
This is a list of referendums related to the European Union, or referendums related to the European Communities, which were predecessors of the European Union. Since 1972, a total of 48 referendums have been held by EU member states, candidate states, and their territories, with several additional referendums held in countries outside of the EU. The referendums have been held most commonly on the subject of whether to become a member of European Union as part of the accession process, although the EU does not require any candidate country to hold a referendum to approve membership or as part of treaty ratification. Other EU-related referendums have been held on the adoption of the euro and on participation in other EU-related policies.
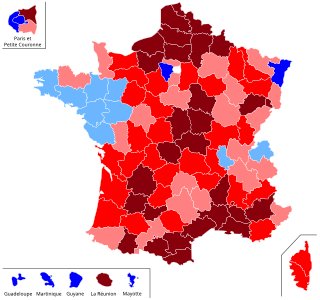
The French referendum on the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was held on 29 May 2005 to decide whether France should ratify the proposed Constitution of the European Union. The result was a victory for the "No" campaign, with 55% of voters rejecting the treaty on a turnout of 69%.
A constitutional referendum was held in the Batavian Republic in 1798. After a previous referendum in 1797 resulted in a coup d'état, a new constitution was written. On 23 April 1798, a referendum was held about the new constitution. Only opponents of the federalists were allowed to vote.

A referendum on the new constitution of France was held in Madagascar on 28 September 1958 as part of a wider referendum held across the French Union. The new constitution would see the country become part of the new French Community if accepted, or result in independence if rejected. It was approved by 77.64% of voters. The country subsequently became independent on 26 June 1960.

A referendum on the new constitution of France was held in Dahomey on 28 September 1958 as part of a wider referendum held across the French Union. The new constitution would see the country become part of the new French Community if accepted, or result in independence if rejected. It was approved by 97.84% of voters.

A referendum on the new constitution of France was held in Gabon on 28 September 1958 as part of a wider referendum held across the French Union. The new constitution would see the country become part of the new French Community if accepted, or result in independence if rejected. It was approved by 92.6% of voters, with a 78.7% turnout.

A constitutional referendum was held in French Dahomey and French Togoland on 21 October 1945 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. In the two territories both questions were approved by large margins. Voter turnout was 83.5%.

A constitutional referendum was held in French Dahomey and French Togoland on 5 May 1946 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. The new proposed new constitution was rejected by 55.4% of voters, with a turnout of 56.7%.

A constitutional referendum was held in Dahomey and French Togoland on 13 October 1946 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. The new proposed new constitution was rejected by 72.8% of voters, with a turnout of 47.5%. However, the constitution was approved by a majority of voters in the overall results.

A constitutional referendum was held in Algeria on 13 October 1946 as part of a wider French constitutional referendum. The proposed new constitution was rejected by 61.6% of voters, with a turnout of 58.5%. However, it was approved by a majority of voters in France and other territories.

A referendum on the new constitution of France was held in the Comoros on 28 September 1958 as part of a wider referendum held across the French Union. The new constitution would see the country become part of the new French Community if accepted, or result in independence if rejected. It was approved by 97.33% of voters.
A constitutional referendum was held in Gabon and Moyen Congo on 5 May 1946 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. The proposed new constitution was rejected by 64% of voters in the territory, and 53% of voters overall.
A constitutional referendum was held in Gabon and Moyen Congo on 13 October 1946 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. Although the proposed new constitution was rejected by 72% of voters in the territory, it was approved 53% of voters overall.
A constitutional referendum was held in Chad and Ubangi-Shari on 13 October 1946 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. The proposed new constitution was rejected by 77.3% of voters, with a turnout of 64.5%. However, the constitution was approved by a majority of voters in the overall results.
A constitutional referendum was held in Mauritania and Senegal on 21 October 1945 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. The first question on the new French National Assembly serving as a constituent assembly was approved by 99% of voters, but the temporary constitution proposed in the second question was rejected by 51% of voters. Both proposals were approved in the overall vote. Voter turnout was 60.4%.
A constitutional referendum was held in French Sudan and Niger on 21 October 1945 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. The first question on the new French National Assembly serving as a constituent assembly was approved by 97% of voters, whilst the temporary constitution proposed in the second question was approved by 86% of voters. Both proposals were also approved in the overall vote. Voter turnout was 79.3%.
A constitutional referendum was held in French Sudan and Niger on 5 May 1946 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. The proposed new constitution was rejected by 48% of voters in the two territories and by 53% of the overall vote. Voter turnout was 58%.
A constitutional referendum was held in French Sudan and Niger on 13 October 1946 as part of the wider French constitutional referendum. The proposed new constitution was rejected by 45% of voters in the two territories, but approved by 57.4% of the overall vote. Voter turnout was 51%.

A constitutional referendum was held in the Republic of the Congo on 25 October 2015 regarding a proposal to change the constitution, primarily to modify the rules regarding presidential terms.

Guinea has had four constitutions. The current constitution was approved by referendum on 19 April 2010 and formally adopted on 7 May.












