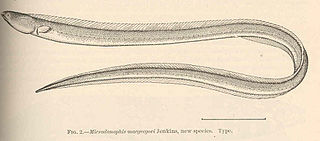
The fringelip snake-eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1870. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific, including Zanzibar, Tanzania, Kosi Bay, South Africa, and the Hawaiian Islands. Its lifestyle is mostly benthic but it sometimes swims at the surface. It is olive brown in colour, with lighter colouring in the ventral region. Males can reach a maximum total length of 39 centimetres (15 in).

The saddled snake-eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by George Tradescant Lay and Edward Turner Bennett in 1839, originally under the genus Ophisurus. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and southeastern Atlantic Ocean, including East and South Africa, the Hawaiian Islands, the Marquesan Islands, the Mangaréva islands, Japan, and Australia. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 70 metres, most often around 0 to 10 metres, and inhabits lagoons and reefs, in which it forms burrows in beds of seagrass and sandy areas. Males can reach a maximum total length of 66 centimetres (2.17 ft).
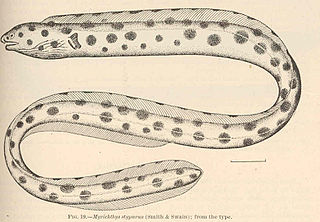
The magnificent snake eel, also known as the Hawaiian spotted snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Conrad Abbott in 1860, originally under the genus Pisoodonophis. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including the Hawaiian Islands, the Leeward Islands, Johnston Island, and Midway Atoll. It dwells at a depth range of 1 to 262 metres, and inhabits crevices, sand and rocks. Males can reach a maximum total length of 78 centimetres (31 in).







