
Acinonyx is a genus within the cat family. The only living species of this genus, the cheetah A. jubatus, lives in open grasslands of Africa and Asia.

Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, Baron Cuvier, known as Georges Cuvier, was a French naturalist and zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuvier was a major figure in natural sciences research in the early 19th century and was instrumental in establishing the fields of comparative anatomy and paleontology through his work in comparing living animals with fossils.

The Chelydridae is a family of turtles that has seven extinct and two extant genera. The extant genera are the snapping turtles, Chelydra and Macrochelys. Both are endemic to the Western Hemisphere. The extinct genera are Acherontemys, Chelydrops, Chelydropsis, Emarginachelys, Macrocephalochelys, Planiplastron, and Protochelydra.

Ailuropoda is the only extant genus in the ursid (bear) subfamily Ailuropodinae. It contains one living and three fossil species of panda.

Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville was a French zoologist and anatomist.

The paleoanthropological site self-proclaimed as the Cradle of Humankind is located about 50 km (31 mi) northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa, in the Gauteng province. Declared a World Heritage site by UNESCO in 1999, the site currently occupies 47,000 hectares (180 sq mi) and contains a complex of limestone caves. The registered name of the site in the list of World Heritage sites is Fossil Hominid Sites of South Africa.

Alcide Charles Victor Marie Dessalines d'Orbigny was a French naturalist who made major contributions in many areas, including zoology, palaeontology, geology, archaeology and anthropology.

Fabrosaurus is a genus of ornithischian dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic. It was originally placed within the now obsolete family Fabrosauridae.

Betasuchus is a genus of theropod dinosaur which lived during the Late Cretaceous Period. Betasuchus is, besides Orthomerus, the only dinosaur genus named from remains found in the Netherlands and the only non-avian theropod found in the Maastrichtian Beds.

Teinurosaurus is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur. Teinurosaurus lived during the Late Jurassic in what is now Portugal. The type species is Teinurosaurus sauvagei. It's been estimated to be 11.4 m in length and 3.6 tonnes in weight.

Erectopus is a basal allosauroid theropod from the Lower Cretaceous of France.

Streptospondylus is a genus of tetanuran theropod dinosaur known from the Late Jurassic period of France, 161 million years ago. It was a medium-sized predator with an estimated length of 6 meters and a weight of 500 kg (1,100lbs).

Ontocetus is an extinct genus of walrus, an aquatic carnivoran of the family Odobenidae, endemic to coastal regions of the southern North Sea and the southeastern coastal regions of the U.S. during the Miocene-Pleistocene. It lived from 13.6 mya—300,000 years ago, existing for approximately 13.3 million years .
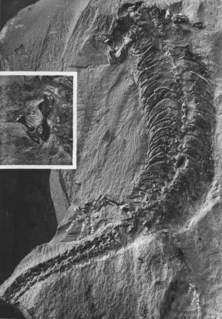
Sauravus is an extinct genus of nectridean lepospondyl within the family Scincosauridae.
Euthecodon is an extinct genus of long-snouted crocodyline crocodilians. It was common throughout much of Africa during the Neogene, with fossils being especially common in Kenya. It existed from the Early Miocene to the Early Pleistocene.
Xixianykus is a genus of alvarezsauroid theropod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous period of China.

Dadoxylon is a form genus of fossil wood, including massive tree trunks. Dadoxlyon is identified from the late Palaeozoic to the end of the Mesozoic, but especially common in the Carboniferous.

Cretalamna is a genus of extinct otodontid shark that lived from the Late Cretaceous to Eocene epoch. It is considered by many to be the ancestor of the largest sharks to have ever lived, Carcharocles angustidens, and Carcharocles megalodon.

The Noisetier Cave, owing its popular name to the Hazel trees that grow in front of its entrance, is located in a mountainside 145 m (476 ft) atop the Vallée d'Aure in the Ardengost commune, Hautes-Pyrénées department in the region Occitania, southern France. During systematic excavations since 1992 Middle Paleolithic stone tools and artifacts attributed to the Neanderthal Mousterian culture were discovered among numerous faunal remains.
Frisiphoca is an extinct genus of phocid belonging to the subfamily Phocinae. It is known from fossils found in the late Miocene of Belgium.

















