
The myxobacteria are a group of bacteria that predominantly live in the soil and feed on insoluble organic substances. The myxobacteria have very large genomes relative to other bacteria, e.g. 9–10 million nucleotides except for Anaeromyxobacter and Vulgatibacter. One species of myxobacteria, Minicystis rosea, has the largest known bacterial genome with over 16 million nucleotides. The second largest is another myxobacteria Sorangium cellulosum. Myxobacteria are included among the delta group of proteobacteria, a large taxon of Gram-negative forms.
Chemical biology is a scientific discipline spanning the fields of chemistry and biology. The discipline involves the application of chemical techniques, analysis, and often small molecules produced through synthetic chemistry, to the study and manipulation of biological systems. In contrast to biochemistry, which involves the study of the chemistry of biomolecules and regulation of biochemical pathways within and between cells, chemical biology deals with chemistry applied to biology.
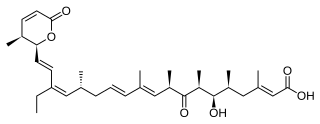
Leptomycins are secondary metabolites produced by Streptomyces spp.

Rhizoxin is an antimitotic agent with anti-tumor activity. It is isolated from a pathogenic plant fungus which causes rice seedling blight.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 also known as cell division protein kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK4 gene. CDK4 is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family.

Staurosporine is a natural product originally isolated in 1977 from the bacterium Streptomyces staurosporeus. It was the first of over 50 alkaloids to be isolated with this type of bis-indole chemical structure. The chemical structure of staurosporine was elucidated by X-ray analysis of a single crystal and the absolute stereochemical configuration by the same method in 1994.
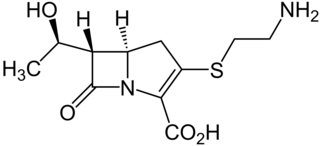
Thienamycin is one of the most potent naturally produced antibiotics known thus far, discovered in Streptomyces cattleya in 1976. Thienamycin has excellent activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and is resistant to bacterial β-lactamase enzymes. Thienamycin is a zwitterion at pH 7.
In enzymology, a phosphonopyruvate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.82) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a gentamicin 2"-nucleotidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Indolocarbazoles (ICZs) are a class of compounds that are under current study due to their potential as anti-cancer drugs and the prospective number of derivatives and uses found from the basic backbone alone. First isolated in 1977, a wide range of structures and derivatives have been found or developed throughout the world. Due to the extensive number of structures available, this review will focus on the more important groups here while covering their occurrence, biological activity, biosynthesis, and laboratory synthesis.

Lactivicin is a non-beta-lactam antibiotic that is active against a range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Lactivicin demonstrates a similar affinity for penicillin-binding proteins to beta-lactam antibiotics and is also susceptible to beta-lactamase enzymes.

Romidepsin, also known as Istodax, is an anticancer agent used in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) and other peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs). Romidepsin is a natural product obtained from the bacterium Chromobacterium violaceum, and works by blocking enzymes known as histone deacetylases, thus inducing apoptosis. It is sometimes referred to as depsipeptide, after the class of molecules to which it belongs. Romidepsin is branded and owned by Gloucester Pharmaceuticals, now a part of Celgene.
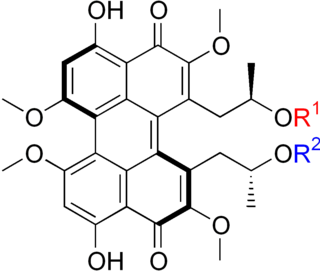
The calphostins are a class of closely related chemical compounds isolated from the fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides. The known calphostins include calphostin A, calphostin B, calphostin C, calphostin D, and calphostin I. The calphostins are inhibitors of protein kinase C (PKC). The most potent member of the series, calphostin C, has found use as a biochemical tool because of this activity.

Callystatin A is a polyketide natural product from the leptomycin family of secondary metabolites. It was first isolated in 1997 from the marine sponge Callyspongia truncata which was collected from the Goto Islands in the Nagasaki Prefecture of Japan by the Kobayashi group. Since then its absolute configuration has been elucidated and callystatin A was discovered to have anti-fungal and anti-tumor activities with extreme potency against the human epidermoid carcinoma KB cells (IG50 = 10 pg/ml) and the mouse lymphocytic leukemia Ll210 cells (IG50 = 20 pg/ml).
Naphthomycins are a group of closely related antimicrobial chemical compounds isolated from Streptomyces. They are considered a subclass of ansamycins.
Actinoplanes friuliensis is a species of bacteria that produces lipopeptide antibiotics with peptidoglycan synthesis-inhibiting activity, called friulimicins.
Micromonospora citrea is an endophytic actinomycete, with type strain DSM 43903T. It produces citreamicins, several types of antibacterial antibiotics.

Cladosporium cladosporioides is a darkly pigmented mold that occurs world-wide on a wide range of materials both outdoors and indoors. It is one of the most common fungi in outdoor air where its spores are important in seasonal allergic disease. While this species rarely causes invasive disease in animals, it is an important agent of plant disease, attacking both the leaves and fruits of many plants. This species produces asexual spores in delicate, branched chains that break apart readily and drift in the air. It is able to grow under low water conditions and at very low temperatures.

Satoshi Ōmura [satoɕi oːmu͍ɽa] is a Japanese biochemist. He is known for the discovery and development of various pharmaceuticals originally occurring in microorganisms. In 2015, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine jointly with William C. Campbell and Tu Youyou.
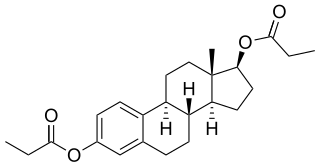
Estradiol dipropionate/hydroxyprogesterone caproate (EDP/OHPC), sold under the brand name EP Hormone Depot, is a combined estrogen–progestogen medication which is used in Japan. It is manufactured by Teikoku Zoki Pharmaceutical Co., Tokyo and contains 1 mg/mL estradiol dipropionate and 50 mg/mL hydroxyprogesterone caproate.













