
Owls are birds from the order Strigiformes, which includes over 200 species of mostly solitary and nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vision, binaural hearing, sharp talons, and feathers adapted for silent flight. Exceptions include the diurnal northern hawk-owl and the gregarious burrowing owl.
Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also called binominal nomenclature or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name or a scientific name; more informally it is also called a Latin name.

The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae and the Ochotonidae (pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek lagos + morphē. There are 110 recent species of lagomorph of which 109 are extant, including 34 species of pika, 42 species of rabbit, and 33 species of hare; the one recently extinct species is the Sardinian pika, which was the last surviving member of its family Prolagidae.

Aster is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. Its circumscription has been narrowed, and it now encompasses around 180 species, all but one of which are restricted to Eurasia; many species formerly in Aster are now in other genera of the tribe Astereae. Aster amellus is the type species of the genus and the family Asteraceae.

A wallaby is a small or middle-sized macropod native to Australia and New Guinea, with introduced populations in New Zealand, Hawaii, the United Kingdom and other countries. They belong to the same taxonomic family as kangaroos and sometimes the same genus, but kangaroos are specifically categorised into the four largest species of the family. The term "wallaby" is an informal designation generally used for any macropod that is smaller than a kangaroo or a wallaroo that has not been designated otherwise.

A booby is a seabird in the genus Sula, part of the family Sulidae. Boobies are closely related to the gannets (Morus), which were formerly included in Sula.

Ovenbirds or furnariids are a large family of small suboscine passerine birds found from Mexico and Central to southern South America. They form the family Furnariidae. This is a large family containing around 315 species and 70 genera. The ovenbird, which breeds in North America, is not a furnariid – rather it is a distantly related bird of the wood warbler family, Parulidae.

The Geoemydidae are one of the largest and most diverse families in the order Testudines (turtles), with about 70 species. The family includes the Eurasian pond and river turtles and Neotropical wood turtles.

Emydidae is a family of testudines (turtles) that includes close to 50 species in 10 genera. Members of this family are commonly called terrapins, pond turtles, or marsh turtles. Several species of Asian box turtles were formerly classified in the family; however, revised taxonomy has separated them to a different family (Geoemydidae). As currently defined, the Emydidae are entirely a Western Hemisphere family, with the exception of two species of pond turtle.

Salamandridae is a family of salamanders consisting of true salamanders and newts. Salamandrids are distinguished from other salamanders by the lack of rib or costal grooves along the sides of their bodies and by their rough skin. Their skin is very granular because of the number of poison glands. They also lack nasolabial grooves. Most species of Salamandridae have moveable eyelids but lack lacrimal glands.

Labrisomids are small blennioids (blennies), percomorph marine fish belonging to the family Labrisomidae. Found mostly in the tropical Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, the family contains about 110 species in 15 genera.
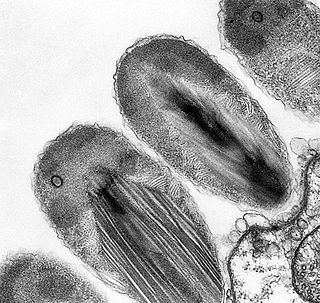
Verrucomicrobia is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated species have been identified in association with eukaryotic hosts including extrusive explosive ectosymbionts of protists and endosymbionts of nematodes residing in their gametes.

The Chlamydiae are a bacterial phylum and class whose members are remarkably diverse, including pathogens of humans and animals, symbionts of ubiquitous protozoa, and marine forms not yet well understood. All of the Chlamydiae that humans have known about for many decades are obligate intracellular bacteria; in 2020 many additional Chlamydiae were discovered in ocean-floor environments, and it is not yet known whether they all have hosts. Historically it was believed that all Chlamydiae had a peptidoglycan-free cell wall, but studies in the 2010s demonstrated a detectable presence of peptidoglycan, as well as other important proteins.

The Drosophilidae are a diverse, cosmopolitan family of flies, which includes fruit flies. Another unrelated family of flies, Tephritidae, also includes species known as "small fruit flies". The best known species of the Drosophilidae is Drosophila melanogaster, within the genus Drosophila, and this species is used extensively for studies concerning genetics, development, physiology, ecology and behaviour. This fruit fly is mostly composed of post-mitotic cells, has a very short lifespan, and shows gradual aging. As in other species, temperature influences the life history of the animal. Several genes have been identified that can be manipulated to extend the lifespan of these insects. Additionally, Drosophila subobscura, also within the genus Drosophila, has been reputed as a model organism for evolutionary-biological studies.

A caiman is an alligatorid belonging to the subfamily Caimaninae, one of two primary lineages within Alligatoridae, the other being alligators.
The Chloroflexi or Chlorobacteria are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for photosynthesis ; and anaerobic halorespirers, which uses halogenated organics as electron acceptors.
Calliclinus geniguttatus is a species of labrisomid blenny native to the Pacific coast of Chile and the Atlantic coast of Argentina. This species primarily preys on amphipods when young, shifting to decapods as they mature. It can reach a length of 12.2 centimetres (4.8 in) TL.
Malagasia is a monotypic genus of trees in the family Proteaceae. The sole species is Malagasia alticola, endemic to Madagascar.

Caprodon is a small genus of fish belonging to the subfamily Anthiinae. It contains three species.















