
The island country of Jersey is a state in which capital punishment has been abolished.

The island country of Jersey is a state in which capital punishment has been abolished.
Until the 19th century, hangings were carried out on Westmount (French : Mont-Patibulaire (gallows hill); Jèrriais : Mont ès Pendus (hill of the hanged men) in Saint Helier. The last such execution was carried out on 3 October 1829, when Philippe Jolin was hanged for murder.
The following execution, that of François Bradley on 11 October 1866, was carried out in public outside the prison in Saint Helier. The law specified hanging in public until 1907. The next execution, therefore, that of Joseph Philip Le Brun on 12 August 1875, also took place under the same conditions. It was the last public hanging in the British Isles (the United Kingdom had abolished public hangings in 1868).
The death sentence passed on Thomas Connan (executed 19 February 1907) necessitated a law change to permit the hanging to take place within the prison walls. During the German occupation from 1940 to 1945, the occupying forces carried out executions by firing squad. The last execution in Jersey was on 9 October 1959, when Francis Joseph Huchet was hanged for murder. [1]
In Jersey, the last death sentence was passed in 1984, but was commuted to life imprisonment.
Capital punishment was abolished by the Homicide (Jersey) Law 1986 in relation to the offence of murder [2] and by the Genocide (Amendment) (Jersey) Law 1987 in relation to the offence of genocide. [3] Technically, the death penalty remained available to a military court, but by the 1986 and 1987 laws the Royal Court of Jersey lost the power of capital sentencing. References to capital punishment in obsolete laws were formally removed by the Criminal Justice (Miscellaneous Provisions) (No. 2) (Jersey) Law 2007. [4]
The Human Rights (Amendment) (Jersey) Order 2006 to give effect to Protocol No. 13 of the European Convention on Human Rights providing for the total abolition of the death penalty. Both of these laws came into effect on 10 December 2006. [5] amended the Human Rights (Jersey) Law 2000 [6]
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is condemned and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Etymologically, the term capital refers to execution by beheading, but executions are carried out by many methods, including hanging, shooting, lethal injection, stoning, electrocution, and gassing.

Capital punishment in the United Kingdom predates the formation of the UK, having been used in Britain and Ireland from ancient times until the second half of the 20th century. The last executions in the United Kingdom were by hanging, and took place in 1964; capital punishment for murder was suspended in 1965 and finally abolished in 1969. Although unused, the death penalty remained a legally defined punishment for certain offences such as treason until it was completely abolished in 1998; the last person to be executed for treason was William Joyce, in 1946. In 2004, Protocol No. 13 to the European Convention on Human Rights became binding on the United Kingdom; it prohibits the restoration of the death penalty as long as the UK is a party to the convention.
Capital punishment in Canada dates to Canada's earliest history, including its period as first a French then a British colony. From 1867 to the elimination of the death penalty for murder on July 26, 1976, 1,481 people had been sentenced to death, and 710 had been executed. Of those executed, 697 were men and 13 women. The only method used in Canada for capital punishment of civilians after the end of the French regime was hanging. The last execution in Canada was the double hanging of Arthur Lucas and Ronald Turpin on December 11, 1962, at Toronto's Don Jail. The National Defence Act prescribed the death penalty for certain military offences until 1999, although no military executions had been carried out since 1946.
Capital punishment was abolished in 2019 in New Hampshire for persons convicted of capital murder. It remains a legal penalty for crimes committed prior to May 30, 2019.

Capital punishment – the process of sentencing convicted offenders to death for the most serious crimes and carrying out that sentence, as ordered by a legal system – first appeared in New Zealand in a codified form when New Zealand became a British colony in 1840. It was first carried out with a public hanging in Victoria Street, Auckland in 1842, while the last execution occurred in 1957 at Mount Eden Prison, also in Auckland. In total, 85 people have been lawfully executed in New Zealand.

The Homicide Act 1957 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was enacted as a partial reform of the common law offence of murder in English law by abolishing the doctrine of constructive malice, reforming the partial defence of provocation, and by introducing the partial defences of diminished responsibility and suicide pact. It restricted the use of the death penalty for murder.

