
The viviparous brotulas form a family, the Bythitidae, of ophidiiform fishes. They are known as viviparous brotulas as they generally bear live young, although there are indications that some species do not. They are generally infrequently seen, somewhat tadpole-like in overall shape and mostly about 5–10 cm (2–4 in) in length, but some species grow far larger and may surpass 60 cm (2 ft).
Lucifuga simile is a species of cavefish in the family Bythitidae. It is endemic to Cuba. It is a demersal species found in freshwater and brackish water. It can reach a length of 8.8 centimetres (3.5 in).
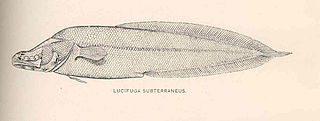
Lucifuga is a genus of viviparous brotulas. Most of the species are native to caves and sinkholes in Cuba and the Bahamas; L. inopinata from deep water off the Galápagos Islands is the only exception. The four species rated by the IUCN are all considered vulnerable. The largest species in the genus reaches about 15 cm (5.9 in) in length.
The New Providence cusk-eel, also known as the Bahama cavefish, is a species of cavefish in the family Bythitidae. It is endemic to the Bahamas, where it has been reported from a small number of marine blue holes, inland caverns and chasms. It is the only known cusk eel species that can occur in surface waters; all others exclusively live in the deep parts of the ocean, or in underwater caves. It was first described in 1970.

Lucifuga subterranea, or the Cuban cusk-eel, is a species of cavefish in the family Bythitidae. It is endemic to Cuba. Within the caves, sinkholes and crevices in which it occurs it is common, it feeds on cirolanid isopods.
Lucifuga dentata is a species of fish in the family Bythitidae. It is endemic to Cuba.

The spotted-tail salamander, also known as a "cave salamander", is a species of brook salamander.

Caloplaca is a lichen genus comprising a number of distinct species. Members of the genus are commonly called firedot lichen, jewel lichen. gold lichens, "orange lichens", but they are not always orange, as in the case of C. albovariegata. The distribution of this lichen genus is worldwide, extending from Antarctica to the high Arctic. It includes a portion of northern North America and the Russian High Arctic. There are about thirty species of Caloplaca in the flora of the British Isles.
Caloplaca obamae is a species of crustose lichen in the fungus genus Caloplaca. It is the first species to be named in honor of United States President Barack Obama. C. obamae was discovered in 2007 by Kerry Knudsen on Santa Rosa Island in California and published in March 2009. Knudsen stated that he chose to honor Obama for "his support of science and scientific education" and wrote the manuscript for publication of the species in the time between Obama's election and his inauguration.

Caloplaca marina, the orange sea lichen, is a crustose, placodioid lichen. It has wide distribution, and can be found near the shore on rocks or walls. Calos in Greek means nice, placa in Greek is shield. Caloplaca therefore means ‘beautiful patches’.

Cucullia lucifuga is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in north, central and southern Europe east to Japan. It is also present in Tibet and Armenia.
Rippon Glacier is a small glacier located in Kemp Land, East Antarctica. It is close east of Seaton Glacier, flowing southward into Edward VIII Ice Shelf.
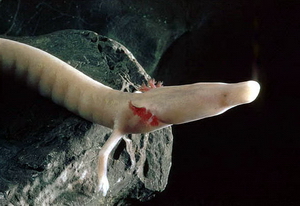
A cave salamander is a type of salamander that primarily or exclusively inhabits caves, a group that includes several species. Some of these animals have developed special, even extreme, adaptations to their subterranean environments. Some species have only rudimentary eyes. Others lack pigmentation, rendering them a pale yellowish or pinkish color.

Gnaphosa lucifuga is a ground spider species with Palearctic distribution.
Troglohyphantes lucifuga is a species of cave spider of the family Linyphiidae. Its distribution is European: France, Italy, Switzerland.

Gripsholms hjorthage is a deer park and nature reserve close to Gripsholm Castle in Södermanland County, Sweden. The deer pasture is dominated by many old oak trees. The area has been used for grazing for a long time, and as a deer park since the end of the 19th century. It was declared a nature reserve in 2001 after the discovery of the red-listed hermit beetle in the area. It is also popular as a recreational area.

Lendemeriella is a genus of crustose lichens in the subfamily Caloplacoideae of the family Teloschistaceae. It has ten species. The genus was circumscribed in 2020 by Sergey Kondratyuk, with Lendemeriella reptans assigned as the type species. The genus name honours the American lichenologist James Lendemer, who co-authored the type species in 2012.
Solitaria is a fungal genus in the family Teloschistaceae. It contains a single species, the corticolous (bark-dwelling), crustose lichen Solitaria chrysophthalma.