The Murder Act 1965 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It abolished the death penalty for murder in Great Britain. The act replaced the penalty of death with a mandatory sentence of imprisonment for life.
Capital punishment in Hong Kong was formally abolished on 23 April 1993 by virtue of the Crimes (Amendment) Ordinance 1993. Before then, capital punishment was the usual sentence given since the establishment of the Crown Colony of Hong Kong for offences such as murder, kidnapping ending in death, and piracy.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Pakistan. Although there have been numerous amendments to the Constitution, there is yet to be a provision prohibiting the death penalty as a punitive remedy.
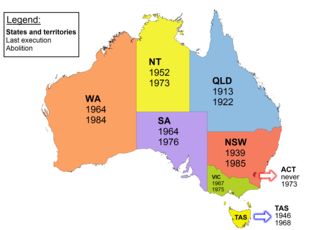
Capital punishment in Australia has been abolished in all jurisdictions since 1985. Queensland abolished the death penalty in 1922. Tasmania did the same in 1968. The Commonwealth abolished the death penalty in 1973, with application also in the Australian Capital Territory and the Northern Territory. Victoria did so in 1975, South Australia in 1976, and Western Australia in 1984. New South Wales abolished the death penalty for murder in 1955, and for all crimes in 1985. In 2010, the Commonwealth Parliament passed legislation prohibiting the re-establishment of capital punishment by any state or territory. Australian law prohibits the extradition or deportation of a prisoner to another jurisdiction if they could be sentenced to death for any crime.
Capital punishment was abolished in Turkey in 2004, and no prisoners have been executed since October 1984. Before that, over 500 convicts sentenced to death were executed. The method of execution was hanging.
Capital punishment is legal in Tonga, but has not been imposed since 1982. The country's lack of executions puts it into the category of a state abolitionist in practice, where it retains the death penalty in law but has had a formal or informal moratorium for at least ten years. Tonga's low rate of murder convictions forms part of the reason for the lack of executions, as well as its courts’ apparent unwillingness to impose the penalty unless it appears absolutely necessary to do so.
Capital punishment refers to the execution of an offender sentenced to death after conviction of a criminal offense. Capital punishment is legal in Afghanistan and can be carried out secretly or publicly due to the current governmental system. The main methods of execution employed by the Afghan government on convicts are hangings and shootings. Stoning, amputation, and flogging are also sometimes used as a method for punishment, and were especially prominent during the late 1990s. Public executions have existed throughout Afghanistan's history. The former Afghan government took important steps away from the use of the death penalty, but they have continued with the Taliban returning to power in August 2021. Some executions have been recently condemned by the United Nations. UN experts have called on Afghan authorities "to halt immediately all forms of torturous, cruel, and degrading forms of punishments." The capital offenses in Afghanistan include a range of crimes from murder to adultery, and are governed by Sharia, along with civil laws.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Jamaica. Currently, the only crime punishable by death is aggravated murder. The method of execution is hanging. Jamaica was originally a British colony. The last person executed in Jamaica was Nathan Foster, who was convicted of murder and hanged in 1988. The Jamaican Parliament had placed a moratorium on the death penalty until 2009, when it was lifted. Since 2009, capital punishment is legal and executions in Jamaica could resume; however, there have been no executions since.
Hanging has been practiced legally in the United States of America from before the nation's birth, up to 1972 when the United States Supreme Court found capital punishment to be in violation of the Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution. Four years later, the Supreme Court overturned its previous ruling, and in 1976, capital punishment was again legalized in the United States. Currently, only New Hampshire has a law specifying hanging as an available secondary method of execution, now only applicable to one person, who was sentenced to capital punishment by the state prior to its repeal in 2019.
Capital punishment in Montenegro was first prescribed by law in 1798. It was abolished on 19 June 2002. The last execution, by shooting, took place on 29 January 1981, and the two last death sentences were pronounced on 11 October 2001. Montenegro is bound by the following international conventions prohibiting capital punishment : Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, as well as Protocols No. 6 and No. 13 to the European Convention on Human Rights. Article 26 of the Montenegrin Constitution (2007) that outlawed the death penalty states: "In Montenegro, capital punishment punishment is forbidden”.
Capital punishment in Malawi is a legal punishment for certain crimes. The country abolished the death penalty following a Malawian Supreme Court ruling in 2021, but it was soon reinstated. However, the country is currently under a death penalty moratorium, which has been in place since the latest execution in 1992.
Capital punishment is not a legal penalty in Samoa. The death penalty was used in the colonial era, but the practice had ceased by the time of independence in 1962, with death sentences being commuted to life imprisonment, and it was formally abolished in 2004. The last execution was carried out in 1952.
Capital punishment is not a legal penalty in Niue. While the death penalty was legal under New Zealand colonial rule, and death sentences were imposed by the courts, no executions were ever carried out. Capital punishment has been illegal in Niue since 1966, when the death penalty was effectively abolished by New Zealand colonial authorities.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Uganda. The death penalty was likely last carried out in 1999, although some sources say the last execution in Uganda took place in 2005. Regardless, Uganda is interchangeably considered a retentionist state with regard to capital punishment, due to absence of "an established practice or policy against carrying out executions," as well as a de facto abolitionist state due to the lack of any executions for over one decade.